
Draw the filing order of atomic orbitals (Moeller chart) diagram when principal quantum number n= 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and l= 0, 1, 2, 3.
Answer
526.5k+ views
Hint: Moeller diagram is the diagrammatic representation of the filling of electrons in the orbitals according to Aufbau principle. The principle explains the rationale for the stable electronic configuration of the elements in respective orbitals.
Complete answer:
Electronic configuration is the order of arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of the atoms in the elements. Electrons enter into the orbitals in increasing order of the energies of the orbitals by one electron at a time. With the entering of each electron, the atomic number increases by one unit and the element formed is a new one. The energy of any given orbital is associated with two quantum numbers, one is principal quantum number and the other is azimuthal quantum number.
Principal quantum number is denoted by n which represents the main energy level and it has the values n=1,2,3…whereas azimuthal quantum number is denoted by l which represents the sub-energy level and they are represented by small-case alphabets s, p, d and f and they have value starting with zero (l=0,1,2...). The total energy of a given orbital is the sum of both main energy and sub-energy as n+l. obeying the Aufbau principle, electrons thus enter the orbital with lowest n+l value to the highest n+l value. The given below figure represents the Moeller chart with n= 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and l= 0, 1, 2, 3 which shows the orderly filling of electrons in respective atomic orbitals.
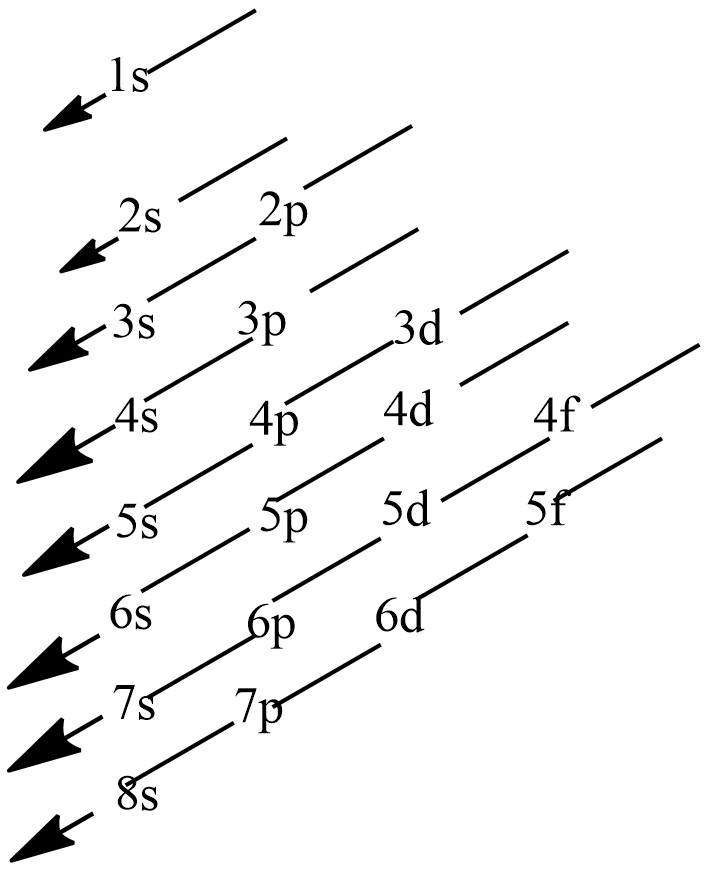
Note:
Aufbau principle is one of the rules of filling the atomic orbitals with electrons to get stable electronic configuration. According to this rule, electrons fill the atomic orbitals in increasing order by filling the lowest energy orbital first and then entering the next lowest energy orbital.
Complete answer:
Electronic configuration is the order of arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of the atoms in the elements. Electrons enter into the orbitals in increasing order of the energies of the orbitals by one electron at a time. With the entering of each electron, the atomic number increases by one unit and the element formed is a new one. The energy of any given orbital is associated with two quantum numbers, one is principal quantum number and the other is azimuthal quantum number.
Principal quantum number is denoted by n which represents the main energy level and it has the values n=1,2,3…whereas azimuthal quantum number is denoted by l which represents the sub-energy level and they are represented by small-case alphabets s, p, d and f and they have value starting with zero (l=0,1,2...). The total energy of a given orbital is the sum of both main energy and sub-energy as n+l. obeying the Aufbau principle, electrons thus enter the orbital with lowest n+l value to the highest n+l value. The given below figure represents the Moeller chart with n= 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and l= 0, 1, 2, 3 which shows the orderly filling of electrons in respective atomic orbitals.

Note:
Aufbau principle is one of the rules of filling the atomic orbitals with electrons to get stable electronic configuration. According to this rule, electrons fill the atomic orbitals in increasing order by filling the lowest energy orbital first and then entering the next lowest energy orbital.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




