
What is the electron and molecular geometry of \[BeC{l_2}\]?
Answer
504k+ views
Hint: The VSEPR hypothesis, or Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory, and the hybridization of the central atom in the molecule can be used to answer this question. According to the hypothesis, the number of electron pairs on the central atom affects the arrangement of these lone pairs surrounding the central atom in compounds with the chemical formula \[X{Y_m}\].
Complete answer:
Beryllium chloride, also known as \[BeC{l_2}\], is an inorganic chemical. At room temperature, it appears as a white or yellow crystal solid. It is available in monomeric and 1-D polymeric forms. Because of the diagonal relationship between beryllium and aluminum, the characteristics of beryllium chloride are comparable to those of aluminum chloride.
Beryllium chloride has a molar mass of \[79.91\]g/mol and a melting point of \[{399^0}C\]. Beryllium Chloride's chemical bonding is explored by writing down its Lewis structure using the Lewis method.
Following the Lewis structure, there is a requirement to comprehend its molecular geometry and the hybridization of the core element, Beryllium. To comprehend the MO diagram of beryllium chloride, the molecular orbital (MO) theory will be applied.
As far as electron and molecular geometry is concerned, they are both linear. Since the central Be atom has no lone pair and two bonding atoms (group / domains), the electron-pair and molecular geometry of \[BeC{l_2} \] is linear and the bond angle is \ [{180^0} \]. The electrons in an atom's outermost shell are depicted in the Lewis structure of any molecule. These electrons will have both bonding and non-bonding properties.
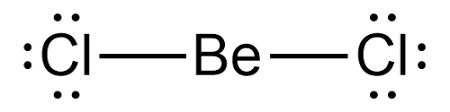
Lewis structure for \[BeC{l_2} \]
Note:
Lewis’s structure is also known as electron dot structure or Lewis dot structure because the valence electrons in the molecule's Lewis structure are depicted as dots. It is a two-dimensional structure in which each atom in the molecule strives to complete its octet by sharing, acquiring, or losing electrons.
Complete answer:
Beryllium chloride, also known as \[BeC{l_2}\], is an inorganic chemical. At room temperature, it appears as a white or yellow crystal solid. It is available in monomeric and 1-D polymeric forms. Because of the diagonal relationship between beryllium and aluminum, the characteristics of beryllium chloride are comparable to those of aluminum chloride.
Beryllium chloride has a molar mass of \[79.91\]g/mol and a melting point of \[{399^0}C\]. Beryllium Chloride's chemical bonding is explored by writing down its Lewis structure using the Lewis method.
Following the Lewis structure, there is a requirement to comprehend its molecular geometry and the hybridization of the core element, Beryllium. To comprehend the MO diagram of beryllium chloride, the molecular orbital (MO) theory will be applied.
As far as electron and molecular geometry is concerned, they are both linear. Since the central Be atom has no lone pair and two bonding atoms (group / domains), the electron-pair and molecular geometry of \[BeC{l_2} \] is linear and the bond angle is \ [{180^0} \]. The electrons in an atom's outermost shell are depicted in the Lewis structure of any molecule. These electrons will have both bonding and non-bonding properties.
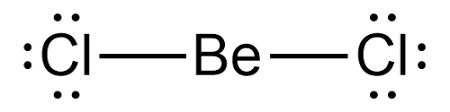
Lewis structure for \[BeC{l_2} \]
Note:
Lewis’s structure is also known as electron dot structure or Lewis dot structure because the valence electrons in the molecule's Lewis structure are depicted as dots. It is a two-dimensional structure in which each atom in the molecule strives to complete its octet by sharing, acquiring, or losing electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE




