
What is endocytosis? Give an example.
Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: As we know endocytosis is the process of ingestion of substances into the cell. The substance to be ingested is surrounded by the cell membrane and then buds off inside the cell thereby forming a vesicle. Basically, we can say that endocytosis is the process by which cells take in substances from outside of the cell by engulfing them in a vesicle.
Complete answer:
Endocytosis is defined as the process of trapping a particle or even a substance from the external environment by the process of engulfing it. The flexibility of the cell membrane helps the cell to engulf the food and also other materials from the external environment. Such a process is called endocytosis.
Two examples of endocytosis are as follows;
Amoeba engulfs its food through the process of endocytosis with the help of pseudopodia.
Pathogens are removed by white blood cells such as neutrophils and monocytes by the process of phagocytosis which is one type of endocytosis.
The three types of endocytosis are;
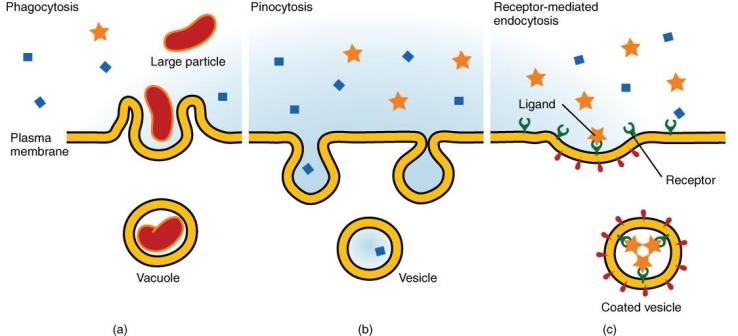
Pinocytosis - also known as cell drinking, is commonly seen in plant and animal cells. During pinocytosis, the cell takes in water and nutrients from the extracellular fluid that it needs to function.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis - is a specialized type of pinocytosis. Macromolecules bind to receptors which are present along the surface of the cell plasma membrane.
Phagocytosis - also known as cell eating, is the process by which cells internalize large particles or cells, for example like damaged cells and bacteria.
The diagram below depicts the different types of endocytosis, which are phagocytosis, pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Note:
We must note that endocytosis is the process of capturing a substance or even a particle from outside of the cell by engulfing it with the cell membrane, and bringing it into the cell. While, exocytosis describes the process of vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane and then releasing their contents to the outside of the cell.
Complete answer:
Endocytosis is defined as the process of trapping a particle or even a substance from the external environment by the process of engulfing it. The flexibility of the cell membrane helps the cell to engulf the food and also other materials from the external environment. Such a process is called endocytosis.
Two examples of endocytosis are as follows;
Amoeba engulfs its food through the process of endocytosis with the help of pseudopodia.
Pathogens are removed by white blood cells such as neutrophils and monocytes by the process of phagocytosis which is one type of endocytosis.
The three types of endocytosis are;
Pinocytosis - also known as cell drinking, is commonly seen in plant and animal cells. During pinocytosis, the cell takes in water and nutrients from the extracellular fluid that it needs to function.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis - is a specialized type of pinocytosis. Macromolecules bind to receptors which are present along the surface of the cell plasma membrane.
Phagocytosis - also known as cell eating, is the process by which cells internalize large particles or cells, for example like damaged cells and bacteria.
The diagram below depicts the different types of endocytosis, which are phagocytosis, pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis.

Note:
We must note that endocytosis is the process of capturing a substance or even a particle from outside of the cell by engulfing it with the cell membrane, and bringing it into the cell. While, exocytosis describes the process of vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane and then releasing their contents to the outside of the cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




