
Why do electrostatic field lines not form closed loops.
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: Electric field describes the influence of a charged particle on its environment. The direction of electric field is described by the electric lines of forces. Electric field lines are open curves which originate from positive charge and terminate into negative charge.
Complete solution:
The electrostatic field due to charged particles is described as the work done to bring a unit charge from infinity to that point in the field. Its SI unit is \[N\,m\]. It is given as-
\[E=\dfrac{F}{q}\]
Here,
\[E\] is the electric field
\[F\] is the force acting on charge \[q\]
\[q\] is the charge present in the field.
The direction of an electric field can be visualized by the electric lines of forces. The electric lines of forces are imaginary lines which give us the direction of the electric field. The electric lines of forces are described as the path followed by a unit positive charge while moving towards a unit negative charge. Therefore, these lines originate from the positive charge and end into the negative charge. Tangent drawn at any point on the electric field lines is the direction of the electric field at that point.
For a conductor, there is no electric field inside it as the charge is distributed on its surface. So, no electric lines of forces are present inside it. This is the reason why electric lines of forces are open lines instead of being closed loops. They originate from the surface and terminate at the surface of charges.
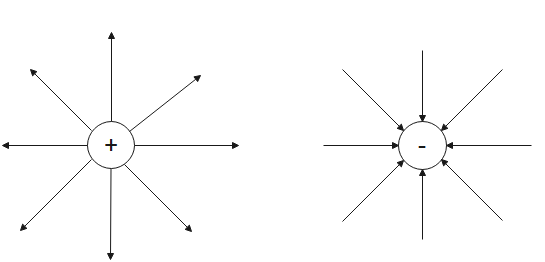
Electric lines of forces are open curves because no electric field lines are present inside charged containers.
Note: The electric lines of forces are visualized differently for different objects. The electric field lines have opposite directions for positive and negative charges. For a positively charged plate, straight lines originate from the plate into infinity. A Gaussian surface is a three dimensional surface around a charged conductor used to calculate the electric field for that conductor.
Complete solution:
The electrostatic field due to charged particles is described as the work done to bring a unit charge from infinity to that point in the field. Its SI unit is \[N\,m\]. It is given as-
\[E=\dfrac{F}{q}\]
Here,
\[E\] is the electric field
\[F\] is the force acting on charge \[q\]
\[q\] is the charge present in the field.
The direction of an electric field can be visualized by the electric lines of forces. The electric lines of forces are imaginary lines which give us the direction of the electric field. The electric lines of forces are described as the path followed by a unit positive charge while moving towards a unit negative charge. Therefore, these lines originate from the positive charge and end into the negative charge. Tangent drawn at any point on the electric field lines is the direction of the electric field at that point.
For a conductor, there is no electric field inside it as the charge is distributed on its surface. So, no electric lines of forces are present inside it. This is the reason why electric lines of forces are open lines instead of being closed loops. They originate from the surface and terminate at the surface of charges.

Electric lines of forces are open curves because no electric field lines are present inside charged containers.
Note: The electric lines of forces are visualized differently for different objects. The electric field lines have opposite directions for positive and negative charges. For a positively charged plate, straight lines originate from the plate into infinity. A Gaussian surface is a three dimensional surface around a charged conductor used to calculate the electric field for that conductor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




