
Establish the relation between drift velocity and electric field. What is mobility? Describe the relation between mobility and velocity.
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: We know that electrons have a negative charge and opposite charges, negative and positive, attract each other. Metals are the conductor of electricity. It means that when a potential difference is applied across a conductor, free electrons gain velocity in the direction opposite to the electric field between successive collisions (and lose velocity when traveling in the direction of the field), thus acquiring a velocity component in that direction in addition to its random thermal velocity. As a result, there is a definite small drift velocity of electrons, which is superimposed on the random motion of free electrons. Due to this drift velocity, there is a net flow of electrons opposite to the direction of the field.
Complete solution:
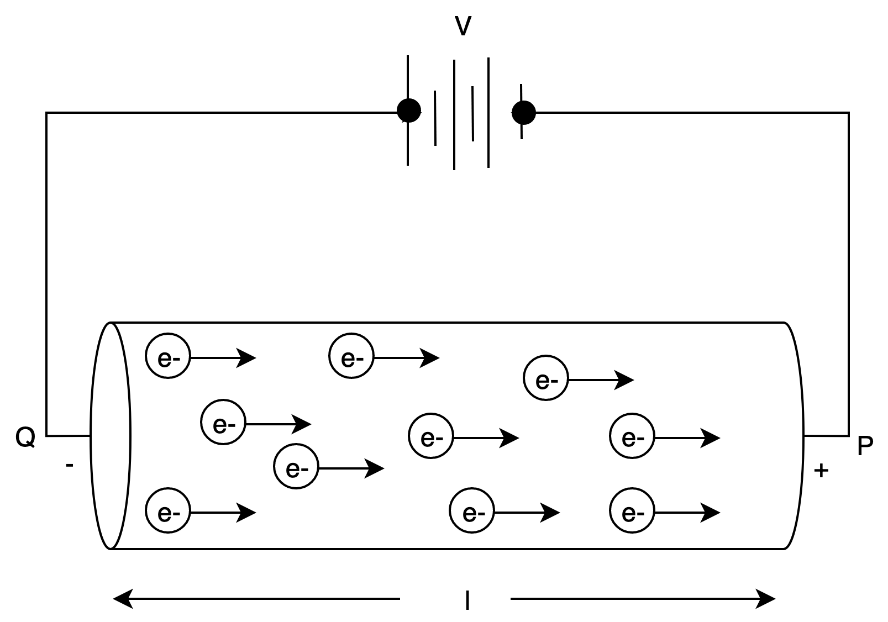
In the above figure a conductor of length $l$ is connected with the potential difference $V$ . point P is positive and point Q is negative. The electric field is developed when we apply some potential difference. In an electric field electrons experience force in the opposite direction of the electric field. Mathematically, the electric field can be expressed as
$E = \dfrac{V}{l}$
And force experienced by free electron
$F = eE$……. Equation (1)
Now if ${m_e}$ be the mass of the electron, the acceleration can be expressed as
$a = \dfrac{F}{{{m_e}}}$
From equation (1) we can write
$\therefore a = \dfrac{{eE}}{{{m_e}}}$
When a conductor is not connected to any battery, free electrons are said to move due to their temperature and hence the name. The value of thermal velocity is very high of order but due to the random motion of electrons in all possible directions, their average thermal velocity turns out to be zero. Keeping this in mind apply the first equation of motion $v = u + at$ , where $v$ is the velocity of the electron after time $t$ and $u$ is the initial velocity which is thermal velocity here. We already have an expression of acceleration.
\[\therefore {v_d} = 0 + \left( {\dfrac{{eE}}{{{m_e}}}} \right)\tau \]
Where, $\tau $ is the time taken by the electron to collapse with the positive side.
The above equation implies that
\[ \Rightarrow {v_d} = \left( {\dfrac{{eE}}{{{m_e}}}} \right)\tau \]
This is the relation between drift velocity and the electric field.
Now define mobility. Mobility is a characteristic of a metal that tells us how quickly an electron moves through metal or any conductor when it is pulled by some electric field. It makes sense that mobility depends on the force applied to electrons due to the electric field. And the force depends on the intensity of the electric field. In the relation established between drift velocity and the electric field, $e$ , ${m_e}$ , and $\tau $ are constant. $\tau $ is constant because it is fixed for a specific conductor. Therefore the term $\dfrac{{e\tau }}{{{m_e}}}$ is constant which is called mobility of electrons in the conductor. We denote it by $\mu $ .
$\therefore \mu = \dfrac{{e\tau }}{{{m_e}}}$
From the relation of drift velocity and electric field we can write that
$\therefore \mu = \dfrac{{{v_d}}}{E}$
Therefore the mobility is defined as the ratio of the drift velocity and the electric field.
If we keep the electric field constant then we can say that $\mu \propto {v_d}$ . More mobility also means more conductivity. Drift velocity increases as mobility increases and vice-versa.
Note: Normally electrons keep moving in the metal in all possible directions with high velocity but their overall average velocity is considered zero. When we say electric current is flowing in some direction the statement is equivalent to say that electrons are flowing in opposite directions. Since electrons move in metal without even creating any potential difference but they do not produce any current. Also, the mass of an electron is very less therefore we neglect the gravitational force.
Complete solution:

In the above figure a conductor of length $l$ is connected with the potential difference $V$ . point P is positive and point Q is negative. The electric field is developed when we apply some potential difference. In an electric field electrons experience force in the opposite direction of the electric field. Mathematically, the electric field can be expressed as
$E = \dfrac{V}{l}$
And force experienced by free electron
$F = eE$……. Equation (1)
Now if ${m_e}$ be the mass of the electron, the acceleration can be expressed as
$a = \dfrac{F}{{{m_e}}}$
From equation (1) we can write
$\therefore a = \dfrac{{eE}}{{{m_e}}}$
When a conductor is not connected to any battery, free electrons are said to move due to their temperature and hence the name. The value of thermal velocity is very high of order but due to the random motion of electrons in all possible directions, their average thermal velocity turns out to be zero. Keeping this in mind apply the first equation of motion $v = u + at$ , where $v$ is the velocity of the electron after time $t$ and $u$ is the initial velocity which is thermal velocity here. We already have an expression of acceleration.
\[\therefore {v_d} = 0 + \left( {\dfrac{{eE}}{{{m_e}}}} \right)\tau \]
Where, $\tau $ is the time taken by the electron to collapse with the positive side.
The above equation implies that
\[ \Rightarrow {v_d} = \left( {\dfrac{{eE}}{{{m_e}}}} \right)\tau \]
This is the relation between drift velocity and the electric field.
Now define mobility. Mobility is a characteristic of a metal that tells us how quickly an electron moves through metal or any conductor when it is pulled by some electric field. It makes sense that mobility depends on the force applied to electrons due to the electric field. And the force depends on the intensity of the electric field. In the relation established between drift velocity and the electric field, $e$ , ${m_e}$ , and $\tau $ are constant. $\tau $ is constant because it is fixed for a specific conductor. Therefore the term $\dfrac{{e\tau }}{{{m_e}}}$ is constant which is called mobility of electrons in the conductor. We denote it by $\mu $ .
$\therefore \mu = \dfrac{{e\tau }}{{{m_e}}}$
From the relation of drift velocity and electric field we can write that
$\therefore \mu = \dfrac{{{v_d}}}{E}$
Therefore the mobility is defined as the ratio of the drift velocity and the electric field.
If we keep the electric field constant then we can say that $\mu \propto {v_d}$ . More mobility also means more conductivity. Drift velocity increases as mobility increases and vice-versa.
Note: Normally electrons keep moving in the metal in all possible directions with high velocity but their overall average velocity is considered zero. When we say electric current is flowing in some direction the statement is equivalent to say that electrons are flowing in opposite directions. Since electrons move in metal without even creating any potential difference but they do not produce any current. Also, the mass of an electron is very less therefore we neglect the gravitational force.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




