
Draw the graph of \[2x + y = 6\] and \[2x - y + 2 = 0.\] Shade the region bounded by these lines and\[x - y\]. Find the area of the shaded region.
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint:
Here, we have to find the area of the shaded region. First, we will draw the graph for the first two equations by plotting points using the equation. Then we will draw the graph for the third equation. Then we will find the region bounded by all these lines and calculate the area of the shaded region.
Formula used:
Area between two curves that intersect each other in the interval \[\left[ {a,b} \right]\] is given by \[\int\limits_a^c {[f(x) - g(x)]dx} + \int\limits_c^b {[f(x) - g(x)]dx} \], where \[c\] is the root of \[f\left( x \right) = g\left( x \right)\].
Complete step by step solution:
We are given with an equation \[2x + y = 6\] and \[2x - y + 2 = 0.\]
Now, We will consider the first equation of line \[2x + y = 6\].
Substituting \[x = 0\] in the equation \[2x + y = 6\], we will get
\[\begin{array}{l}2\left( 0 \right) + y = 6\\ \Rightarrow y = 6\end{array}\]
Substituting \[x = 1\]in the equation \[2x + y = 6\], we will get
\[\begin{array}{l}2\left( 1 \right) + y = 6\\ \Rightarrow y = 4\end{array}\]
Substituting \[x = 2\]in the equation \[2x + y = 6\], we will get
\[\begin{array}{l}4 + y = 6\\ \Rightarrow y = 2\end{array}\]
So, we will get the coordinates for the line \[2x + y = 6\] as \[\left( {0,6} \right)\], \[\left( {1,4} \right)\] and \[\left( {2,2} \right)\].
Now, We have to consider the second equation of line \[2x - y + 2 = 0\]
Substituting \[x = 0\] in the equation \[2x + y = 6\], we will get \[y = 2\].
Substituting \[y = 0\] in the equation \[2x + y = 6\], we will get \[x = - 1\].
Substituting \[x = 2\]in the equation \[2x + y = 6\], we will get
\[\begin{array}{l}4 + 2 = y\\ \Rightarrow y = 6\end{array}\]
So, we will get the coordinates for the line \[2x - y + 2 = 0\] as \[\left( {0,2} \right)\], \[\left( { - 1,0} \right)\]and \[\left( {2,6} \right)\].
Now, we have to draw a graph with these coordinates. We will get a straight line for these linear equations.
Now, we have to consider the equation \[x - y = 0\].
Substituting \[x = 0\], we will get \[y = 0\]
Substituting \[x = 1\], we will get \[y = 1\]
Substituting \[x = 2\], we will get \[y = 2\]
So, we will get the coordinates for the line \[x - y = 0\] as (0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 2).
Now, we have to plot the graph for that we have to find the area bounded by the lines.
Area between two curves that intersect each other in the interval \[\left[ {a,b} \right]\] is given by \[\int\limits_a^c {[f(x) - g(x)]dx} + \int\limits_c^b {[f(x) - g(x)]dx} \],
Area of bounded region \[ = \int\limits_{ - 2}^0 {2x + 2 - xdx} + \int\limits_0^4 {2x + 2 - xdx} \]
By integration and substituting the limit, we will get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of bounded region\[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {1( - 2 - 2) - 2(2 - 4) + 2(4 + 2)} \right]\]
Simplifying the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of bounded region\[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 4 + 4 + 12} \right]\]
Adding and subtracting the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of bounded region\[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {12} \right]\]
Dividing 12 by 2, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of bounded region \[ = 6\]
Now we will draw the graph of \[2x + y = 6\] and, Then we will shade the area bounded by the lines.
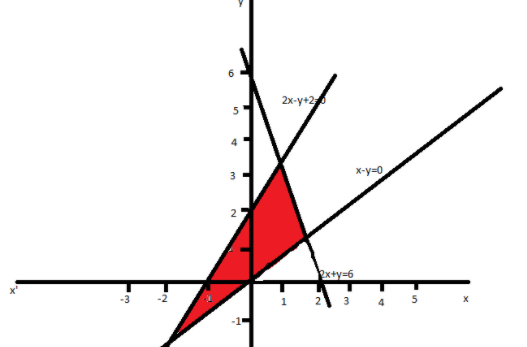
The region showed in red is the required area.
Note:
The line, which is at the highest, should be \[f\left( x \right)\] and the line which is at the lowest should be \[g\left( x \right)\]. We should know that in the differentiation we have product rule and quotient rule. But in the case of Integration, we don’t have such rules. Integration is a method of summing up the discrete data. While substituting the limit the lower limit value has to be subtracted from the upper limit value.
Here, we have to find the area of the shaded region. First, we will draw the graph for the first two equations by plotting points using the equation. Then we will draw the graph for the third equation. Then we will find the region bounded by all these lines and calculate the area of the shaded region.
Formula used:
Area between two curves that intersect each other in the interval \[\left[ {a,b} \right]\] is given by \[\int\limits_a^c {[f(x) - g(x)]dx} + \int\limits_c^b {[f(x) - g(x)]dx} \], where \[c\] is the root of \[f\left( x \right) = g\left( x \right)\].
Complete step by step solution:
We are given with an equation \[2x + y = 6\] and \[2x - y + 2 = 0.\]
Now, We will consider the first equation of line \[2x + y = 6\].
Substituting \[x = 0\] in the equation \[2x + y = 6\], we will get
\[\begin{array}{l}2\left( 0 \right) + y = 6\\ \Rightarrow y = 6\end{array}\]
Substituting \[x = 1\]in the equation \[2x + y = 6\], we will get
\[\begin{array}{l}2\left( 1 \right) + y = 6\\ \Rightarrow y = 4\end{array}\]
Substituting \[x = 2\]in the equation \[2x + y = 6\], we will get
\[\begin{array}{l}4 + y = 6\\ \Rightarrow y = 2\end{array}\]
So, we will get the coordinates for the line \[2x + y = 6\] as \[\left( {0,6} \right)\], \[\left( {1,4} \right)\] and \[\left( {2,2} \right)\].
Now, We have to consider the second equation of line \[2x - y + 2 = 0\]
Substituting \[x = 0\] in the equation \[2x + y = 6\], we will get \[y = 2\].
Substituting \[y = 0\] in the equation \[2x + y = 6\], we will get \[x = - 1\].
Substituting \[x = 2\]in the equation \[2x + y = 6\], we will get
\[\begin{array}{l}4 + 2 = y\\ \Rightarrow y = 6\end{array}\]
So, we will get the coordinates for the line \[2x - y + 2 = 0\] as \[\left( {0,2} \right)\], \[\left( { - 1,0} \right)\]and \[\left( {2,6} \right)\].
Now, we have to draw a graph with these coordinates. We will get a straight line for these linear equations.
Now, we have to consider the equation \[x - y = 0\].
Substituting \[x = 0\], we will get \[y = 0\]
Substituting \[x = 1\], we will get \[y = 1\]
Substituting \[x = 2\], we will get \[y = 2\]
So, we will get the coordinates for the line \[x - y = 0\] as (0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 2).
Now, we have to plot the graph for that we have to find the area bounded by the lines.
Area between two curves that intersect each other in the interval \[\left[ {a,b} \right]\] is given by \[\int\limits_a^c {[f(x) - g(x)]dx} + \int\limits_c^b {[f(x) - g(x)]dx} \],
Area of bounded region \[ = \int\limits_{ - 2}^0 {2x + 2 - xdx} + \int\limits_0^4 {2x + 2 - xdx} \]
By integration and substituting the limit, we will get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of bounded region\[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {1( - 2 - 2) - 2(2 - 4) + 2(4 + 2)} \right]\]
Simplifying the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of bounded region\[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 4 + 4 + 12} \right]\]
Adding and subtracting the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of bounded region\[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {12} \right]\]
Dividing 12 by 2, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of bounded region \[ = 6\]
Now we will draw the graph of \[2x + y = 6\] and, Then we will shade the area bounded by the lines.

The region showed in red is the required area.
Note:
The line, which is at the highest, should be \[f\left( x \right)\] and the line which is at the lowest should be \[g\left( x \right)\]. We should know that in the differentiation we have product rule and quotient rule. But in the case of Integration, we don’t have such rules. Integration is a method of summing up the discrete data. While substituting the limit the lower limit value has to be subtracted from the upper limit value.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




