
Draw a well labeled circuit diagram of a potentiometer to measure the internal resistance of a cell. Write the working formula (Derivation not necessary).
Answer
520.7k+ views
Hint: A potentiometer is a passive circuit element which is used to measure the voltage in a circuit with high accuracy. It can also measure the internal resistance of a cell or battery. Moreover it is used to compare the e.m.f of two cells. It has a wire made up of constantan, which is a high resistance metal.
Complete answer:
A potentiometer is a passive electronic component. It contains the following circuit elements:
a.)Rheostat
b.)Constantan wire
c.)Meter stick
d.)Copper plates
e.)Ammeter
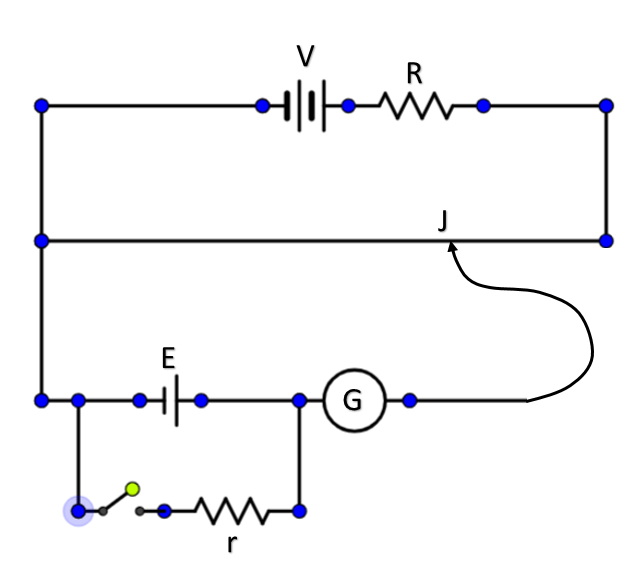
These all elements are mounted on a huge wooden board. It works on the principle that voltage drop in a circuit is directly proportional to the length of the wire. Potentiometers work by varying the position of a sliding contact across a uniform resistance. In a potentiometer, the entire input voltage is applied across the whole length of the resistor and the output voltage is the voltage drop between the fixed and sliding contact.
Working to measure internal resistance: As per its working principle, after the current starts flowing in the wire because of battery ‘V’, we check the null point by sliding jockey ‘J’. At a point, the net reading of the galvanometer becomes zero. In that case, voltage drop in that part of wire equals the emf ‘E’. Hence we can measure the resistance and calculate the internal resistance of the cell.
Generally we know ‘V’ and ‘R’. ‘E’ can be measured first and finally ‘r’ can be calculated using:
$E=V\left( \dfrac{r}{R}+1 \right)$
Note:
Potentiometer has many applications like comparing emf of cells, measuring internal resistance of cells, measuring voltage etc. Moreover it measures the voltage very accurately as compared to other devices. But as mentioned above, it’s a huge setup on a wooden board. Hence due to its bulky nature, it’s not practically usable.
Complete answer:
A potentiometer is a passive electronic component. It contains the following circuit elements:
a.)Rheostat
b.)Constantan wire
c.)Meter stick
d.)Copper plates
e.)Ammeter

These all elements are mounted on a huge wooden board. It works on the principle that voltage drop in a circuit is directly proportional to the length of the wire. Potentiometers work by varying the position of a sliding contact across a uniform resistance. In a potentiometer, the entire input voltage is applied across the whole length of the resistor and the output voltage is the voltage drop between the fixed and sliding contact.
Working to measure internal resistance: As per its working principle, after the current starts flowing in the wire because of battery ‘V’, we check the null point by sliding jockey ‘J’. At a point, the net reading of the galvanometer becomes zero. In that case, voltage drop in that part of wire equals the emf ‘E’. Hence we can measure the resistance and calculate the internal resistance of the cell.
Generally we know ‘V’ and ‘R’. ‘E’ can be measured first and finally ‘r’ can be calculated using:
$E=V\left( \dfrac{r}{R}+1 \right)$
Note:
Potentiometer has many applications like comparing emf of cells, measuring internal resistance of cells, measuring voltage etc. Moreover it measures the voltage very accurately as compared to other devices. But as mentioned above, it’s a huge setup on a wooden board. Hence due to its bulky nature, it’s not practically usable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




