
Electromagnetic radiation with maximum wavelength is:
(A) Ultraviolet
(B) Radiowave
(C) X-ray
(D) Infrared
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: It is the electromagnetic radiation which is used in communication technologies such as mobile phones, Wi-Fi, television, radio and so on. Heinrich Hertz discovered this type of waves. It is used to separate electrons from atoms and molecules, chemical changes in DNA and even in cooking food at home.
Complete step by step answer:
- Clark Maxwell first told that the radio waves existed. Heinrich Hertz demonstrated this wave in the lab.
- Like other electromagnetic radiations, they also travel at the speed of the light in the vacuum.
- They are formed by the electric charges under acceleration. These electric charges flow in a special metal conductor called antenna, then transmitted through a transmitter and finally received by the radio receiver. Radio waves occurring naturally are by lightning and astronomical objects.
- Electromagnetic radiation with maximum wavelength is the radio wave.
- The frequency ranges between 300 gigahertz (GHz) to 30 hertz (Hz).
- The representation of various types of electromagnetic radiation and its relation with energy and wavelength is shown in the following figure.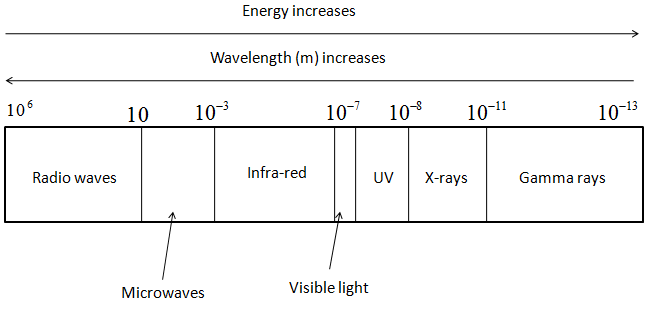
- Thus, from the figure, we can say that Radio waves will have least energy and will have the highest wavelength amongst them all.
-Nowadays, it is used as broadcasting radar, communication satellite, computer network, wireless devices such as earphones, computers and so on.
-Wi-Fi uses radio waves through wireless internet routers popularly known as LAN. It uses frequencies between 2.4 to 5.8 GHz.
So, the correct option is (B) Radiowave.
Note:
The wavelength of a wave is inversely proportional to the energy of the wave. Thus, we can say that as the wavelength of a wave increases, its energy decreases and as its wavelength decreases, its energy increases.
Complete step by step answer:
- Clark Maxwell first told that the radio waves existed. Heinrich Hertz demonstrated this wave in the lab.
- Like other electromagnetic radiations, they also travel at the speed of the light in the vacuum.
- They are formed by the electric charges under acceleration. These electric charges flow in a special metal conductor called antenna, then transmitted through a transmitter and finally received by the radio receiver. Radio waves occurring naturally are by lightning and astronomical objects.
- Electromagnetic radiation with maximum wavelength is the radio wave.
- The frequency ranges between 300 gigahertz (GHz) to 30 hertz (Hz).
- The representation of various types of electromagnetic radiation and its relation with energy and wavelength is shown in the following figure.

- Thus, from the figure, we can say that Radio waves will have least energy and will have the highest wavelength amongst them all.
-Nowadays, it is used as broadcasting radar, communication satellite, computer network, wireless devices such as earphones, computers and so on.
-Wi-Fi uses radio waves through wireless internet routers popularly known as LAN. It uses frequencies between 2.4 to 5.8 GHz.
So, the correct option is (B) Radiowave.
Note:
The wavelength of a wave is inversely proportional to the energy of the wave. Thus, we can say that as the wavelength of a wave increases, its energy decreases and as its wavelength decreases, its energy increases.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




