
Draw the ray diagram of Compound microscope when the image is formed at (near point) least distance of distinct vision.
Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint:The things we explore in our surroundings are macroscopic, for which we do not require any special arrangement to observe. But in nature, there are many objects which our eyes fail to detect. To observe these small objects a microscope is used. It has arrangements of the lens which magnify the things and we are able to see them. That minimum distance at which the normal eye can detect objects distinctly is the least distance of distinct vision.
Complete answer:
An apparatus which has mainly two convex lenses and which trends to magnify the image of small objects so that it can be seen, is known as a compound microscope. The ray diagram when the image is formed at least distance of distinct vision:
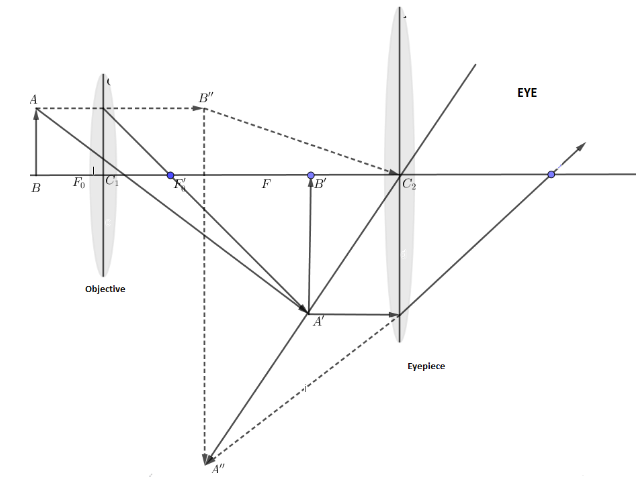
From the above diagram, we can see the image formed by the lens (objective) acts as an object for the lens (eyepiece). The eyepiece forms the image at a distance which is the least distance of distinct vision. In this way, the image gets magnified as it suffers two refractions through a convex lens.
Note: $AB$ which is the object that is focused by objective and forms the first image between the pole and center of curvature of the eyepiece. Now this image is the object for the eyepiece which is kept between the focus and center of curvature of the eyepiece and forms the second (final)image which seems to converge at least the distance of distinct vision.
Complete answer:
An apparatus which has mainly two convex lenses and which trends to magnify the image of small objects so that it can be seen, is known as a compound microscope. The ray diagram when the image is formed at least distance of distinct vision:

From the above diagram, we can see the image formed by the lens (objective) acts as an object for the lens (eyepiece). The eyepiece forms the image at a distance which is the least distance of distinct vision. In this way, the image gets magnified as it suffers two refractions through a convex lens.
Note: $AB$ which is the object that is focused by objective and forms the first image between the pole and center of curvature of the eyepiece. Now this image is the object for the eyepiece which is kept between the focus and center of curvature of the eyepiece and forms the second (final)image which seems to converge at least the distance of distinct vision.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




