
Enlist seven pairs of contrasting characters selected by Mendel.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Useful features include their rapid life cycle and the production of lots and lots of seeds. It also typically self-fertilizes, meaning that the same plant makes both the sperm and the egg that come together in fertilization. It is also easy to cross or mate in a controlled way.
Complete answer:
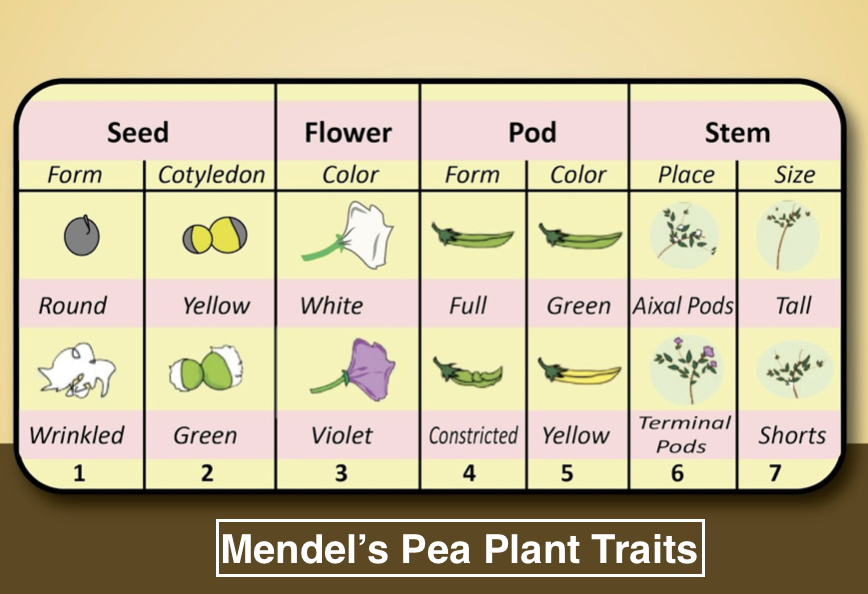
Seven pair of contrasting characters selected by Mendel is:
1. Pea shape (round or wrinkled)
2. Pea color (green or yellow)
3. Pod shape (constricted or inflated)
4. Pod color (green or yellow)
5. Flower color (purple or white)
6. Plant size (tall or dwarf)
7. Position of flowers (axial or terminal)
Mendel's Laws of Heredity are usually stated as:
1) The Law of Segregation: Each inherited trait is described by a gene pair. Parental genes are arbitrarily separated from the sex cells so that sex cells contain just a single gene of the pair. Offspring, subsequently, inherit one genetic allele from each parent when sex cells unite in fertilization.
2) The Law of Independent Assortment: Genes for various traits are sorted independently from each other so that the inheritance of one trait is not dependent on the inheritance of another.
3) The Law of Dominance: An organism with alternate various forms of a gene will express the form that is dominant.
The genetic experiments Mendel did with pea plants took him eight years (1856- 1863) and he distributed his outcome in 1865. During this time, Mendel grew over 10,000 pea plants, monitoring offspring number and type. Mendel's work and his Laws of Inheritance were not acknowledged in his time. It wasn't until 1900, after the rediscovery of his Laws, that his trial results were perceived.
Note:
- The scientist studied the inheritance of traits in pea plants. He proposed a model where pairs of "heritable elements," or genes, determine traits.
- Genes come in various versions or alleles. A dominant allele conceals a recessive allele and determines the organism's appearance.
- A Punnett square can be utilized to predict genotypes (allele combinations) and phenotypes (observable traits) of offspring from genetic crosses.
- A test cross can be utilized to determine whether an organism with a dominant phenotype is homozygous or heterozygous.
Complete answer:
Seven pair of contrasting characters selected by Mendel is:
1. Pea shape (round or wrinkled)
2. Pea color (green or yellow)
3. Pod shape (constricted or inflated)
4. Pod color (green or yellow)
5. Flower color (purple or white)
6. Plant size (tall or dwarf)
7. Position of flowers (axial or terminal)

Mendel's Laws of Heredity are usually stated as:
1) The Law of Segregation: Each inherited trait is described by a gene pair. Parental genes are arbitrarily separated from the sex cells so that sex cells contain just a single gene of the pair. Offspring, subsequently, inherit one genetic allele from each parent when sex cells unite in fertilization.
2) The Law of Independent Assortment: Genes for various traits are sorted independently from each other so that the inheritance of one trait is not dependent on the inheritance of another.
3) The Law of Dominance: An organism with alternate various forms of a gene will express the form that is dominant.
The genetic experiments Mendel did with pea plants took him eight years (1856- 1863) and he distributed his outcome in 1865. During this time, Mendel grew over 10,000 pea plants, monitoring offspring number and type. Mendel's work and his Laws of Inheritance were not acknowledged in his time. It wasn't until 1900, after the rediscovery of his Laws, that his trial results were perceived.
Note:
- The scientist studied the inheritance of traits in pea plants. He proposed a model where pairs of "heritable elements," or genes, determine traits.
- Genes come in various versions or alleles. A dominant allele conceals a recessive allele and determines the organism's appearance.
- A Punnett square can be utilized to predict genotypes (allele combinations) and phenotypes (observable traits) of offspring from genetic crosses.
- A test cross can be utilized to determine whether an organism with a dominant phenotype is homozygous or heterozygous.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




