
During meiosis- I, the bivalent chromosomes clearly appear as tetrads using
(a) Diakinesis
(b) Diplotene
(c) Pachytene
(d) Zygotene
Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: This process is associated with the synapse formation. This is the third stage of Prophase- I in the reductional division. This stage is characterized by the appearance of recombination nodules.
Complete step by step answer:
In pachytene, the bivalent chromosomes clearly appear as a tetrad.
While these chromosomes were formed in the zygotene stage of the prophase- I by the process of association of synaptonemal complexes called synapsis.
So, the correct answer is ‘Pachytene’.
Additional information:
- In the zygotene stage, the chromosomes start pairing in the association of the synaptonemal complex which is not clearly visible in this short stage.
- This bivalent chromosome is visible in the pachytene stage.
- Pachytene involves the formation of two chromatids of the same chromosome known as sister chromatids.
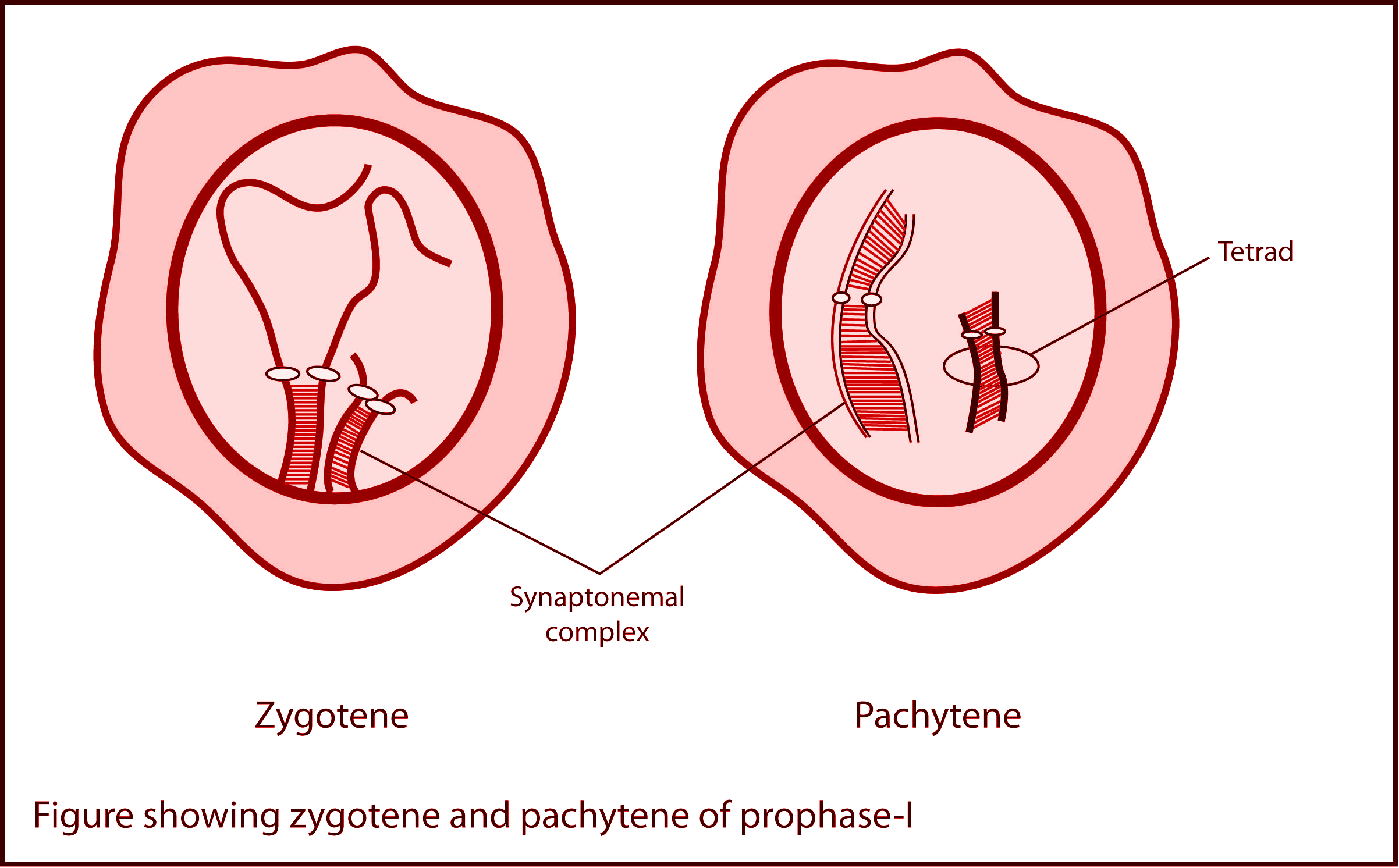
- The two chromatids of the two different homologous chromosomes are known as non- sister chromatids.
- Let’s learn some events that occur during the Pachytene:
- In this stage, the exchange of genetic material (DNA) between non- sister chromatids of the homologous chromosomes is called crossing- over.
- This process is an enzyme- mediated process and that enzyme is recombinase.
- Crossing over leads to the recombination of genetic material on the two chromosomes.
- By the end of the stage, the recombination between the homologous chromosomes is complete and the two chromatids leave the chromosomes linked at the site of crossing over.
- This pachytene enters into the Diplotene stage of prophase- I where the synaptonemal complex is dissolved and the bivalent gets separated from each other.
Note:
- Meiosis is called a reductional division.
- In these, the number of chromosomes is reduced to half.
- This brings out variations in human beings.
Complete step by step answer:
In pachytene, the bivalent chromosomes clearly appear as a tetrad.
While these chromosomes were formed in the zygotene stage of the prophase- I by the process of association of synaptonemal complexes called synapsis.
So, the correct answer is ‘Pachytene’.
Additional information:
- In the zygotene stage, the chromosomes start pairing in the association of the synaptonemal complex which is not clearly visible in this short stage.
- This bivalent chromosome is visible in the pachytene stage.
- Pachytene involves the formation of two chromatids of the same chromosome known as sister chromatids.

- The two chromatids of the two different homologous chromosomes are known as non- sister chromatids.
- Let’s learn some events that occur during the Pachytene:
- In this stage, the exchange of genetic material (DNA) between non- sister chromatids of the homologous chromosomes is called crossing- over.
- This process is an enzyme- mediated process and that enzyme is recombinase.
- Crossing over leads to the recombination of genetic material on the two chromosomes.
- By the end of the stage, the recombination between the homologous chromosomes is complete and the two chromatids leave the chromosomes linked at the site of crossing over.
- This pachytene enters into the Diplotene stage of prophase- I where the synaptonemal complex is dissolved and the bivalent gets separated from each other.
Note:
- Meiosis is called a reductional division.
- In these, the number of chromosomes is reduced to half.
- This brings out variations in human beings.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




