
Draw electron dot structure of Sodium (Na), Oxygen (O).
Answer
496.8k+ views
Hint: The valence electrons of an atom are represented by Lewis symbols (also known as Lewis dot diagrams or electron dot diagrams). Lewis structures (also called Lewis dot structures or electron dot structures) are diagrams that show how the valence electrons of atoms in a molecule are represented. The valence electrons of atoms and molecules, whether they exist as lone pairs or inside bonds, may be visualized using these Lewis symbols and Lewis structures.
Complete answer:
A positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons make up an atom. The electrical force between them maintains electrons ‘bound' to the nucleus, allowing them to remain within a fixed distance. According to careful research, not all electrons in an atom have the same average position or energy. The electrons are said to ‘reside' in various principal energy levels, which exist at various radii from the nucleus and have rules about how many electrons they can accommodate.
To write the Lewis symbol for an atom, you must first figure out how many valence electrons the element has. The periodic table's layout can assist you in determining this information. Because we know that an element's chemical reactivity is determined by the number of valence electrons, the table lists the elements in order of valence electrons.
Here Sodium has 11 electrons so, it can be depicted as
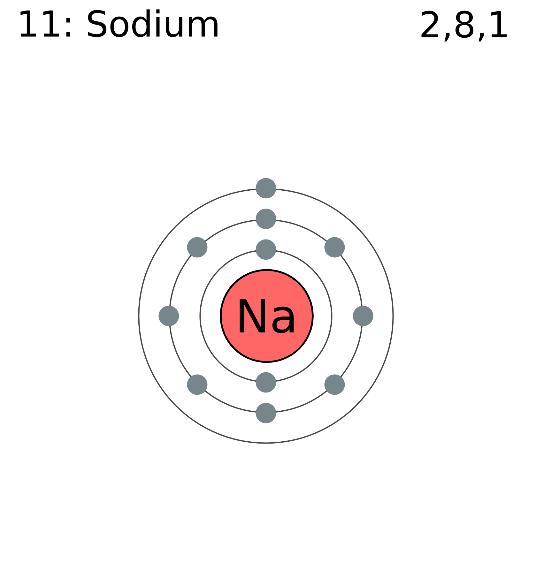
Here Oxygen has 8 electrons so, it can be depicted as
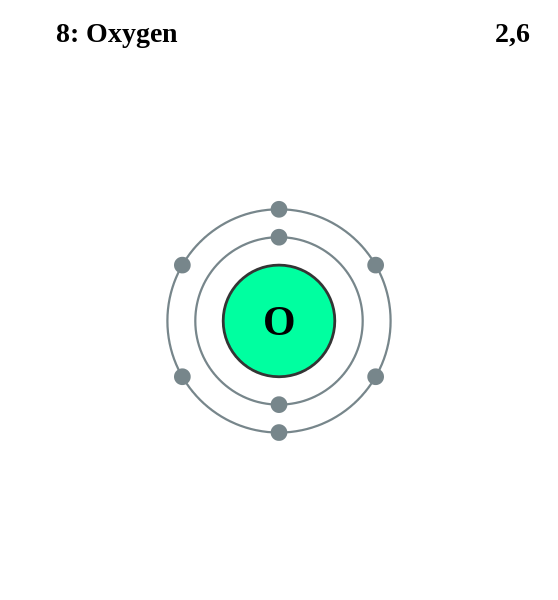
Note:
In order to achieve greater stability or a lower energy state, atoms gain, lose, or share electrons in their valence level. Bonds between atoms develop in this way, resulting in the bound atoms being in a lower energy state than when they were alone. Atoms achieve this more stable state by having a valence level that can hold as many electrons as possible. The most stable arrangement for the first principal energy level is two electrons, whereas for all other levels outside of the first, eight electrons are required to achieve the most stable state.
Complete answer:
A positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons make up an atom. The electrical force between them maintains electrons ‘bound' to the nucleus, allowing them to remain within a fixed distance. According to careful research, not all electrons in an atom have the same average position or energy. The electrons are said to ‘reside' in various principal energy levels, which exist at various radii from the nucleus and have rules about how many electrons they can accommodate.
To write the Lewis symbol for an atom, you must first figure out how many valence electrons the element has. The periodic table's layout can assist you in determining this information. Because we know that an element's chemical reactivity is determined by the number of valence electrons, the table lists the elements in order of valence electrons.
Here Sodium has 11 electrons so, it can be depicted as

Here Oxygen has 8 electrons so, it can be depicted as

Note:
In order to achieve greater stability or a lower energy state, atoms gain, lose, or share electrons in their valence level. Bonds between atoms develop in this way, resulting in the bound atoms being in a lower energy state than when they were alone. Atoms achieve this more stable state by having a valence level that can hold as many electrons as possible. The most stable arrangement for the first principal energy level is two electrons, whereas for all other levels outside of the first, eight electrons are required to achieve the most stable state.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




