
During meiosis I, chromosome number
(a)Is reduced to half
(b)Doubles up
(c)Remains the same
(d)Either A or B
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Human beings have 23 chromosome pairs, which make up a total of 46 chromosomes. During the phase of meiosis I, the cells are haploid. In this step, the number of chromosomes is equal to what 12 pm of a day denotes. In a complete year, it signifies the interval of six months. This is also called semi-annual.
Complete answer:
The type of cell division by which gamete cells (eggs and sperm) are formed in meiosis. Two consecutive nuclear divisions and one cytoplasmic division are involved in meiosis, forming four haploid cells. Each haploid cell is genetically distinct from the originating parent cell. A single set of chromosomes constitute the haploid cells. The reduction division during which the number of chromosomes is reduced to half is the first division (meiosis I). In humans (2n = 46) who have 23 pairs of chromosomes, at the end of meiosis I, the number of chromosomes is halved (n = 23).
Additional Information: The chromatids are divided by the second division (meiosis II). As the number of chromosomes remains the same as that produced following meiosis I, it is called equational division.
The most known cause of miscarriage and the most common genetic cause of developmental defects are abnormalities in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an irregular number of chromosomes).
So, the correct answer is, ‘Is reduced to half’.
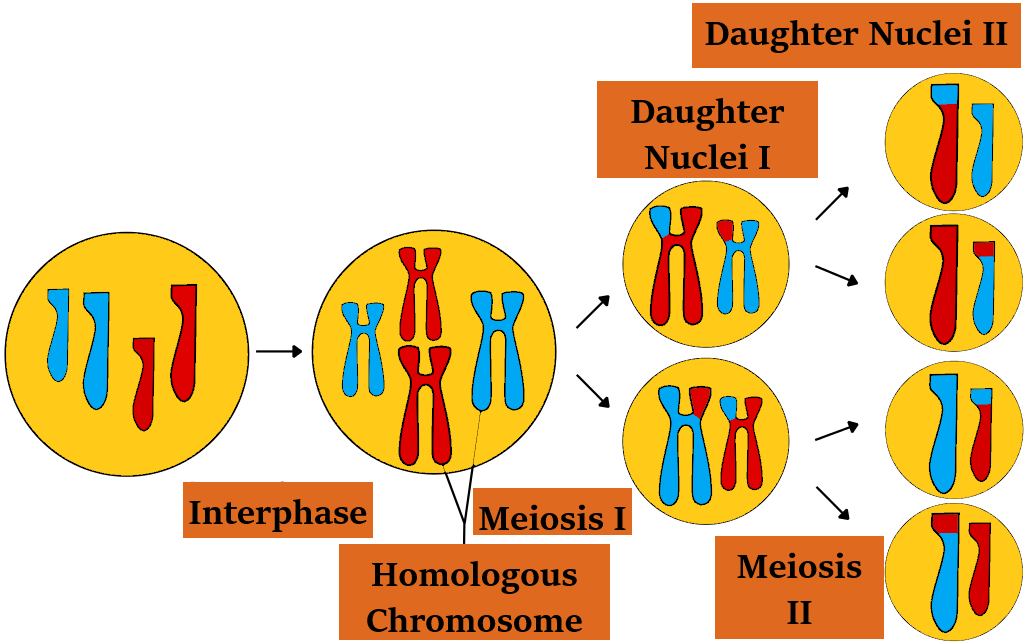
Note: The replication of DNA precedes the beginning of Meiosis I. It is this step that generates genetic diversity. It is created by homologous chromosomes (bivalent chromosomes) crossing over and random positioning. Later, during fertilization, the haploid cells from a male and female formed by meiosis can combine to form a cell again with two copies of each chromosome, the zygote.
Complete answer:
The type of cell division by which gamete cells (eggs and sperm) are formed in meiosis. Two consecutive nuclear divisions and one cytoplasmic division are involved in meiosis, forming four haploid cells. Each haploid cell is genetically distinct from the originating parent cell. A single set of chromosomes constitute the haploid cells. The reduction division during which the number of chromosomes is reduced to half is the first division (meiosis I). In humans (2n = 46) who have 23 pairs of chromosomes, at the end of meiosis I, the number of chromosomes is halved (n = 23).
Additional Information: The chromatids are divided by the second division (meiosis II). As the number of chromosomes remains the same as that produced following meiosis I, it is called equational division.
The most known cause of miscarriage and the most common genetic cause of developmental defects are abnormalities in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an irregular number of chromosomes).
So, the correct answer is, ‘Is reduced to half’.

Note: The replication of DNA precedes the beginning of Meiosis I. It is this step that generates genetic diversity. It is created by homologous chromosomes (bivalent chromosomes) crossing over and random positioning. Later, during fertilization, the haploid cells from a male and female formed by meiosis can combine to form a cell again with two copies of each chromosome, the zygote.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




