
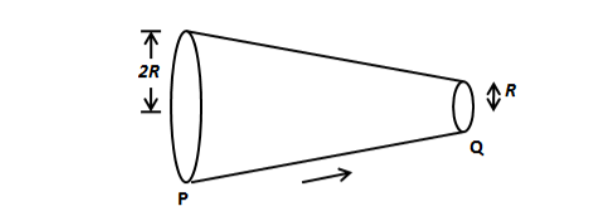
Electric current is passing through a solid conductor PQ from P to Q. The electric
current densities at P and Q are in the ratio:
A. 1 : 2
B. 2 : 1
C. 1 : 4
D. 4 : 1

Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint:The current density is the ratio of current to the cross sectional area. Express the current density at point P and Q. Take the ratio of these current densities to get the required answer. The area of the circular loop of radius R is \[\pi {R^2}\].
Formula used:
Current density, \[j = \dfrac{I}{A}\]
Here, I is the current and A is the area.
Complete step by step answer:
We know when the current flows through a given area, the current density in this area is
expressed as,
\[j = \dfrac{I}{A}\]
Here, I is the current and A is the area.
We can see in the figure, the area of the circular loop at position P and Q is different. Let’s
express the current density at position P as follows,
\[{j_1} = \dfrac{I}{{\pi {{\left( {2R} \right)}^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {j_1} = \dfrac{I}{{4\pi {R^2}}}\] …… (1)
Let’s express the current density at position Q as follows,
\[{j_2} = \dfrac{I}{{\pi {R^2}}}\] …… (2)
Dividing equation (1) by equation (2), we get,
\[\dfrac{{{j_1}}}{{{j_2}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{I}{{4\pi {R^2}}}}}{{\dfrac{I}{{\pi {R^2}}}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{j_1}}}{{{j_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{4}\]
\[ \therefore {j_1}:{j_2} = 1:4\]
So, the correct answer is option (C).
Note:Students often don’t get the difference between the current and current density. The current is the rate of flow of charges per unit time. The current density is the current flowing per unit area of the cross section. If the area of the cross section is greater, the current density decreases. Remember, the current density is also a vector quantity like current.
Formula used:
Current density, \[j = \dfrac{I}{A}\]
Here, I is the current and A is the area.
Complete step by step answer:
We know when the current flows through a given area, the current density in this area is
expressed as,
\[j = \dfrac{I}{A}\]
Here, I is the current and A is the area.
We can see in the figure, the area of the circular loop at position P and Q is different. Let’s
express the current density at position P as follows,
\[{j_1} = \dfrac{I}{{\pi {{\left( {2R} \right)}^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {j_1} = \dfrac{I}{{4\pi {R^2}}}\] …… (1)
Let’s express the current density at position Q as follows,
\[{j_2} = \dfrac{I}{{\pi {R^2}}}\] …… (2)
Dividing equation (1) by equation (2), we get,
\[\dfrac{{{j_1}}}{{{j_2}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{I}{{4\pi {R^2}}}}}{{\dfrac{I}{{\pi {R^2}}}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{j_1}}}{{{j_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{4}\]
\[ \therefore {j_1}:{j_2} = 1:4\]
So, the correct answer is option (C).
Note:Students often don’t get the difference between the current and current density. The current is the rate of flow of charges per unit time. The current density is the current flowing per unit area of the cross section. If the area of the cross section is greater, the current density decreases. Remember, the current density is also a vector quantity like current.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




