
Electric intensity is –
A. a scalar quantity
B. a vector quantity
C. neither scalar nor vector
D. sometimes scalar and sometimes vector
Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint: Electric field is the force experienced by a unit positive charge kept at that point. Relation between electric field intensity E, force F and q is given by \[q \times E = F\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
Electric field at a point is measured in terms of Electric field intensity or electric intensity E. Electric intensity in an electric field at a point is the force experienced by a unit positive charge kept at that point.
Now, we consider point charge placed at point O in air as shown in figure. A test charge \[{q_0}\] is placed at point A at a distance r from point O.
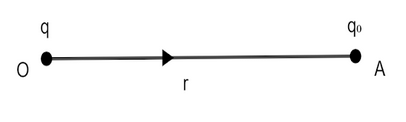
According to Coulomb’s law, the test charge \[{q_0}\] experience force F due to point charge q. It is given by,
\[F = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{q{q_0}}}{{{r^2}}}\] …..(1)
By definition, electric intensity at point B is given as,
\[E = \dfrac{F}{{{q_0}}}\] …..(2)
Using equation (1) and (2) we can write,
\[E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{q}{{{r^2}}}\]
The direction of F is along the line joining the points O and A, passing away from the charge q if q is positive and toward q, if q is negative. So, the direction is the same as force.
Hence, electric intensity is a vector quantity.
Force in vector form,
\[\vec F = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{q{q_0}}}{{{{\vec r}^3}}}\hat r\]
Electric intensity in vector form is,
\[\vec E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{q}{{{{\vec r}^3}}}\hat r\]
where, \[\vec r\] is a position vector and \[\hat r\] is a unit vector.
Note: Electric intensity is also known as electric field and electric field intensity. Every charged particle creates an electric field around it in which the effect of electric force is experienced by another charge. The SI unit of electric intensity is Newton per coulomb and dimension is \[\left[ {ML{T^{ - 3}}{A^{ - 1}}} \right]\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
Electric field at a point is measured in terms of Electric field intensity or electric intensity E. Electric intensity in an electric field at a point is the force experienced by a unit positive charge kept at that point.
Now, we consider point charge placed at point O in air as shown in figure. A test charge \[{q_0}\] is placed at point A at a distance r from point O.

According to Coulomb’s law, the test charge \[{q_0}\] experience force F due to point charge q. It is given by,
\[F = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{q{q_0}}}{{{r^2}}}\] …..(1)
By definition, electric intensity at point B is given as,
\[E = \dfrac{F}{{{q_0}}}\] …..(2)
Using equation (1) and (2) we can write,
\[E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{q}{{{r^2}}}\]
The direction of F is along the line joining the points O and A, passing away from the charge q if q is positive and toward q, if q is negative. So, the direction is the same as force.
Hence, electric intensity is a vector quantity.
Force in vector form,
\[\vec F = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{q{q_0}}}{{{{\vec r}^3}}}\hat r\]
Electric intensity in vector form is,
\[\vec E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{q}{{{{\vec r}^3}}}\hat r\]
where, \[\vec r\] is a position vector and \[\hat r\] is a unit vector.
Note: Electric intensity is also known as electric field and electric field intensity. Every charged particle creates an electric field around it in which the effect of electric force is experienced by another charge. The SI unit of electric intensity is Newton per coulomb and dimension is \[\left[ {ML{T^{ - 3}}{A^{ - 1}}} \right]\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




