
Each unit cell of NaCl consists of 14 ${\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^{\text{ - }}}$ ions and __________
A.13 ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{ + }}}$ ions
B.14 ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{ + }}}$ ions
C.6 ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{ + }}}$ ions
D.8 ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{ + }}}$ ions
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint:NaCl is formed by repeating the face centred cubic unit cell. And have 1:1 stoichiometric ratio between Na and Cl. Sodium in this case occupies octahedral voids in the lattice structure.
Complete step by step answer:
-In order to calculate the number of sodium and chloride ions we should first be aware of the structure of NaCl unit cells or its crystal structure. So, talking about NaCl crystal structure, NaCl is made of face-centered cubic unit cells. Sodium ions being smaller occupies the octahedral voids and Chloride ions having comparatively larger size are located on the corners and centres of each face of the unit cell of NaCl.
-As you can see in the following diagram, the red dots represent lattice points where chloride ions are present and green dots represent octahedral voids where sodium ions are present.
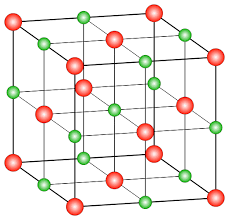
-In the lattice structure of NaCl there are 13 octahedral voids (12 edge centres + 1 body centre) and Chloride ions occupies corners and centres of each face of the cube thus there are 14 chloride ions in each unit cell. Thus, in each unit cell of NaCl there are 14 chloride ions and 13 sodium ions.
Hence option (A) is the correct answer.
Additional information: Please note that the smallest repeating unit of a crystal structure with the same geometry is known as a unit cell. There are many types of unit cell, cubic crystal structure is one of them and it consists of three different unit cells (1) plain cubic (2) face-centred cubic, and (3) body-centred cubic. NaCl has a face-centred cubic structure.
Note:
While calculating the number of sodium ions, always remember they occupy octahedral voids because of their smaller size and one sodium ion is also present at the body centre. The size of cation is comparatively smaller than that of anion because of greater attraction between nucleus and the outermost shell in case of cation as compared to anion.
Complete step by step answer:
-In order to calculate the number of sodium and chloride ions we should first be aware of the structure of NaCl unit cells or its crystal structure. So, talking about NaCl crystal structure, NaCl is made of face-centered cubic unit cells. Sodium ions being smaller occupies the octahedral voids and Chloride ions having comparatively larger size are located on the corners and centres of each face of the unit cell of NaCl.
-As you can see in the following diagram, the red dots represent lattice points where chloride ions are present and green dots represent octahedral voids where sodium ions are present.

-In the lattice structure of NaCl there are 13 octahedral voids (12 edge centres + 1 body centre) and Chloride ions occupies corners and centres of each face of the cube thus there are 14 chloride ions in each unit cell. Thus, in each unit cell of NaCl there are 14 chloride ions and 13 sodium ions.
Hence option (A) is the correct answer.
Additional information: Please note that the smallest repeating unit of a crystal structure with the same geometry is known as a unit cell. There are many types of unit cell, cubic crystal structure is one of them and it consists of three different unit cells (1) plain cubic (2) face-centred cubic, and (3) body-centred cubic. NaCl has a face-centred cubic structure.
Note:
While calculating the number of sodium ions, always remember they occupy octahedral voids because of their smaller size and one sodium ion is also present at the body centre. The size of cation is comparatively smaller than that of anion because of greater attraction between nucleus and the outermost shell in case of cation as compared to anion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




