
Draw a right angle and construct its bisector.
Answer
526.8k+ views
Hint: Take a point P on a line l. Use the orthodox method to construct a right angle. To construct the bisector of this right angle, draw an arc with centre at R and another arc with centre at V with same radius intersecting each other. Join the intersection point and P. This is the bisector of the right angle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we need to draw a right angle and then construct its bisector.
First, let us understand what an angle bisector is.
Angle bisector is a line that splits an angle into two equal angles.
Now, follow the given steps to draw a right angle and then construct its bisector:
(1) Draw a line l and mark a point P on it. Draw an arc of convenient radius, while taking point P as centre. Let it intersect line I at R.
(2) Taking R as centre and with the same radius as before, draw an arc intersecting the previously drawn arc at S.
(3) Taking S as centre and with the same radius as before, draw an arc intersecting the arc at T.
(4) Taking S and T as centres, draw arcs of same radius to intersect each other at U.
(5) Join PU. PU is the required ray making a right angle with line l. Let it intersect the major arc at point V.
(6) Now, taking R and V as centres, draw arcs with radius more than half of RV to intersect each other at W. Join PW.
PW is the required bisector of this right angle.
Following is the final diagram after construction:
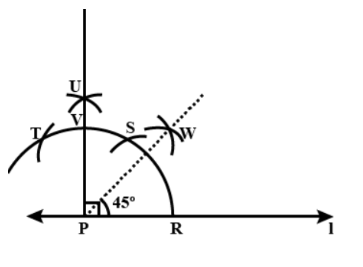
Note: In this question, note that in step 2, it is very important to keep the radius the same as used in step 1 to draw the major arc else you will get a wrong answer. Also, note that in step 6, it is very important to keep the radius more than half of RV.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we need to draw a right angle and then construct its bisector.
First, let us understand what an angle bisector is.
Angle bisector is a line that splits an angle into two equal angles.
Now, follow the given steps to draw a right angle and then construct its bisector:
(1) Draw a line l and mark a point P on it. Draw an arc of convenient radius, while taking point P as centre. Let it intersect line I at R.
(2) Taking R as centre and with the same radius as before, draw an arc intersecting the previously drawn arc at S.
(3) Taking S as centre and with the same radius as before, draw an arc intersecting the arc at T.
(4) Taking S and T as centres, draw arcs of same radius to intersect each other at U.
(5) Join PU. PU is the required ray making a right angle with line l. Let it intersect the major arc at point V.
(6) Now, taking R and V as centres, draw arcs with radius more than half of RV to intersect each other at W. Join PW.
PW is the required bisector of this right angle.
Following is the final diagram after construction:

Note: In this question, note that in step 2, it is very important to keep the radius the same as used in step 1 to draw the major arc else you will get a wrong answer. Also, note that in step 6, it is very important to keep the radius more than half of RV.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




