
What is the electron sea model?
(a) The model of metallic bonding where electrons float free in a sea of electrons around metal atoms.
(b) Where electrons float free in a sea of salt water.
(c) The model of metallic bonding where electrons are fixed in place in a sea of metal atoms.
(d) A model depicting the different bonds that electrons can make.
(e) The model of metallic bonding where protons float free in a sea of electrons around metal atoms.
Answer
528.4k+ views
Hint: We know most metals have low electronegativity hence the electrons are not held very tightly by the metal atoms. Therefore, we can imagine them to be moving on the surface of the metal free from each other. This forms the basis of the Electron Sea Model.
Complete step by step solution:
We can see in metallic bonding there are no atoms with higher electronegativities for the electron density to be transferred to. This could mean that in metallic bonding for the metal atom to become more stable it should release its electron density but without transferring the electrons to another atom. Hence we can say the electrons are now free to move between atoms without being bonded to any particular atom.
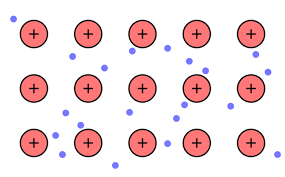
Thus, we can conclude that Option (A) the model of metallic bonding where electrons float free in a sea of electrons around metal atoms is the correct answer.
Additional information:
The free electrons on the surface are the sea of electrons. From this model of freely moving electrons we can find the explanation of the properties of electric conductivity, malleability, luster, and heat conductivity in metals. It also helps scientists to picture the behavior of electrons in metallic bonding.
Note: This model established by Dirac has some drawbacks too. There are certain characteristics that we cannot explain by this model, such as the formation of certain alloys between metals with specific compositions or the stability of collective metal bonds, among others but these are easily explained by the Quantum model.
Complete step by step solution:
We can see in metallic bonding there are no atoms with higher electronegativities for the electron density to be transferred to. This could mean that in metallic bonding for the metal atom to become more stable it should release its electron density but without transferring the electrons to another atom. Hence we can say the electrons are now free to move between atoms without being bonded to any particular atom.

Thus, we can conclude that Option (A) the model of metallic bonding where electrons float free in a sea of electrons around metal atoms is the correct answer.
Additional information:
The free electrons on the surface are the sea of electrons. From this model of freely moving electrons we can find the explanation of the properties of electric conductivity, malleability, luster, and heat conductivity in metals. It also helps scientists to picture the behavior of electrons in metallic bonding.
Note: This model established by Dirac has some drawbacks too. There are certain characteristics that we cannot explain by this model, such as the formation of certain alloys between metals with specific compositions or the stability of collective metal bonds, among others but these are easily explained by the Quantum model.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




