
How many enolizable hydrogens are there in the following compound?
2-methylcyclohex2-en-1one
A.2
B.3
C.4
D.7
Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: An enolizable ketone is one that has one or more alpha hydrogens in its molecule. The first carbon atom that binds to a functional group, such as a carbonyl, is referred to as the alpha carbon in organic molecules. The beta carbon is the second carbon atom, and the scheme continues to name them in alphabetical order using Greek characters.
Complete answer:
Keto–enol tautomerism is a chemical equilibrium between a keto form (a ketone or an aldehyde) and an enol in organic chemistry (an alcohol). Tautomers are said to exist between the keto and enol varieties. Since the interconversion of the two modes requires the passage of an alpha hydrogen atom as well as the reorganisation of bonding electrons, the isomerism is classified as tautomerism.
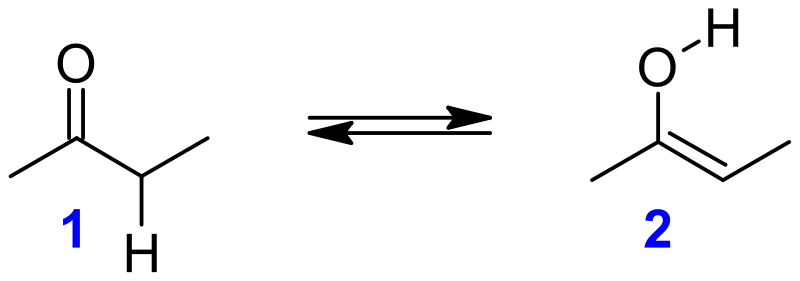
Alkenols, or enols, are a type of reactive structure or intermediate in organic chemistry that is described as an alkene (olefin) with a hydroxyl group attached to one end of the alkene double bond. The expressions enol and alkanol are portmanteau of "-ene"/"alkene" and the "-ol" suffix suggesting the hydroxyl group of alcohols, with the first term's terminal "-e" dropped. Deprotonation, or the elimination of a hydrogen adjacent (-) to the carbonyl ring, is often used in the production of enols. The consequence of not returning this proton at the end of the stepwise procedure is an anion known as an enolate.
2-methylcyclohex2-en-1one
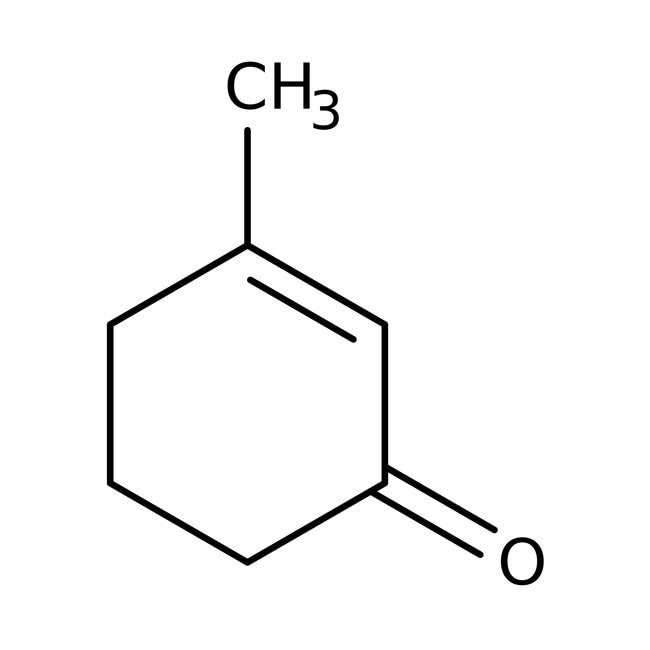
In the above structure, when "$\alpha$" - Hydrogen in the molecule of an aldehyde or ketone is replaced as hydrogen ion, an enolate ion is formed.
\[\alpha - H\] with respect to – C=O is 2
\[\alpha - H\] with respect to double bond is 5
Total \[\alpha - H\] observed = 2 + 5 = 7
Hence option D is correct.
Note:
The nomenclature may also be used to describe hydrogen atoms bound to carbon atoms. An alpha-hydrogen atom is a hydrogen atom attached to an alpha carbon atom; a hydrogen atom attached to a beta carbon atom is a beta hydrogen atom, and so on.
This naming standard does not conform to IUPAC nomenclature, which promotes carbons to be named by number rather than Greek letter, but it is still widely used, particularly for determining the relative position of carbon atoms to other functional groups.
Complete answer:
Keto–enol tautomerism is a chemical equilibrium between a keto form (a ketone or an aldehyde) and an enol in organic chemistry (an alcohol). Tautomers are said to exist between the keto and enol varieties. Since the interconversion of the two modes requires the passage of an alpha hydrogen atom as well as the reorganisation of bonding electrons, the isomerism is classified as tautomerism.

Alkenols, or enols, are a type of reactive structure or intermediate in organic chemistry that is described as an alkene (olefin) with a hydroxyl group attached to one end of the alkene double bond. The expressions enol and alkanol are portmanteau of "-ene"/"alkene" and the "-ol" suffix suggesting the hydroxyl group of alcohols, with the first term's terminal "-e" dropped. Deprotonation, or the elimination of a hydrogen adjacent (-) to the carbonyl ring, is often used in the production of enols. The consequence of not returning this proton at the end of the stepwise procedure is an anion known as an enolate.
2-methylcyclohex2-en-1one

In the above structure, when "$\alpha$" - Hydrogen in the molecule of an aldehyde or ketone is replaced as hydrogen ion, an enolate ion is formed.
\[\alpha - H\] with respect to – C=O is 2
\[\alpha - H\] with respect to double bond is 5
Total \[\alpha - H\] observed = 2 + 5 = 7
Hence option D is correct.
Note:
The nomenclature may also be used to describe hydrogen atoms bound to carbon atoms. An alpha-hydrogen atom is a hydrogen atom attached to an alpha carbon atom; a hydrogen atom attached to a beta carbon atom is a beta hydrogen atom, and so on.
This naming standard does not conform to IUPAC nomenclature, which promotes carbons to be named by number rather than Greek letter, but it is still widely used, particularly for determining the relative position of carbon atoms to other functional groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




