
Draw a schematic sketch of pBR322 plasmid and label the following in it.
A) Any two restriction sites
B) Ori and rop genes
C) An antibiotic resistant gene
Answer
578.7k+ views
Hint: pBR322 is a plasmid and was one of the first commonly used E. coli cloning vectors. Formed in 1977, it was named after Francisco Bolivar Zapata and Raymond L. Rodriguez. The genes present in pBR322 for tetracycline and ampicillin resistance enzymes, as well as sites where it can be cut by definite restriction endonucleases and identical DNA sequences inserted.
Complete answer:
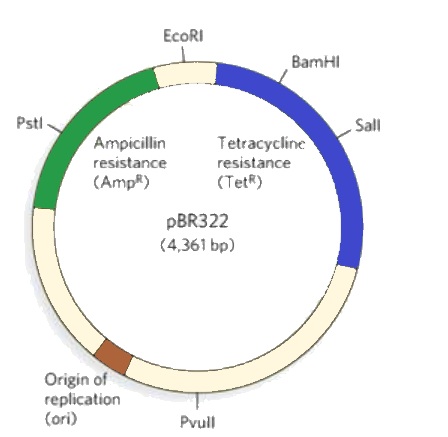
pBR322 is a 4,362-bp ds DNA plasmid cloning vehicle aimed to authorize the easy and rapid formation of cloned recombinant DNA portions. It has two antibiotic resistance genes, an origin of replication, and a multiplicity of functional restriction sites for cloning or subcloning restriction segments. pBR327 is alike to pBR322, apart from that it is the absence of all nucleotides between 1,427 and 2,516.
An origin of replication is a DNA series in which replication is initiated on a gene, plasmid or virus is the cause of replication. Rop is a small protein responsible for keeping ColE1 and associated bacterial plasmids down in their copy number.
These sequences are removed to reduce the size of the cloning vector and to eradicate sequences, which obstruct the expression of cloned DNA in eukaryotic cells. pBR322 and pBR322-derivative plasmids are very ordinary plasmid vectors.
Opening the plasmid with an RE and adding a companionable DNA segment with DNA ligase inactivates this resistance gene.
Hence, the correct answer is option ().
Note: Plasmids and bacteriophages are often used as a cloning vector in the DNA recombinant machinery. The ease with which plasmids can be tailored and replicated makes it an immense device in genetic engineering and biotechnology. For genetic engineering function, plasmids are artificially geared up in the lab. The lab-developed plasmids, which are used as a vector, enclose an origin of replication, cloning site, and selection marker.
Complete answer:

pBR322 is a 4,362-bp ds DNA plasmid cloning vehicle aimed to authorize the easy and rapid formation of cloned recombinant DNA portions. It has two antibiotic resistance genes, an origin of replication, and a multiplicity of functional restriction sites for cloning or subcloning restriction segments. pBR327 is alike to pBR322, apart from that it is the absence of all nucleotides between 1,427 and 2,516.
An origin of replication is a DNA series in which replication is initiated on a gene, plasmid or virus is the cause of replication. Rop is a small protein responsible for keeping ColE1 and associated bacterial plasmids down in their copy number.
These sequences are removed to reduce the size of the cloning vector and to eradicate sequences, which obstruct the expression of cloned DNA in eukaryotic cells. pBR322 and pBR322-derivative plasmids are very ordinary plasmid vectors.
Opening the plasmid with an RE and adding a companionable DNA segment with DNA ligase inactivates this resistance gene.
Hence, the correct answer is option ().
Note: Plasmids and bacteriophages are often used as a cloning vector in the DNA recombinant machinery. The ease with which plasmids can be tailored and replicated makes it an immense device in genetic engineering and biotechnology. For genetic engineering function, plasmids are artificially geared up in the lab. The lab-developed plasmids, which are used as a vector, enclose an origin of replication, cloning site, and selection marker.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




