
Electron $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization with suitable example.
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: The concept of intermixing of different orbitals of atoms and then redistribution of energy to give equivalent energy of new orbitals, identical shape, and symmetrical orientation in space is hybridization. As a result of hybridization, new orbitals are formed known as hybrid orbitals, and bonds formed by hybrid orbitals are called hybrid bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
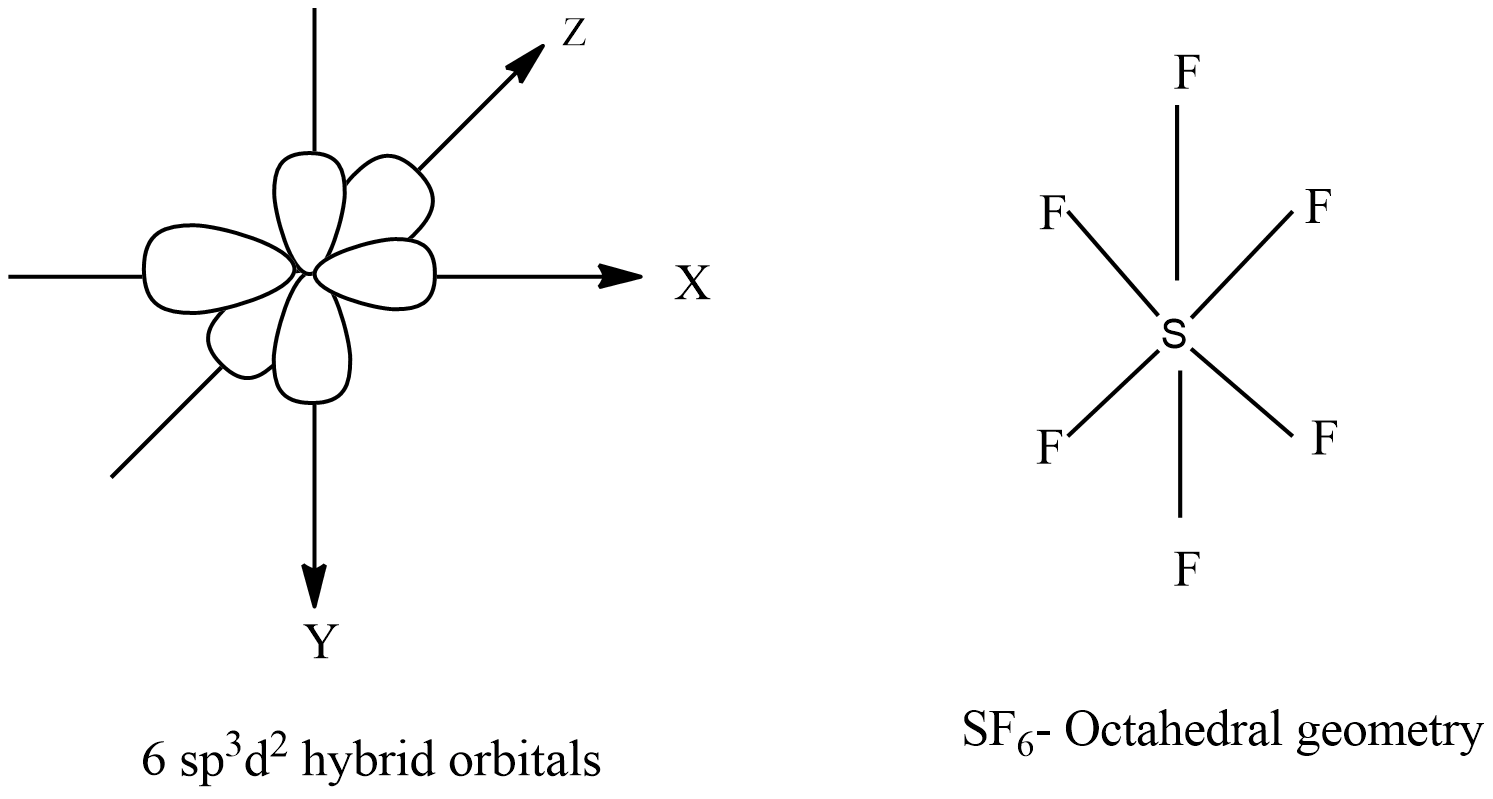
-$s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ Hybridization: When one s-orbital, three p-orbitals, and two d-orbitals hybridize to give six equivalent $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals of equal energy. This hybridization is called $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization.
-Properties: six equivalent $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals are directed towards the six corners of a regular octahedron.
-Out of six hybrid orbitals, four are lying in one plane while the remaining two are directed above and below the plane containing four hybrid orbitals.
-Geometry is octahedral and bond angle is ${{90}^{o}}$. For example, sulfur hexafluoride $S{{F}_{6}}$. The central atom of this molecule, which is involved in the $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization is sulfur (S). The atomic number of sulfur is 16, and electronic configuration is: $[Ne]3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{4}}3{{d}^{0}}$(ground state)
-The outer shell electrons in sulfur excited from the ground state to a higher energy state, then the electronic configuration will be: $[Ne]3{{s}^{1}}3{{p}^{3}}3{{d}^{2}}$ (Higher energy state). The six equivalent $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals of sulfur are bonding with 6 p-orbital of F atoms resulting in the formation of a geometrical shape.
Note: The characteristics of hybridization are the number of hybrid orbitals formed are equal to the number atomic orbitals which orbitals undergo hybridization and these hybrid orbitals are equivalent in energy with shape. The stability of hybrid orbitals more than atomic orbitals and these hybrid orbitals have different orientations in space.
Complete step by step solution:
-$s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ Hybridization: When one s-orbital, three p-orbitals, and two d-orbitals hybridize to give six equivalent $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals of equal energy. This hybridization is called $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization.
-Properties: six equivalent $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals are directed towards the six corners of a regular octahedron.
-Out of six hybrid orbitals, four are lying in one plane while the remaining two are directed above and below the plane containing four hybrid orbitals.
-Geometry is octahedral and bond angle is ${{90}^{o}}$. For example, sulfur hexafluoride $S{{F}_{6}}$. The central atom of this molecule, which is involved in the $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization is sulfur (S). The atomic number of sulfur is 16, and electronic configuration is: $[Ne]3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{4}}3{{d}^{0}}$(ground state)
-The outer shell electrons in sulfur excited from the ground state to a higher energy state, then the electronic configuration will be: $[Ne]3{{s}^{1}}3{{p}^{3}}3{{d}^{2}}$ (Higher energy state). The six equivalent $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals of sulfur are bonding with 6 p-orbital of F atoms resulting in the formation of a geometrical shape.

Note: The characteristics of hybridization are the number of hybrid orbitals formed are equal to the number atomic orbitals which orbitals undergo hybridization and these hybrid orbitals are equivalent in energy with shape. The stability of hybrid orbitals more than atomic orbitals and these hybrid orbitals have different orientations in space.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




