
During mitosis ER and nucleolus begin to disappear at
(a) Early metaphase
(b) Late metaphase
(c) Early prophase
(d) Late prophase
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: It is the stage of cell division that starts after the interphase where chromosome condensation occurs.
Complete answer: Prophase is the first stage in both mitosis and meiosis of cell division. At interphase, the two copies of the identical chromosomes are replicated forming sister chromatids. They then enter the prophase and start chromosome condensation and disappearance of the nucleolus along with the endoplasmic reticulum.
Additional information:
1. Mitosis is a type of cell division where the replicated chromosomes are divided into two new nuclei.
2. The daughter cells formed will have identical chromosome copies.
3. The process of mitosis is divided into several stages, they are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
4. The prophase stage is divided into two: early prophase and late prophase.
5. During prophase, the chromosomes start to condense and form mitotic spindles.
6. Each chromosome has two chromatids that are joined at the center called the centromere.
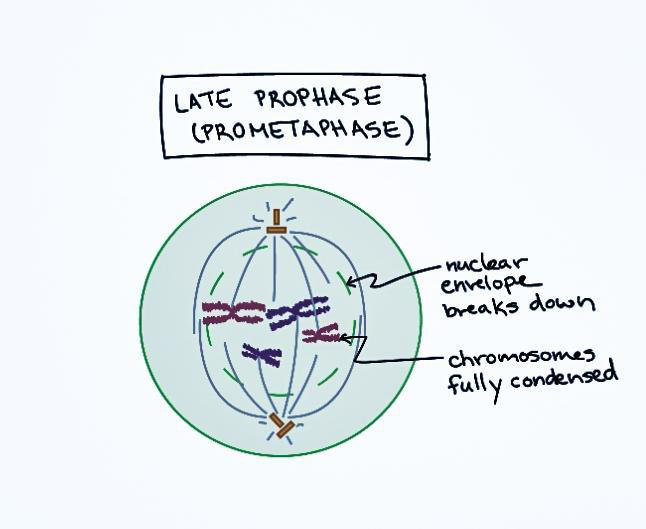
7. After this, prometaphase starts which is also called late prophase.
8. In this stage, the nuclear lamina will phosphorylate and disintegrate the nuclear envelope.
9. The breakdown of nucleoli will result in the stoppage of ribosome production leading to the disintegration of the endoplasmic reticulum.
10. This is known as open mitosis and occurs in a few multicellular organisms.
So, the correct answer is ‘Late prophase’.
Note: The term mitosis was coined in 1882 by Walther Flemming. The term was derived from the Greek word mitos meaning ‘warp thread'. Another term karyokinesis was introduced in 1878 by Schleicher or equational division coined in 1887 by August Weismann.
The term prophase is a Greek word meaning ‘before stage’.
Complete answer: Prophase is the first stage in both mitosis and meiosis of cell division. At interphase, the two copies of the identical chromosomes are replicated forming sister chromatids. They then enter the prophase and start chromosome condensation and disappearance of the nucleolus along with the endoplasmic reticulum.
Additional information:
1. Mitosis is a type of cell division where the replicated chromosomes are divided into two new nuclei.
2. The daughter cells formed will have identical chromosome copies.
3. The process of mitosis is divided into several stages, they are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
4. The prophase stage is divided into two: early prophase and late prophase.
5. During prophase, the chromosomes start to condense and form mitotic spindles.
6. Each chromosome has two chromatids that are joined at the center called the centromere.
7. After this, prometaphase starts which is also called late prophase.
8. In this stage, the nuclear lamina will phosphorylate and disintegrate the nuclear envelope.
9. The breakdown of nucleoli will result in the stoppage of ribosome production leading to the disintegration of the endoplasmic reticulum.
10. This is known as open mitosis and occurs in a few multicellular organisms.
So, the correct answer is ‘Late prophase’.
Note: The term mitosis was coined in 1882 by Walther Flemming. The term was derived from the Greek word mitos meaning ‘warp thread'. Another term karyokinesis was introduced in 1878 by Schleicher or equational division coined in 1887 by August Weismann.
The term prophase is a Greek word meaning ‘before stage’.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




