
How do you draw Lewis structures for polyatomic ions?
Answer
556.8k+ views
Hint: The Lewis structure is a way of representing the bonding between the atoms with the help of electrons as dots. It also indicates the presence of non-bonded electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
The polyatomic ions are a combination of more than one atom which leads to the formation of charged species. As for example ammonium ion is a cationic species carrying a net positive charge. The ammonium ion is composed of one nitrogen atom and four hydrogen atoms.
The positive charge resides on the central atom which is nitrogen for ammonium ion. The nitrogen atom is an element in the periodic table with atomic number \[7\] and electronic configuration \[\left[ {He} \right]2{s^2}2{p^3}\]. Thus the valency of nitrogen atoms is \[3\]. But for making bonds with the fourth hydrogen ion (\[{H^ + }\]), it loses the electron pairs and becomes a positively charged ion. The Lewis structure of ammonium ions is shown as
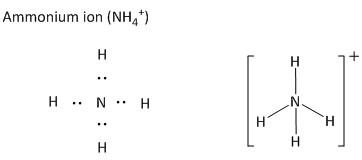
In a similar way the anionic polyatomic ions are drawn by indicating the bonds and the lone pairs in the form of electrons as dots. As for example the hydroxide ion is an anionic polyatomic ion. It is composed of one oxygen atom and one hydrogen atom.
The oxygen is an element in the periodic table with atomic number \[8\] and electronic configuration \[\left[ {He} \right]2{s^2}2{p^4}\]. Thus oxygen atom has six numbers of electrons in the outermost shell and shows a valency of \[2\]. It forms one bond with the hydrogen atom thus has an excess of one electron of the octet and hence carries a unit negative charge. The Lewis structure of hydroxide ion is shown as

Note:
The positive charge outside the bracket indicates the charge carried by the nitrogen atom. This is due to the electrochemical imbalance of \[ + 1\] created after making the fourth bond with one hydrogen atom. The negative charge outside the bracket indicates the charge carried by the oxygen atom. This is due to the electrochemical imbalance of \[ - 1\] created after making the bond with one hydrogen atom.
Complete step by step answer:
The polyatomic ions are a combination of more than one atom which leads to the formation of charged species. As for example ammonium ion is a cationic species carrying a net positive charge. The ammonium ion is composed of one nitrogen atom and four hydrogen atoms.
The positive charge resides on the central atom which is nitrogen for ammonium ion. The nitrogen atom is an element in the periodic table with atomic number \[7\] and electronic configuration \[\left[ {He} \right]2{s^2}2{p^3}\]. Thus the valency of nitrogen atoms is \[3\]. But for making bonds with the fourth hydrogen ion (\[{H^ + }\]), it loses the electron pairs and becomes a positively charged ion. The Lewis structure of ammonium ions is shown as

In a similar way the anionic polyatomic ions are drawn by indicating the bonds and the lone pairs in the form of electrons as dots. As for example the hydroxide ion is an anionic polyatomic ion. It is composed of one oxygen atom and one hydrogen atom.
The oxygen is an element in the periodic table with atomic number \[8\] and electronic configuration \[\left[ {He} \right]2{s^2}2{p^4}\]. Thus oxygen atom has six numbers of electrons in the outermost shell and shows a valency of \[2\]. It forms one bond with the hydrogen atom thus has an excess of one electron of the octet and hence carries a unit negative charge. The Lewis structure of hydroxide ion is shown as

Note:
The positive charge outside the bracket indicates the charge carried by the nitrogen atom. This is due to the electrochemical imbalance of \[ + 1\] created after making the fourth bond with one hydrogen atom. The negative charge outside the bracket indicates the charge carried by the oxygen atom. This is due to the electrochemical imbalance of \[ - 1\] created after making the bond with one hydrogen atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




