
Esters are functional isomers of:
(A) Hydroxyaldehyde
(B) Ketone
(C) Diketone
(D) Diol
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: Isomerism is a phenomenon of organic chemistry in which more than one species has the same chemical formula but different structures. Those compounds who have same chemical formula but different properties and the arrangement of atoms in their molecule are called isomers
Complete answer:
Isomerism is of two types (a) Structural and (b) Stereo. Functional isomerism is a type of structural isomerism. Those molecules that have the same molecular formula but have different functional groups in their compounds are called functional isomers and this phenomenon is called functional isomerism.
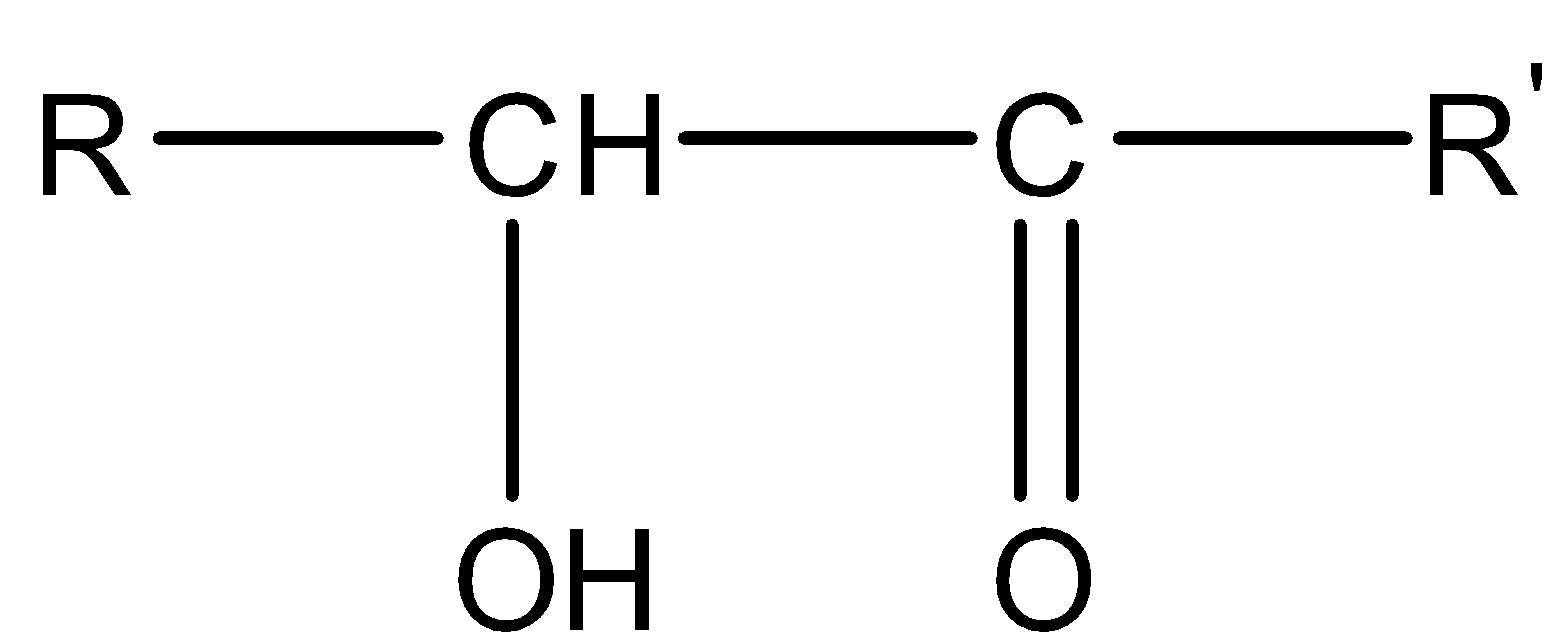
Esters are produced when the carboxylic acid is reacted with alcohol in the presence of a catalyst. Concentrated sulphuric acid is used as a in this reaction. This reaction is called the esterification reaction. The general formula of esters is \[R - CO - O{R'}\].
Hydroxycarbonyl compounds are the compounds that have a hydroxyl ($ - OH$) group on the carbonyl carbon of aldehyde or ketone. Their general formula is
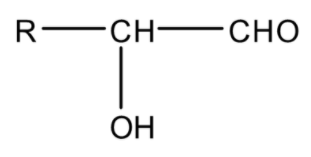 OR
OR
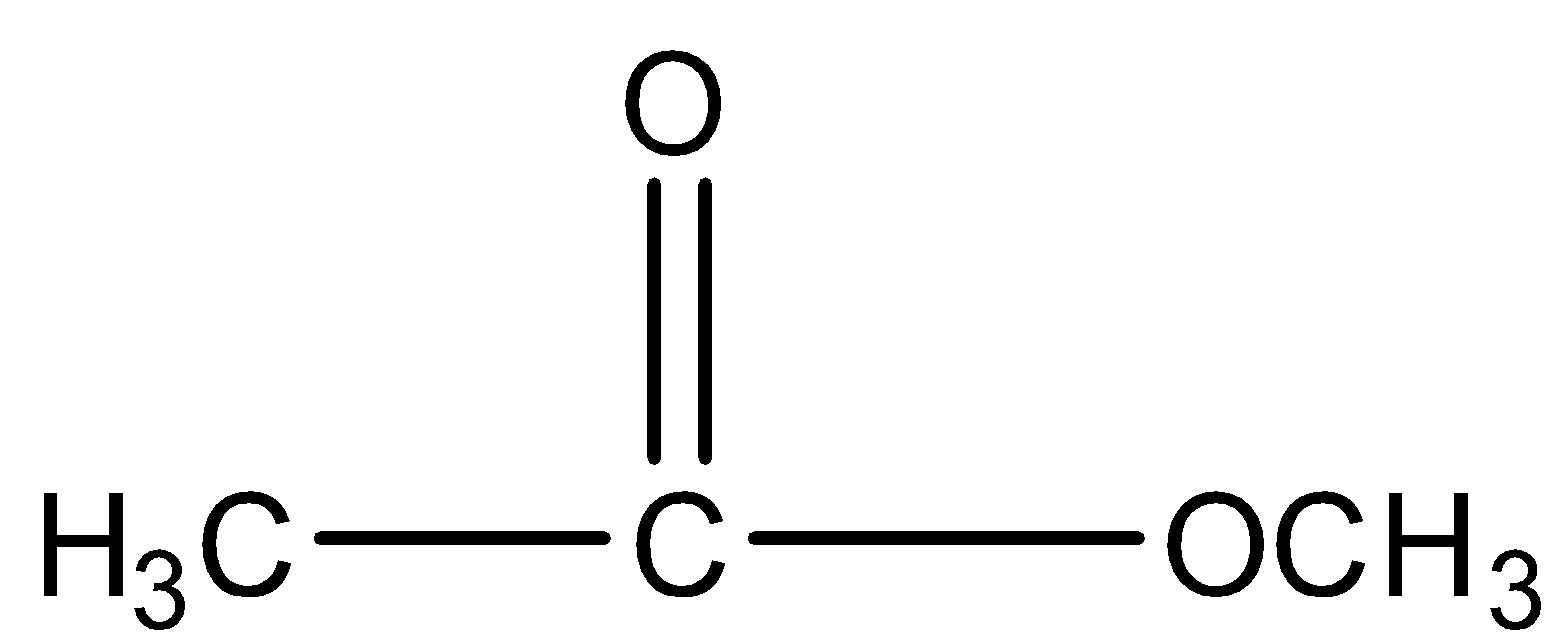
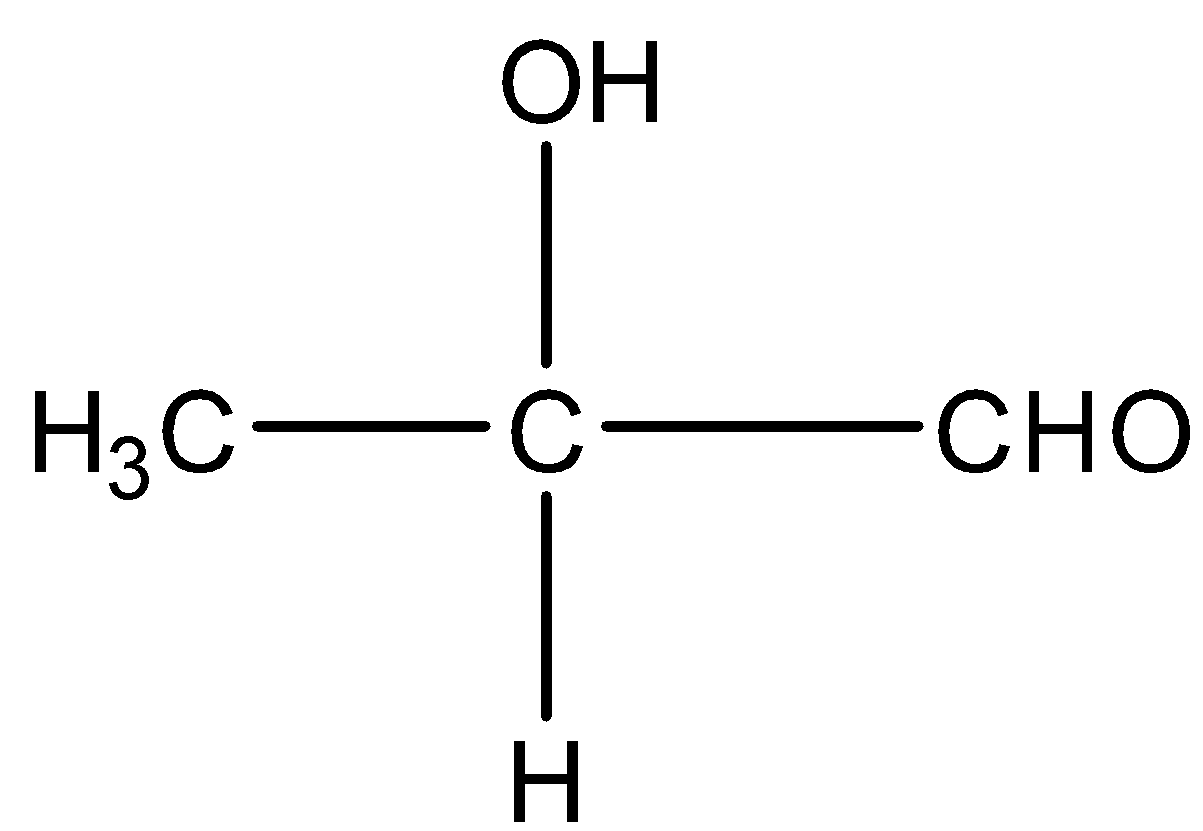
Take the example of Methyl ethanoate and $2 - $ hydroxy propanal. Both have molecular formula \[{C_3}{H_6}{O_2}\] and their structure will be:
 and
and
From these two compounds, we can deduce that the molecular formula is the same but the functional group is different. Hence, these are functional isomers of each other.
Monocarboxylic acids are also functional isomers of esters because both have the same molecular formula but different functional groups. For example; methyl ethanoate and propanoic acid both have chemical formula \[{C_3}{H_6}{O_2}\] but their chemical structure is different.
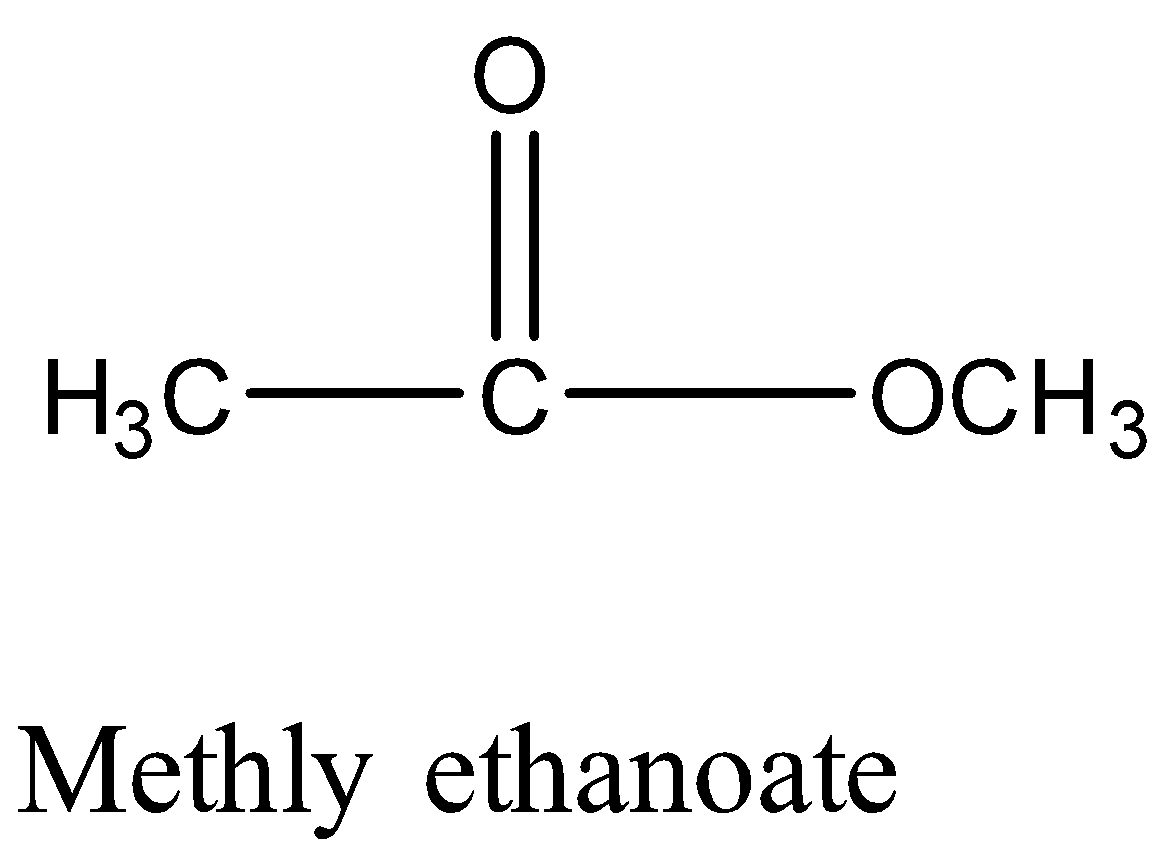
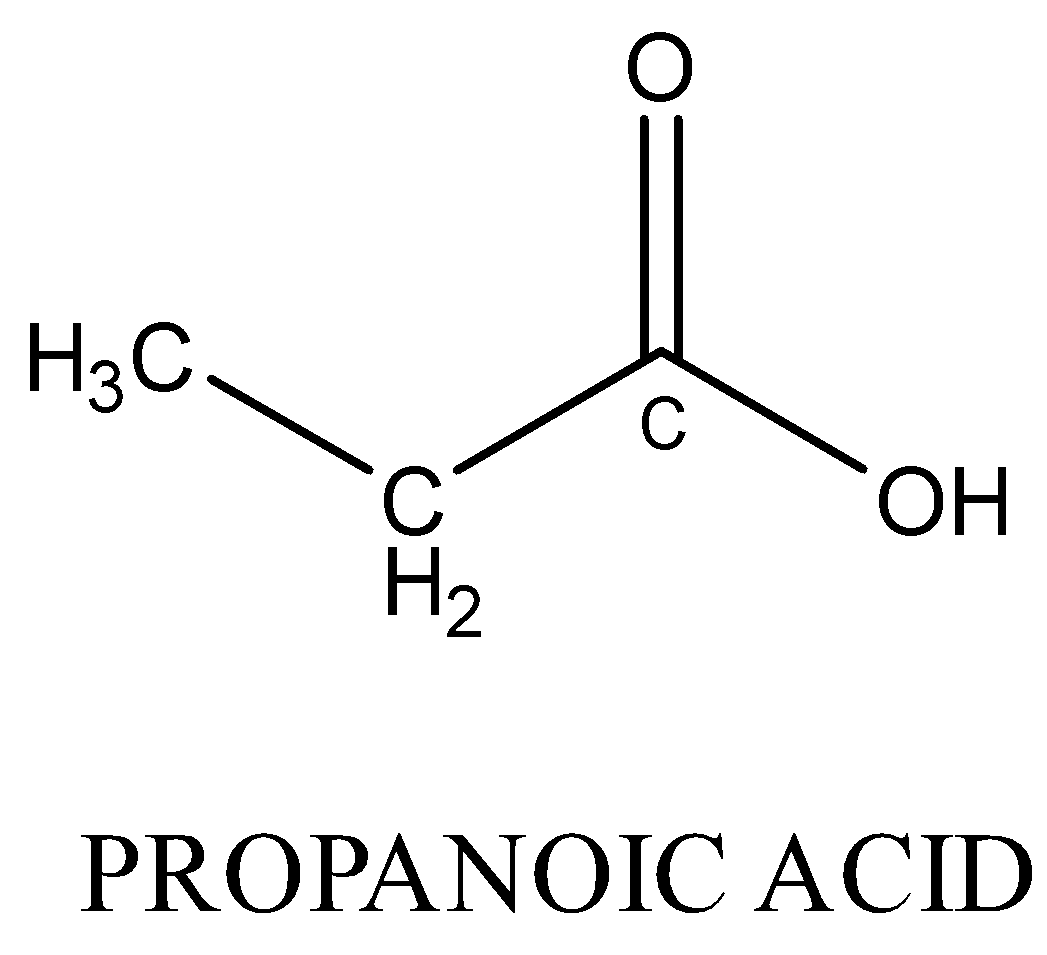
Therefore, Option (A) is correct.
Note:
So, The Functional isomers of esters are Hydroxycarbonyl compounds and carboxylic acids The functional group in carboxylic acid is $ - COOH$, in esters it is \[R - CO - O{R'}\]. Both have the same molecular formula but different functional groups.
Complete answer:
Isomerism is of two types (a) Structural and (b) Stereo. Functional isomerism is a type of structural isomerism. Those molecules that have the same molecular formula but have different functional groups in their compounds are called functional isomers and this phenomenon is called functional isomerism.
Esters are produced when the carboxylic acid is reacted with alcohol in the presence of a catalyst. Concentrated sulphuric acid is used as a in this reaction. This reaction is called the esterification reaction. The general formula of esters is \[R - CO - O{R'}\].
Hydroxycarbonyl compounds are the compounds that have a hydroxyl ($ - OH$) group on the carbonyl carbon of aldehyde or ketone. Their general formula is


Take the example of Methyl ethanoate and $2 - $ hydroxy propanal. Both have molecular formula \[{C_3}{H_6}{O_2}\] and their structure will be:


From these two compounds, we can deduce that the molecular formula is the same but the functional group is different. Hence, these are functional isomers of each other.
Monocarboxylic acids are also functional isomers of esters because both have the same molecular formula but different functional groups. For example; methyl ethanoate and propanoic acid both have chemical formula \[{C_3}{H_6}{O_2}\] but their chemical structure is different.


Therefore, Option (A) is correct.
Note:
So, The Functional isomers of esters are Hydroxycarbonyl compounds and carboxylic acids The functional group in carboxylic acid is $ - COOH$, in esters it is \[R - CO - O{R'}\]. Both have the same molecular formula but different functional groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




