
Draw structure of 2 oxoacids of phosphorus in which oxidation number of phosphorus is $ + 3 $ .
Answer
551.1k+ views
Hint: An oxoacid (sometimes called an oxyacid) is an oxygen-containing acid. An oxoacid is an acid that contains oxygen, to be more precise. At least one other element is contained. Has at least one oxygen bonded hydrogen atom.
Complete step by step answer
Basically, oxoacids are acids that contain oxygen as an ingredient. As such, a variety of oxoacids are known to form from Phosphorus, such as: $ {H_3}P{O_4} $ , $ {H_3}P{O_3} $ , etc. It is tetrahedrally surrounded by other atoms in phosphorous oxoacids. All these acids are commonly known to form at least one P = O bond and one P-OH bond.
In addition to P= O bonds and P-OH bonds in phosphorus oxoacids where the oxidation state of phosphorus is less than $ + 5 $ , P-P or P-H bonds are also observed. In general, these acids are seen as too disproportionate to either lower or higher states of oxidation. For instance, it provides phosphine and phosphoric acid when phosphorous acid is heated.
PHOSPHONIC ACID:
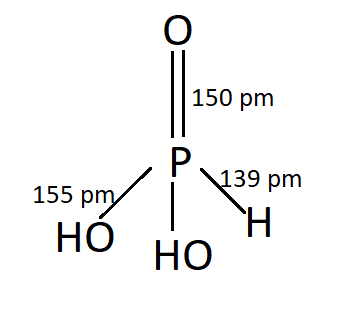
P has an oxidation number of $ + 3 $ . This is Dibasic.
$ {P_4}{O_6} + 6{H_2}O \to 4{H_3}P{O_3} $
$ PC{l_3} + 3{H_2}O \to {H_3}P{O_3} + 3HCl $
$ {H_4}{P_2}{O_5} $ :
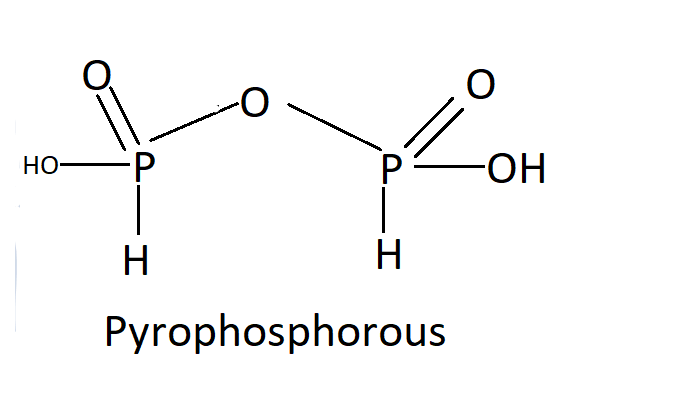
In oxoacids, the P-H bonds cannot go through ionization to provide $ {H^ + } $ ions, whereas the $ H $ atoms attached to oxygen in P-OH form are ionizable. Therefore, we can assume that only the oxygen-attached $ H $ atoms induce basicity. As a consequence of phosphorous acid, $ H_3PO_3 $ is dibasic due to the existence of two P-OH bonds, while $ H3PO4 $ is tribasic due to the presence of three P-OH bonds due to phosphoric acid. Phosphorus oxoacids that have P-H bonds have effective reducing properties.
Note
Metaphosphoric acid may not function as a monomer, yet occurs in the form of cyclic metaphosphoric acid as a cyclic trimer or in the form of poly metaphosphoric acid as a linear polymer. Acids with P-H bonds have effective reduction properties.
Complete step by step answer
Basically, oxoacids are acids that contain oxygen as an ingredient. As such, a variety of oxoacids are known to form from Phosphorus, such as: $ {H_3}P{O_4} $ , $ {H_3}P{O_3} $ , etc. It is tetrahedrally surrounded by other atoms in phosphorous oxoacids. All these acids are commonly known to form at least one P = O bond and one P-OH bond.
In addition to P= O bonds and P-OH bonds in phosphorus oxoacids where the oxidation state of phosphorus is less than $ + 5 $ , P-P or P-H bonds are also observed. In general, these acids are seen as too disproportionate to either lower or higher states of oxidation. For instance, it provides phosphine and phosphoric acid when phosphorous acid is heated.
PHOSPHONIC ACID:

P has an oxidation number of $ + 3 $ . This is Dibasic.
$ {P_4}{O_6} + 6{H_2}O \to 4{H_3}P{O_3} $
$ PC{l_3} + 3{H_2}O \to {H_3}P{O_3} + 3HCl $
$ {H_4}{P_2}{O_5} $ :

In oxoacids, the P-H bonds cannot go through ionization to provide $ {H^ + } $ ions, whereas the $ H $ atoms attached to oxygen in P-OH form are ionizable. Therefore, we can assume that only the oxygen-attached $ H $ atoms induce basicity. As a consequence of phosphorous acid, $ H_3PO_3 $ is dibasic due to the existence of two P-OH bonds, while $ H3PO4 $ is tribasic due to the presence of three P-OH bonds due to phosphoric acid. Phosphorus oxoacids that have P-H bonds have effective reducing properties.
Note
Metaphosphoric acid may not function as a monomer, yet occurs in the form of cyclic metaphosphoric acid as a cyclic trimer or in the form of poly metaphosphoric acid as a linear polymer. Acids with P-H bonds have effective reduction properties.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




