
How can I draw an orbital diagram for chloride ions?
Answer
549.6k+ views
Hint: In a neutral atom, numbers of electron are always equal to number of proton because electron contains negative charge while proton contains positive charge and in any neutral atom the number of positive charge is always equal to the number of positive charge but during the formation of an ion, the number of positive charge and negative charge gets disturbed.
In a cation, number of electrons \[=\text{ }Z\text{ }\] Number of positive charge
In an anion, number of electrons \[=\text{ }Z+\] number of negative charge
Where \[Z=\] Atomic number
Complete step by step answer:
In our nature, various elements are present, some exist in native form while some exist in combined form. Those elements which are electronegative in nature are known as Non metal while those are electropositive in nature are known as metal.
Non metal have incomplete valence shell and they try to complete their valence shell by gaining electron form a metal which have $1\,\text{or}\,\text{2}$ electron in their valence shell which readily they loses and forms a bond called ionic bond which non metal.
Here, we have to make an orbital diagram of chloride ions. Chlorine atom belongs to halogen family, the electronic configuration of halogen family a is $n{{s}^{2}}n{{p}^{5}}$ i.e., it require only one electron to complete their octet and behaves vice a noble gas.
The orbital diagram of valence shell of chlorine is
$\text{Cl}-3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{5}}$
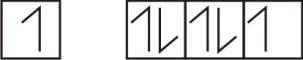
In an orbital, electrons are filled according to Hund’s Rule, Autobuses rule and Paul’s exclusion principle. Here if chlorine atoms gain electrons then it forms chloride ions.
$\text{Cl}+{{e}^{-}}\to \text{C}{{\text{l}}^{-}}$
$3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{5}}$ $3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{5}}$
Orbital diagram of chloride ion is as follows:
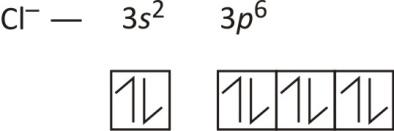
Note: Hund’s rule states that electron pairing in an orbital does not take place until all the orbitals are not half filled. Once all the orbits get half filled, then pairing will start.
Paul’s exclusion principle states that ‘’ two electrons in an atom, can have game value of all four quantum numbers
Autbaus principle states that ‘’electrons are filled in increasing order in an orbital.
In a cation, number of electrons \[=\text{ }Z\text{ }\] Number of positive charge
In an anion, number of electrons \[=\text{ }Z+\] number of negative charge
Where \[Z=\] Atomic number
Complete step by step answer:
In our nature, various elements are present, some exist in native form while some exist in combined form. Those elements which are electronegative in nature are known as Non metal while those are electropositive in nature are known as metal.
Non metal have incomplete valence shell and they try to complete their valence shell by gaining electron form a metal which have $1\,\text{or}\,\text{2}$ electron in their valence shell which readily they loses and forms a bond called ionic bond which non metal.
Here, we have to make an orbital diagram of chloride ions. Chlorine atom belongs to halogen family, the electronic configuration of halogen family a is $n{{s}^{2}}n{{p}^{5}}$ i.e., it require only one electron to complete their octet and behaves vice a noble gas.
The orbital diagram of valence shell of chlorine is
$\text{Cl}-3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{5}}$

In an orbital, electrons are filled according to Hund’s Rule, Autobuses rule and Paul’s exclusion principle. Here if chlorine atoms gain electrons then it forms chloride ions.
$\text{Cl}+{{e}^{-}}\to \text{C}{{\text{l}}^{-}}$
$3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{5}}$ $3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{5}}$
Orbital diagram of chloride ion is as follows:

Note: Hund’s rule states that electron pairing in an orbital does not take place until all the orbitals are not half filled. Once all the orbits get half filled, then pairing will start.
Paul’s exclusion principle states that ‘’ two electrons in an atom, can have game value of all four quantum numbers
Autbaus principle states that ‘’electrons are filled in increasing order in an orbital.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




