
Draw schematic diagram of a refrigerator. Define its coefficient of performance and mention the expression.
Answer
572.4k+ views
Hint: A device which takes heat from a cold body and transfers it to a hot body is called a refrigerator. It does the reverse of a heat engine. Work by the external agent must be done so that the process of refrigeration goes on. First we will draw the schematic diagram of a refrigerator and from that we will define the coefficient of performance of the refrigerator.
Complete answer:
The schematic diagram of a refrigerator is shown below.
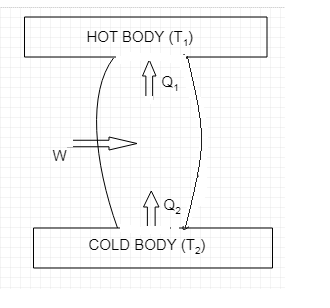
As we can see from the diagram it takes ${{Q}_{2}}$ amount of heat from the cold body which is at a lower temperature of ${{T}_{2}}$. $W$ amount of work is done by the external agent and a total of
${{Q}_{1}}={{Q}_{2}}+W$ amount of heat is given to the hot body which is at a higher temperature of ${{T}_{1}}$.
The purpose of a refrigerator is to remove as much heat from the cold body at the expense of as little work required to run the refrigerator. Thus the coefficient of performance $K$ of a refrigerator is defined as the ratio of the heat taken from the cold body to the amount of work required to run the refrigerator, Thus
$K=\dfrac{{{Q}_{2}}}{W}$.
Now
$\begin{align}
& {{Q}_{1}}={{Q}_{2}}+W \\
& or\dfrac{W}{{{Q}_{2}}}=(\dfrac{{{Q}_{1}}}{{{Q}_{2}}}-1) \\
\end{align}$
Now as in Carnot’s engine, if we use ideal gas as a working substance then it can be shown
$\dfrac{{{Q}_{1}}}{{{Q}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{T}_{1}}}{{{T}_{2}}}$, thus
$\dfrac{W}{{{Q}_{2}}}=(\dfrac{{{T}_{1}}}{{{T}_{2}}}-1)=(\dfrac{{{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{2}}})$
Therefore the coefficient of performance
$K=\dfrac{{{Q}_{2}}}{W}=\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}}}$
Note:
A refrigerator can have a coefficient of performance greater than 1. In a heat engine, heat cannot be fully converted to work, similarly a refrigerator cannot work without some external work done on the system i.e. the coefficient of performance cannot be infinite. A good refrigerator should have its value around 5 or 6.
Complete answer:
The schematic diagram of a refrigerator is shown below.

As we can see from the diagram it takes ${{Q}_{2}}$ amount of heat from the cold body which is at a lower temperature of ${{T}_{2}}$. $W$ amount of work is done by the external agent and a total of
${{Q}_{1}}={{Q}_{2}}+W$ amount of heat is given to the hot body which is at a higher temperature of ${{T}_{1}}$.
The purpose of a refrigerator is to remove as much heat from the cold body at the expense of as little work required to run the refrigerator. Thus the coefficient of performance $K$ of a refrigerator is defined as the ratio of the heat taken from the cold body to the amount of work required to run the refrigerator, Thus
$K=\dfrac{{{Q}_{2}}}{W}$.
Now
$\begin{align}
& {{Q}_{1}}={{Q}_{2}}+W \\
& or\dfrac{W}{{{Q}_{2}}}=(\dfrac{{{Q}_{1}}}{{{Q}_{2}}}-1) \\
\end{align}$
Now as in Carnot’s engine, if we use ideal gas as a working substance then it can be shown
$\dfrac{{{Q}_{1}}}{{{Q}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{T}_{1}}}{{{T}_{2}}}$, thus
$\dfrac{W}{{{Q}_{2}}}=(\dfrac{{{T}_{1}}}{{{T}_{2}}}-1)=(\dfrac{{{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{2}}})$
Therefore the coefficient of performance
$K=\dfrac{{{Q}_{2}}}{W}=\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}}}$
Note:
A refrigerator can have a coefficient of performance greater than 1. In a heat engine, heat cannot be fully converted to work, similarly a refrigerator cannot work without some external work done on the system i.e. the coefficient of performance cannot be infinite. A good refrigerator should have its value around 5 or 6.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




