
How many esters with the molecular formula \[{C_5}{H_{10}}{O_2}\] can be made by reacting a primary alcohol with a carboxylic acid?
A. \[4\]
B. \[5\]
C. \[6\]
D. \[8\]
Answer
552.3k+ views
Hint: The reaction of an organic carboxylic acid and an alcohol in presence of acid leads to formation of esters. Esters are an important class of organic compounds which are sweet and pleasant smelling compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
Esters are a class of organic compounds which are referred to as the derivatives of carboxylic acids. The ester compound is represented by the general formula .
The reaction of a carboxylic acid with alcohol is termed a condensation reaction. The term condensation means the two molecules get linked up liberating a molecule of water. The reaction is shown as
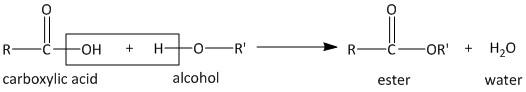
The given ester compound has the molecular formula \[{C_5}{H_{10}}{O_2}\]. It contains five carbon atoms in total. The condition of the formation of ester is that the alcohol part involved is a primary alcohol. Thus we have to find the possible primary alcohols which can form the ester compound.
The acid must have a single carbon atom. The following compounds are possible with a primary alcohol.
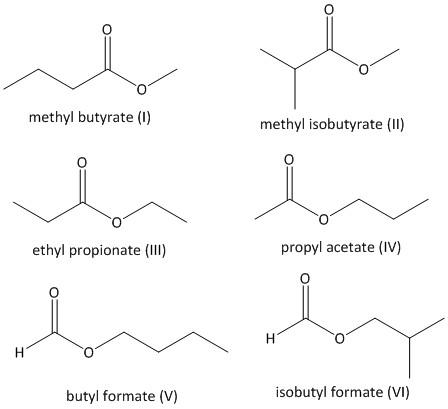
The structure I and II contains methyl alcohol which is a primary alcohol. The structure III contains ethyl alcohol and the structure IV contains propyl alcohol. The structure V contains n-butyl alcohol and the structure VI contains isobutyl alcohol. In all cases the alcohol is a primary alcohol.
Hence six esters with the molecular formula \[{C_5}{H_{10}}{O_2}\] can be made by reacting a primary alcohol with a carboxylic acid.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Unlike esters which are derivatives of carboxylic acids, amides and anhydrides and acid chlorides are the other derivatives of carboxylic acids. The esters are easily prepared by heating a mixture of carboxylic acid and alcohol in presence of acid. The acid catalyzes the esterification reaction to proceed faster.
Complete step by step answer:
Esters are a class of organic compounds which are referred to as the derivatives of carboxylic acids. The ester compound is represented by the general formula .
The reaction of a carboxylic acid with alcohol is termed a condensation reaction. The term condensation means the two molecules get linked up liberating a molecule of water. The reaction is shown as

The given ester compound has the molecular formula \[{C_5}{H_{10}}{O_2}\]. It contains five carbon atoms in total. The condition of the formation of ester is that the alcohol part involved is a primary alcohol. Thus we have to find the possible primary alcohols which can form the ester compound.
The acid must have a single carbon atom. The following compounds are possible with a primary alcohol.

The structure I and II contains methyl alcohol which is a primary alcohol. The structure III contains ethyl alcohol and the structure IV contains propyl alcohol. The structure V contains n-butyl alcohol and the structure VI contains isobutyl alcohol. In all cases the alcohol is a primary alcohol.
Hence six esters with the molecular formula \[{C_5}{H_{10}}{O_2}\] can be made by reacting a primary alcohol with a carboxylic acid.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Unlike esters which are derivatives of carboxylic acids, amides and anhydrides and acid chlorides are the other derivatives of carboxylic acids. The esters are easily prepared by heating a mixture of carboxylic acid and alcohol in presence of acid. The acid catalyzes the esterification reaction to proceed faster.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




