
Edge length of a cube is 400pm. Its body diagonal (in pm) would be:
[A] 566
[B] 600
[C] 500
[D] 693
Answer
588k+ views
HINT: Body diagonal of a cube uses the diagonal drawn between two vertices which are not on the same face. To solve this use the formula of the diagonal of a cube that is the square root of the sum of squares of length, breadth and height of a cube. For a cube all these will be equal so use the edge length to find the required diagonal.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: We know that body diagonal of any polyhedron is a line connecting two vertices that do not lie on the same face.
Pictorially we can represent it as -
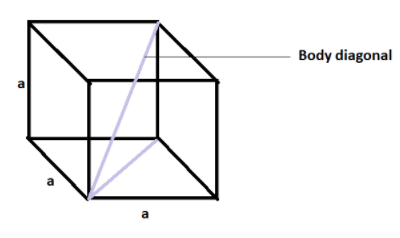
Where ‘a’ is the edge length which is equal for all the edges as it is a cube.
Now, we know that we can write the diagonal of a cuboid as $\sqrt{{{l}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$ , where l is the length of the cuboid, b is the breadth of the cuboid and h is the height of the cuboid.
In the given question we have a cube. Therefore, length, breadth and height all are equal to each other.
Therefore, we can write that the diagonal of the cube will be $\sqrt{3{{a}^{2}}}$ that is $\sqrt{3}a$ where ‘a’ is the edge length.
Here, the edge length is given to us as 400pm.
Therefore, we can write that the body diagonal of the cube will be $\sqrt{3}\times 400$ pm = 692.82 pm.
We can understand from the above calculation that the body diagonal of the cube is 692.82 pm which is almost equal to 693 pm.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [D] 693.
NOTE: Using the body diagonal of a cubic unit cell and the radius of the cations and the anions we find the limiting value of the radius for a particular geometry which is known as the limiting radius ratio rule. Its application is in the prediction of crystal geometry. It also gives us an idea about thermal stability of carbonates, tendency of metal ions to form hydrated salts etc.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: We know that body diagonal of any polyhedron is a line connecting two vertices that do not lie on the same face.
Pictorially we can represent it as -

Where ‘a’ is the edge length which is equal for all the edges as it is a cube.
Now, we know that we can write the diagonal of a cuboid as $\sqrt{{{l}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$ , where l is the length of the cuboid, b is the breadth of the cuboid and h is the height of the cuboid.
In the given question we have a cube. Therefore, length, breadth and height all are equal to each other.
Therefore, we can write that the diagonal of the cube will be $\sqrt{3{{a}^{2}}}$ that is $\sqrt{3}a$ where ‘a’ is the edge length.
Here, the edge length is given to us as 400pm.
Therefore, we can write that the body diagonal of the cube will be $\sqrt{3}\times 400$ pm = 692.82 pm.
We can understand from the above calculation that the body diagonal of the cube is 692.82 pm which is almost equal to 693 pm.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [D] 693.
NOTE: Using the body diagonal of a cubic unit cell and the radius of the cations and the anions we find the limiting value of the radius for a particular geometry which is known as the limiting radius ratio rule. Its application is in the prediction of crystal geometry. It also gives us an idea about thermal stability of carbonates, tendency of metal ions to form hydrated salts etc.
| Limiting radius ratio of cation to anion | Structure |
| 0 - 0.155 | Linear |
| 0.155 - 0.225 | Trigonal planar |
| 0.225 - 0.414 | Tetrahedral |
| 0.414 - 0.732 | Octahedral |
| 0.414 – 0.732 | Square planar |
| 0.732 – 0.1 | Body centred cubic. |
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




