
Electric field due to an infinite sheet of charge having surface density $\sigma $ is $E$. The electric field due to an infinite conducting sheet of the same surface density of charge is
A. $\dfrac{E}{2}$
B. $E$
C. $2E$
D. $4E$
Answer
520.8k+ views
Hint: The electric field of the infinite charged sheet can be calculated using the Gauss theorem. A cylindrical Gaussian surface is considered, which is intersecting the sheet. By using the Gauss law, the electric field on the three surfaces is derived.
Formula used:
Gauss law states that,
$\phi = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Where $\phi $ is the electric flux, $q$ is the charge, and ${\varepsilon _0}$ is the electric constant.
Complete step by step solution:
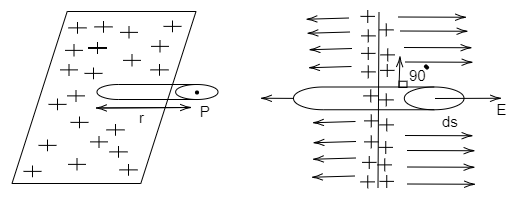
Consider a Gaussian volume as a cylinder, which intersects as shown in figure. The total flux over the Gaussian surface is defined by,
Total flux = Flux in curved surface + Flux in flat surface 1 + Flux in flat surface 2
$\phi = \oint {{{\vec E}_1}.d\vec s} = \int\limits_{Curve} {{E_1}.ds.\cos \theta } + \int\limits_{Flat - 1} {{E_1}.ds.\cos \theta } + \int\limits_{Flat - 2} {{E_1}.ds.\cos \theta } $
Since, the angle between electric field of lines and curved face, flat face-1 and flat face-2 are ${90^ \circ }$, ${0^ \circ }$ and ${0^ \circ }$.
Thus,
$\phi = \int\limits_{Curve} {{E_1}.ds.\cos 90} + \int\limits_{Flat - 1} {{E_1}.ds.\cos 0} + \int\limits_{Flat - 2} {{E_1}.ds.\cos 0} $
Since, $\cos 90 = 0$ and $\cos 0 = 1$
Then,
\[\phi = 0 + \int\limits_{} {{E_1}.ds} + \int\limits_{} {{E_1}.ds} \]
Since, $E$ is always constant.
Then,
\[\phi = {E_1}\int\limits_{} {ds} + {E_1}\int\limits_{} {ds} = 2{E_1}\int {ds} \]
The value of the integral $\int {ds} $ is area. So, $\int {ds} = A$
Hence, $\phi = 2{E_1}A\;.............................................\left( 1 \right)$
By Gauss theorem,
$\phi = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\;.......................................\left( 2 \right)$
By equating the equations (1) and (2), we get
$
2{E_1}A = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} \\
{E_1} = \dfrac{q}{{2{\varepsilon _0}A}} \\
$
The charge inside the Gaussian surface is defined by, $q = \sigma A$
Where $\sigma $ is the charge density and $A$ is the area.
Thus,
$
{E_1} = \dfrac{{\sigma A}}{{2{\varepsilon _0}A}} \\
{E_1} = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}}} \\
$
Since, Electric field due to an infinite sheet of charge having surface density $\sigma $ is $E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Then, ${E_1} = \dfrac{E}{2}$
$\therefore$ Electric field due to an infinite conducting sheet of the same surface density of charge is $ \dfrac{E}{2}$. Hence the option (A) is correct.
Note:
The sheet is a conducting sheet, so the electric field is half of the normal infinite sheet. The Gaussian surface must be intersected through the plane of the conducting sheet. The electric field is completely dependent on the charge density and the area of the surface and also depends on the electric constant.
Formula used:
Gauss law states that,
$\phi = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Where $\phi $ is the electric flux, $q$ is the charge, and ${\varepsilon _0}$ is the electric constant.
Complete step by step solution:

Consider a Gaussian volume as a cylinder, which intersects as shown in figure. The total flux over the Gaussian surface is defined by,
Total flux = Flux in curved surface + Flux in flat surface 1 + Flux in flat surface 2
$\phi = \oint {{{\vec E}_1}.d\vec s} = \int\limits_{Curve} {{E_1}.ds.\cos \theta } + \int\limits_{Flat - 1} {{E_1}.ds.\cos \theta } + \int\limits_{Flat - 2} {{E_1}.ds.\cos \theta } $
Since, the angle between electric field of lines and curved face, flat face-1 and flat face-2 are ${90^ \circ }$, ${0^ \circ }$ and ${0^ \circ }$.
Thus,
$\phi = \int\limits_{Curve} {{E_1}.ds.\cos 90} + \int\limits_{Flat - 1} {{E_1}.ds.\cos 0} + \int\limits_{Flat - 2} {{E_1}.ds.\cos 0} $
Since, $\cos 90 = 0$ and $\cos 0 = 1$
Then,
\[\phi = 0 + \int\limits_{} {{E_1}.ds} + \int\limits_{} {{E_1}.ds} \]
Since, $E$ is always constant.
Then,
\[\phi = {E_1}\int\limits_{} {ds} + {E_1}\int\limits_{} {ds} = 2{E_1}\int {ds} \]
The value of the integral $\int {ds} $ is area. So, $\int {ds} = A$
Hence, $\phi = 2{E_1}A\;.............................................\left( 1 \right)$
By Gauss theorem,
$\phi = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\;.......................................\left( 2 \right)$
By equating the equations (1) and (2), we get
$
2{E_1}A = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} \\
{E_1} = \dfrac{q}{{2{\varepsilon _0}A}} \\
$
The charge inside the Gaussian surface is defined by, $q = \sigma A$
Where $\sigma $ is the charge density and $A$ is the area.
Thus,
$
{E_1} = \dfrac{{\sigma A}}{{2{\varepsilon _0}A}} \\
{E_1} = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}}} \\
$
Since, Electric field due to an infinite sheet of charge having surface density $\sigma $ is $E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Then, ${E_1} = \dfrac{E}{2}$
$\therefore$ Electric field due to an infinite conducting sheet of the same surface density of charge is $ \dfrac{E}{2}$. Hence the option (A) is correct.
Note:
The sheet is a conducting sheet, so the electric field is half of the normal infinite sheet. The Gaussian surface must be intersected through the plane of the conducting sheet. The electric field is completely dependent on the charge density and the area of the surface and also depends on the electric constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




