
Enzymes required to remove RNA primer during DNA replication is?
A) Primase
B) DNA polymerase I
C) DNA polymerase II
D) Ligase
Answer
510.9k+ views
Hint: DNA replication is the process by which the DNA makes copies of itself. It occurs naturally during cell division. It can also occur artificially using PCR techniques by using RNA primer. The RNA primer is the short strand of nucleotide.
Complete answer:
A primer is a short segment of nucleic acid that initiates DNA synthesis. The enzyme primase helps in the synthesis of the primer. It is an RNA polymerase. The primer helps in the Synthesis of leading or continuous strands. It is fast with the help of a single primer, while the synthesis of lagging or discontinuous strands is slow and requires many primers.
The polymerase enzyme assembles the DNA or RNA. Now, DNA polymerase I, is also called the Kornberg enzyme and for exonuclease activity, it is used to remove RNA primer formed by UV rays. It is also used to fill the gaps between the fragments. For polymerase activity, it nearly adds up to 1000 nucleotides per minute.
DNA polymerase II, polymerase activity allows the rate of 50 Nucleotides per minute. It never requires a primer. It synthesizes mRNA from DNA. DNA polymerase III, the polymerase activity rate of 20000 bp per second. It is involved in the synthesis of lagging and leading strands.
The diagram below shows the replication of DNA.
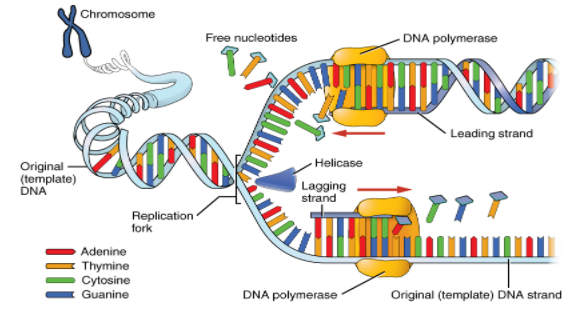
Ligase: The replication is discontinuous in the form of a short Okazaki fragment on the other template strand; this is called the lagging daughter strand. The discontinuously synthesised fragments are later joined by the enzymes DNA ligase.
Hence, the correct answer is option ‘B’ i.e, DNA polymerase I.
Note: Watson and crick had immediately proposed a scheme for DNA replication while proposing the double-helical structure of DNA. The scheme suggested that the two strands would separate and act as a template for the synthesis of new complementary strands. After the completion of replication, each DNA molecule would have one parental and one newly synthesis strand.
Complete answer:
A primer is a short segment of nucleic acid that initiates DNA synthesis. The enzyme primase helps in the synthesis of the primer. It is an RNA polymerase. The primer helps in the Synthesis of leading or continuous strands. It is fast with the help of a single primer, while the synthesis of lagging or discontinuous strands is slow and requires many primers.
The polymerase enzyme assembles the DNA or RNA. Now, DNA polymerase I, is also called the Kornberg enzyme and for exonuclease activity, it is used to remove RNA primer formed by UV rays. It is also used to fill the gaps between the fragments. For polymerase activity, it nearly adds up to 1000 nucleotides per minute.
DNA polymerase II, polymerase activity allows the rate of 50 Nucleotides per minute. It never requires a primer. It synthesizes mRNA from DNA. DNA polymerase III, the polymerase activity rate of 20000 bp per second. It is involved in the synthesis of lagging and leading strands.
The diagram below shows the replication of DNA.

Ligase: The replication is discontinuous in the form of a short Okazaki fragment on the other template strand; this is called the lagging daughter strand. The discontinuously synthesised fragments are later joined by the enzymes DNA ligase.
Hence, the correct answer is option ‘B’ i.e, DNA polymerase I.
Note: Watson and crick had immediately proposed a scheme for DNA replication while proposing the double-helical structure of DNA. The scheme suggested that the two strands would separate and act as a template for the synthesis of new complementary strands. After the completion of replication, each DNA molecule would have one parental and one newly synthesis strand.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




