
Draw ray diagrams for the following positions and explain the nature and position of the image. Object is placed between F and optic centre C for a convex lens.
Answer
572.4k+ views
Hint: Ray diagrams help us understand how the lights bouncing off the objects get reflected and refracted to form images. There are rules that are followed for drawing ray diagrams, n incident ray parallel to the principal axis will refract through the lens and travel through the focal point on the opposite side of the lens, An incident ray coming through the focal point on the way to the lens will refract through the lens and will travel parallel to the principal axis, An incident ray that passes through the optical centre of the lens will continue in the same path or direction that it had when it entered the lens and will go undisturbed. Following these rules, we can make the ray diagram.
Complete answer:
The position and nature of image formed by lenses and mirrors are best understood through the use of ray diagrams. These ray diagrams help us understand how the lights bouncing off the objects get reflected and refracted to form images and thus help us understand the nature of positions of said images.
For ray diagrams of lenses there are certain basic rules that are followed. These rules are as follows.
A) An incident ray parallel to the principal axis will refract through the lens and travel through the focal point on the opposite side of the lens.
B) An incident ray coming through the focal point on the way to the lens will refract through the lens and will travel parallel to the principal axis.
C) An incident ray that passes through the optical centre of the lens will continue in the same path or direction that it had when it entered the lens and will go undisturbed.
Let us follow these rules and make the ray diagram of an object placed between F and C of a convex lens
Here the object AB is kept between focus F and centre C. For ray diagram we take a ray parallel to the axis, that after refraction goes through the focus. And a ray passing through the centre C that will go without any deviation as seen in the diagram.
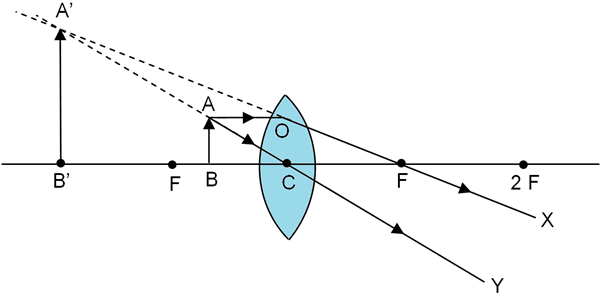
As seen in the diagram the rays diverge after refraction and thus will never meet. So the rays are traced back to intersect. So, they will seem to meet on the same side of the object. After intersection the image A’B’ is formed. As seen from the diagram, this image formed is Virtual, erect, enlarged and on the same side of the object.
Note:
This property of convex lens to form magnified erect and enlarged images is used extensively in the field of science. It is used to make magnifying glass and other optical tools like telescopes, binoculars etc. And thus lenses are used in almost all the fields like exploration, space science, medicinal sciences etc.
Complete answer:
The position and nature of image formed by lenses and mirrors are best understood through the use of ray diagrams. These ray diagrams help us understand how the lights bouncing off the objects get reflected and refracted to form images and thus help us understand the nature of positions of said images.
For ray diagrams of lenses there are certain basic rules that are followed. These rules are as follows.
A) An incident ray parallel to the principal axis will refract through the lens and travel through the focal point on the opposite side of the lens.
B) An incident ray coming through the focal point on the way to the lens will refract through the lens and will travel parallel to the principal axis.
C) An incident ray that passes through the optical centre of the lens will continue in the same path or direction that it had when it entered the lens and will go undisturbed.
Let us follow these rules and make the ray diagram of an object placed between F and C of a convex lens
Here the object AB is kept between focus F and centre C. For ray diagram we take a ray parallel to the axis, that after refraction goes through the focus. And a ray passing through the centre C that will go without any deviation as seen in the diagram.

As seen in the diagram the rays diverge after refraction and thus will never meet. So the rays are traced back to intersect. So, they will seem to meet on the same side of the object. After intersection the image A’B’ is formed. As seen from the diagram, this image formed is Virtual, erect, enlarged and on the same side of the object.
Note:
This property of convex lens to form magnified erect and enlarged images is used extensively in the field of science. It is used to make magnifying glass and other optical tools like telescopes, binoculars etc. And thus lenses are used in almost all the fields like exploration, space science, medicinal sciences etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




