
What is the electron configuration for Fr?
Answer
528.3k+ views
Hint: The atomic numbers of various elements lead to the electron configuration. The atomic number is equal to the number of electrons in any atom. The electronic configuration has the filling of these electrons into the orbital. The filling of electrons is through the Aufbau principle that determines the electron configuration of elements.
Complete answer:
Electronic configuration of any element tells us the total number of electrons in that atom which is equal to the atomic number of that element. Electronic configuration of any element consists of filling the orbital with electrons. The filling of electrons in various orbitals is according to a principle of Aufbau that takes place from the lower energy level to the higher energy level. The filling takes place in s, p, d, and f subshells. These subshells are written along with the number of shells, like 1,2, 3, etc.
The diagrammatic representation of the Aufbau diagram is as follows:
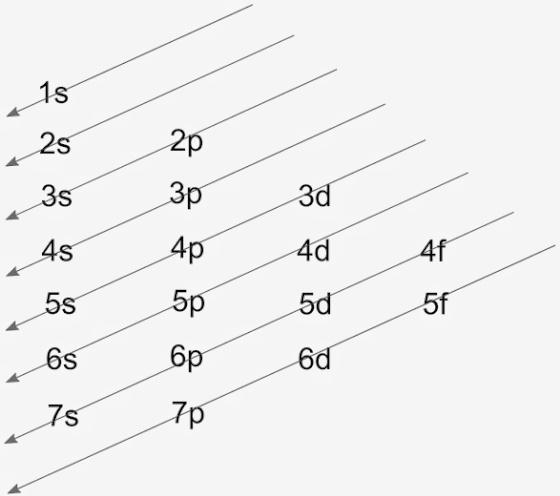
The arrows denote the order of the filling of electrons. s orbital can accommodate 2 electrons, p can have 6, d can have 10, while f can have 14 electrons filled.
Now, we have been given the element Fr which is francium, according to the periodic table, it has an atomic number of 87. So, the filling of electrons will take place as,
Fr = 87, $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}3{{d}^{10}}4{{s}^{2}}4{{p}^{6}}4{{d}^{10}}5{{s}^{2}}5{{p}^{6}}4{{f}^{14}}5{{d}^{10}}6{{s}^{2}}6{{p}^{6}}7{{s}^{1}}$
This configuration when rounded to the nearest noble gas, Radon, Rn having 86 atomic number, the configuration becomes, Fr = $[Rn]7{{s}^{1}}$
Hence, the electron configuration for Fr is $[Rn]7{{s}^{1}}$.
Note:
Fr is the element of group 1 of the family alkali metals that has hydrogen, lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium. These all have one electron in the outer shell that makes them highly reactive metals. Apart from this electronic configuration, the configuration can also be written in shells of K, L, M, N, that can have 2, 8, 18, 32 electrons respectively.
Complete answer:
Electronic configuration of any element tells us the total number of electrons in that atom which is equal to the atomic number of that element. Electronic configuration of any element consists of filling the orbital with electrons. The filling of electrons in various orbitals is according to a principle of Aufbau that takes place from the lower energy level to the higher energy level. The filling takes place in s, p, d, and f subshells. These subshells are written along with the number of shells, like 1,2, 3, etc.
The diagrammatic representation of the Aufbau diagram is as follows:

The arrows denote the order of the filling of electrons. s orbital can accommodate 2 electrons, p can have 6, d can have 10, while f can have 14 electrons filled.
Now, we have been given the element Fr which is francium, according to the periodic table, it has an atomic number of 87. So, the filling of electrons will take place as,
Fr = 87, $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}3{{d}^{10}}4{{s}^{2}}4{{p}^{6}}4{{d}^{10}}5{{s}^{2}}5{{p}^{6}}4{{f}^{14}}5{{d}^{10}}6{{s}^{2}}6{{p}^{6}}7{{s}^{1}}$
This configuration when rounded to the nearest noble gas, Radon, Rn having 86 atomic number, the configuration becomes, Fr = $[Rn]7{{s}^{1}}$
Hence, the electron configuration for Fr is $[Rn]7{{s}^{1}}$.
Note:
Fr is the element of group 1 of the family alkali metals that has hydrogen, lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium. These all have one electron in the outer shell that makes them highly reactive metals. Apart from this electronic configuration, the configuration can also be written in shells of K, L, M, N, that can have 2, 8, 18, 32 electrons respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




