
Draw the resonating structures of the following molecules -
(i) Phenol
(ii) Nitrobenzene
Answer
600.3k+ views
Hint: Resonance structures are a set of Lewis Structures which collectively describes the electronic bonding of a single polyatomic species including fractional bonds and fractional charges. They are capable of describing the delocalized electrons that cannot be expressed by a single Lewis formula.
Complete step by step solution:
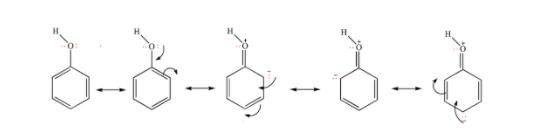
Phenol is highly acidic as it has a partial positive charge on the oxygen atom due to resonance, the anion formed due to loss of a hydrogen ion is also resonance stabilized.
Now, phenol is an aromatic compound in which the OH group is directly attached to the \[s{{p}^{2}}\] hybridized carbon of benzene ring. As the OH group easily donates electrons, the lone pair on oxygen participates in delocalization with electrons of the benzene ring system and the negative charge will be delocalized on -ortho and -para position.
The following are the resonating structures of phenol:
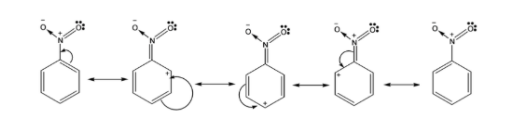
Nitrogen dioxide present on the benzene ring is a deactivating group which deactivates the benzene ring by the inductive effect in the presence of an electronegative atom that withdraws the electrons away from the ring.
In nitrobenzene, because the positive charge is always at ortho and para positions in nitrobenzene, it has a meta directing effect that means it is easier to attach electrophilic groups at meta position than ortho and para groups.
The following are the resonating structures of nitrobenzene:
Note: Order of activating groups:
\[-N{{H}_{2}}\,>\,N{{R}_{2}}\,>\,-OH,\,-OR\,>-NHCOR\,>-C{{H}_{3}}\] and other alkyl groups
Order of deactivating groups:
\[-N{{O}_{2}}\,>\,C{{F}_{3}}\,>\,\,-COR\,>-CN\,>-C{{O}_{2}}R\,>-S{{O}_{3}}H\,>\text{halogens}\]
Place the empty octet on the most substituted carbon (remember carbocation stability) Avoid placing positive charge adjacent to electron withdrawing groups if possible.
Complete step by step solution:
Phenol is highly acidic as it has a partial positive charge on the oxygen atom due to resonance, the anion formed due to loss of a hydrogen ion is also resonance stabilized.
Now, phenol is an aromatic compound in which the OH group is directly attached to the \[s{{p}^{2}}\] hybridized carbon of benzene ring. As the OH group easily donates electrons, the lone pair on oxygen participates in delocalization with electrons of the benzene ring system and the negative charge will be delocalized on -ortho and -para position.
The following are the resonating structures of phenol:

Nitrogen dioxide present on the benzene ring is a deactivating group which deactivates the benzene ring by the inductive effect in the presence of an electronegative atom that withdraws the electrons away from the ring.
In nitrobenzene, because the positive charge is always at ortho and para positions in nitrobenzene, it has a meta directing effect that means it is easier to attach electrophilic groups at meta position than ortho and para groups.
The following are the resonating structures of nitrobenzene:

Note: Order of activating groups:
\[-N{{H}_{2}}\,>\,N{{R}_{2}}\,>\,-OH,\,-OR\,>-NHCOR\,>-C{{H}_{3}}\] and other alkyl groups
Order of deactivating groups:
\[-N{{O}_{2}}\,>\,C{{F}_{3}}\,>\,\,-COR\,>-CN\,>-C{{O}_{2}}R\,>-S{{O}_{3}}H\,>\text{halogens}\]
Place the empty octet on the most substituted carbon (remember carbocation stability) Avoid placing positive charge adjacent to electron withdrawing groups if possible.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




