
Draw structure and write geometry of $PC{l_3}$ and $PC{l_5}$.
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: $VSEPR$ theory is used to predict the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs surrounding the central atom. $VSEPR$ Theory is valence shell electron pair repulsion theory.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know $VSEPR$ theory is used to predict the shape of compounds. $PC{l_3}$ have $3$ bond pairs and $1$ lone pair. According to this theory if a molecule has $3$ bond pairs and $1$ lone pair it will possess trigonal pyramidal geometry. The structure of this molecule is shown below:
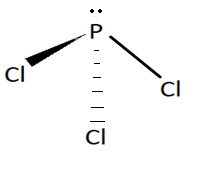
Structure of $PC{l_3}$
$PC{l_5}$ has $5$ bond pairs and $0$ lone pair. According to valence shell electron pair repulsion theory molecules having such bond pair and lone pair possess trigonal bipyramidal geometry. Therefore $PC{l_3}$ has trigonal bipyramidal geometry. Structure of $PC{l_5}$ is shown below:
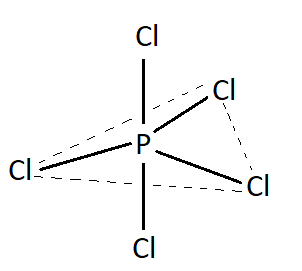
This is the structure of$PC{l_5}$.
Additional information:
$VSEPR$ theory was unable to explain the exact shape of molecules in many cases. Taking the direction of electron pairs doesn’t seem to be very rational.
To explain the concept of shapes of molecules clearly hybridization was introduced. It involves intermixing of two or more atomic orbitals of slightly different energies but of the same atom so that redistribution of energy takes place between them resulting in the formation of an equal number of new orbitals which are called hybrid orbitals which will have the same energy, size, and shape.
For molecules or ions having regular geometry, change in electronegativity of the central atom or the surrounding atom has no effect on the bond angle.
The actual structure is in between all the contributing structures and is called a resonance hybrid. The different individual structures are called resonating structures or canonical forms. This phenomenon is called resonance.
Note:
Different compounds have different geometry according to the number of lone pairs and bond pair. So remember the number of bond pairs and lone pairs for which different geometries of compounds are formed.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know $VSEPR$ theory is used to predict the shape of compounds. $PC{l_3}$ have $3$ bond pairs and $1$ lone pair. According to this theory if a molecule has $3$ bond pairs and $1$ lone pair it will possess trigonal pyramidal geometry. The structure of this molecule is shown below:

Structure of $PC{l_3}$
$PC{l_5}$ has $5$ bond pairs and $0$ lone pair. According to valence shell electron pair repulsion theory molecules having such bond pair and lone pair possess trigonal bipyramidal geometry. Therefore $PC{l_3}$ has trigonal bipyramidal geometry. Structure of $PC{l_5}$ is shown below:

This is the structure of$PC{l_5}$.
Additional information:
$VSEPR$ theory was unable to explain the exact shape of molecules in many cases. Taking the direction of electron pairs doesn’t seem to be very rational.
To explain the concept of shapes of molecules clearly hybridization was introduced. It involves intermixing of two or more atomic orbitals of slightly different energies but of the same atom so that redistribution of energy takes place between them resulting in the formation of an equal number of new orbitals which are called hybrid orbitals which will have the same energy, size, and shape.
For molecules or ions having regular geometry, change in electronegativity of the central atom or the surrounding atom has no effect on the bond angle.
The actual structure is in between all the contributing structures and is called a resonance hybrid. The different individual structures are called resonating structures or canonical forms. This phenomenon is called resonance.
Note:
Different compounds have different geometry according to the number of lone pairs and bond pair. So remember the number of bond pairs and lone pairs for which different geometries of compounds are formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




