
How would you draw the product of the hydration of$\text{2-butene}$?
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint $\text{2-butene}$ Is a four carbon containing unsaturated hydrocarbon molecule, which have double bond in between ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}\text{-}{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}$ carbon atom.
Alkene is an electron rich centre, so electrophilic addition reaction is the characteristic reaction of alkene.
Addition of water molecules in the presence of acid is known as hydration of alkene. During hydration $\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ -bond}$ of alkene is broken and formation of $\text{C-H and C-OH}$ takes place.
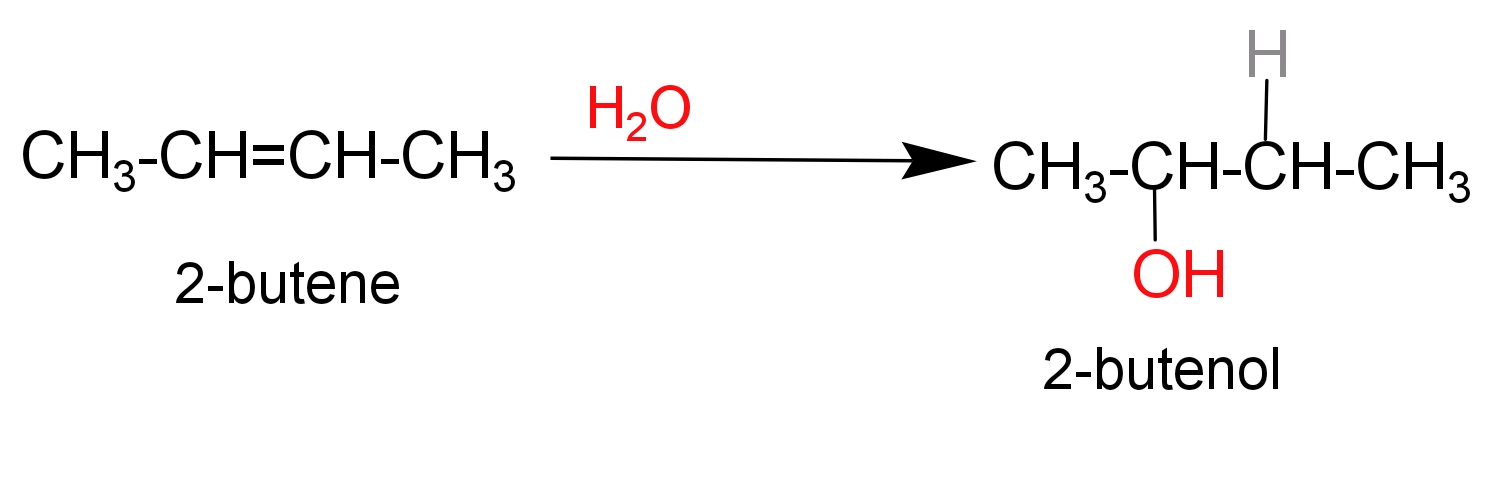
Complete Step by step solution –
Hydration product of $\text{2-butene}$leads to the formation of$\text{2-butanol}$. $\text{2-butanol}$ Is a four carbon saturated alcoholic compound in which hydroxyl group is attached in ${{\text{2}}^{\text{nd}}}$carbon of butane chain.
Two draw$\text{2-butanol}$, firstly we will draw a four carbon saturated carbon chain and attached $\text{(-OH)}$ group in the second carbon atom.
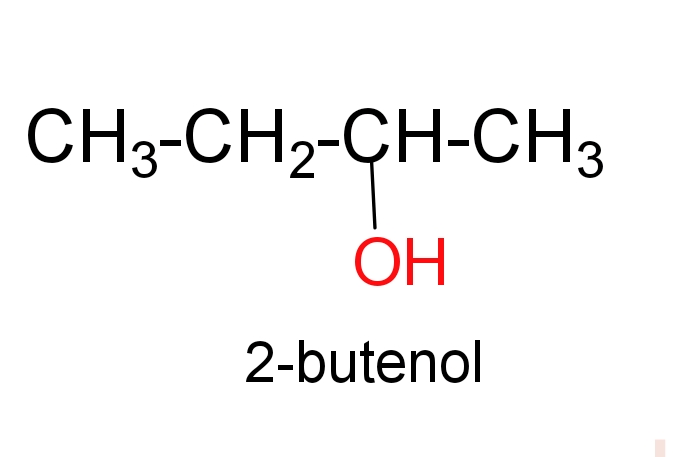
Additional information –
During the addition of an unsymmetrical reagent we follow the Markownikoff ‘s rule. According to this rule the negative part of the unsymmetrical reagent adds to a less hydrogenated or more substituted carbon atom of the double bond and positive part adds with the less substituted part of the double bond.
Addition of $\text{HBr}$to an alkene in the presence of peroxide is an example of electrophilic addition reaction. It does not follow the markownikoff’s rule during the addition of electrophile in the unsymmetrical alkene. Alcohol is chemically hydroxy derivative of alkane.
Note – All the examples of electrophilic addition reactions involve the formation of stable carbocation leading to the formation of stable carbocation leading to the formation of addition products according to the markownikoff’s rule.
Alkene is an electron rich centre, so electrophilic addition reaction is the characteristic reaction of alkene.
Addition of water molecules in the presence of acid is known as hydration of alkene. During hydration $\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ -bond}$ of alkene is broken and formation of $\text{C-H and C-OH}$ takes place.

Complete Step by step solution –
Hydration product of $\text{2-butene}$leads to the formation of$\text{2-butanol}$. $\text{2-butanol}$ Is a four carbon saturated alcoholic compound in which hydroxyl group is attached in ${{\text{2}}^{\text{nd}}}$carbon of butane chain.
Two draw$\text{2-butanol}$, firstly we will draw a four carbon saturated carbon chain and attached $\text{(-OH)}$ group in the second carbon atom.

Additional information –
During the addition of an unsymmetrical reagent we follow the Markownikoff ‘s rule. According to this rule the negative part of the unsymmetrical reagent adds to a less hydrogenated or more substituted carbon atom of the double bond and positive part adds with the less substituted part of the double bond.
Addition of $\text{HBr}$to an alkene in the presence of peroxide is an example of electrophilic addition reaction. It does not follow the markownikoff’s rule during the addition of electrophile in the unsymmetrical alkene. Alcohol is chemically hydroxy derivative of alkane.
Note – All the examples of electrophilic addition reactions involve the formation of stable carbocation leading to the formation of stable carbocation leading to the formation of addition products according to the markownikoff’s rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




