
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image by a convex lens when an object is placed in front of the lens between its optical centre and principal focus.
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: We will draw the ray diagram of this image formation by the knowledge of how the image is formed when the object is kept at different positions on the principle axis of a convex lens. A convex lens is internally bent on both sides. They usually concentrate a beam of light from outside and focus on the other side. This point is known as focus or principal focus. The focal length of a convex lens is the distance from the centre of lens to the focus. Optical centre is double the distance to the focus. If a parallel ray to the principal axis refracts through a convex lens, it will pass through the focus and if a ray refracts through the pole of the lens, it will not have any change in its path.
Complete step by step answer:
First, We will draw the raw diagram of the image formation. Here, the object is placed between the optical centre \[{{C}_{1}}\] and focus \[{{F}_{1}}\].
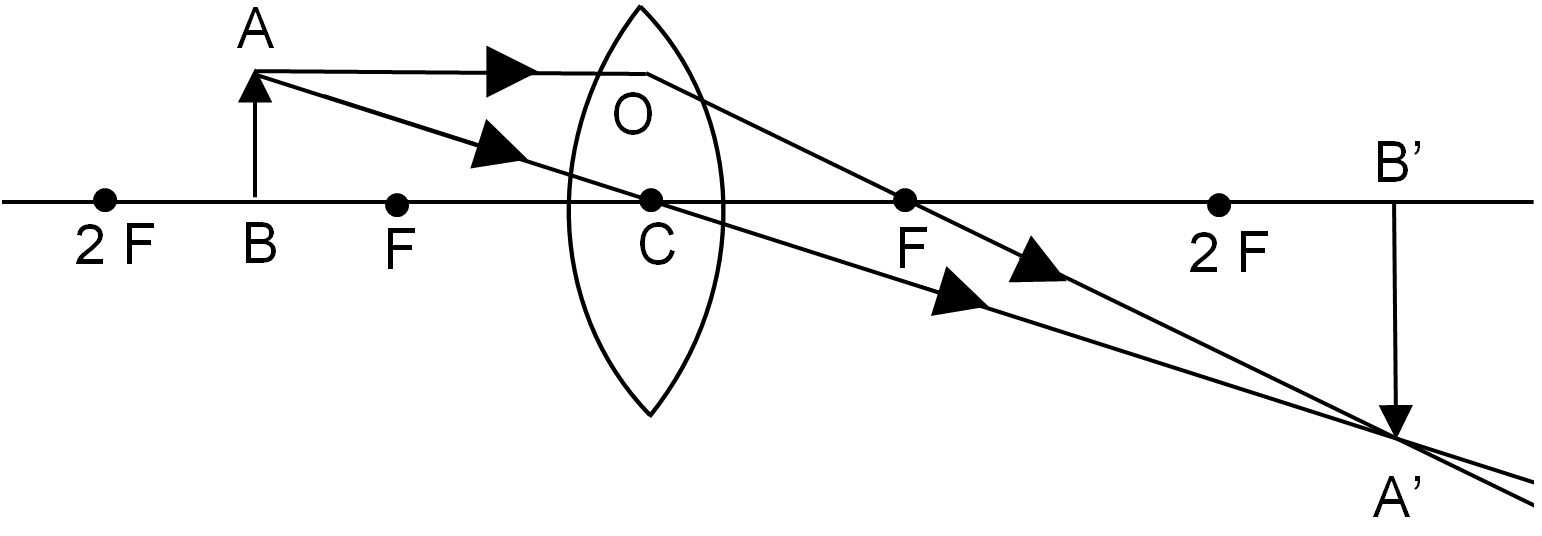
Here, \[AB\] represents the object and \[A'B'\] is the image formed.
Now, if we consider the properties of the image formed, the image is erect and enlarged. That means the image will be having more length than the object and it will be inverted.
We can also take a simple magnifying lens as an example of a convex lens. If we place an object a little longer than the focal length in front of it, a magnified and upright image is produced on the same face as the object.
Note:
If we look at the application of a lens in various appliances, we can see that a simple lens can focus light, but it will not be of good quality. So, we usually combine various lenses to avoid distortions and aberrations. When we look inside a camera, we can see that it is having a number of lenses placed at a particular distance for better image quality. While drawing ray diagrams we must have the knowledge that parallel rays to the lens are focused at the focal point and rays through poles will not be having any change.
Complete step by step answer:
First, We will draw the raw diagram of the image formation. Here, the object is placed between the optical centre \[{{C}_{1}}\] and focus \[{{F}_{1}}\].

Here, \[AB\] represents the object and \[A'B'\] is the image formed.
Now, if we consider the properties of the image formed, the image is erect and enlarged. That means the image will be having more length than the object and it will be inverted.
We can also take a simple magnifying lens as an example of a convex lens. If we place an object a little longer than the focal length in front of it, a magnified and upright image is produced on the same face as the object.
Note:
If we look at the application of a lens in various appliances, we can see that a simple lens can focus light, but it will not be of good quality. So, we usually combine various lenses to avoid distortions and aberrations. When we look inside a camera, we can see that it is having a number of lenses placed at a particular distance for better image quality. While drawing ray diagrams we must have the knowledge that parallel rays to the lens are focused at the focal point and rays through poles will not be having any change.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




