
Ethyl acetate is treated with excess of methyl magnesium iodide in dry ether. The reaction mixture is treated with water. The organic products obtained are?
(A) \[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}\overset{OH}{\mathop{\overset{|}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}\,and\,C{{H}_{3}}OH\]
(B) \[{{(C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}})}_{2}}\overset{OH}{\mathop{\overset{|}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,C{{H}_{3\,}}and\,C{{H}_{3}}OH\]
(C) ${{\left( C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}} \right)}_{3}}COH\,and\,C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$
(D) ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}COH\,and\,C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$
Answer
540.6k+ views
Hint:So in the given reaction, the reactant is methyl magnesium bromide which can be also called as Grignard reagent as the alkyl magnesium halides are Grignard reagent and it is a good nucleophile hence the reaction will be a nucleophilic addition reaction.
Complete step-by-step answer: So in the question reaction with various steps are given after completion of each step we will obtain a product which on treatment with another reagent will give entirely different product.
The first reactant here is ethyl acetate with methyl magnesium iodide. We know that ethyl acetate is an acetate molecule which has which has ethyl group as the alkyl chain and the molecular formulae is$C{{H}_{3}}C{{O}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}$.
And we know that the other reactant is Grignard reagent, all the alkyl magnesium halides are Grignard reagent, which is a good nucleophile for the electrophilic species like carbonyl groups. So the reaction involved here is nucleophilic addition reaction.
The double bond present in O atom of acetate molecule shift towards the O atoms giving it a negative charge and the C atom will be positively charged.
The methyl group in Grignard reagent will have partial negative charge and the Mg will have positive charge. The negatively charged C in Grignard reagent attacks the C and an adduct is formed, it is hydrolyzed and gets a ketone.
Since in the question it is given that excess of Grignard reagent is used, hence this ketone will again react with the Grignard reagent following the same mechanism as above and is treated with water, the final product obtained is an alcohol.
The reaction mechanism is as follows:
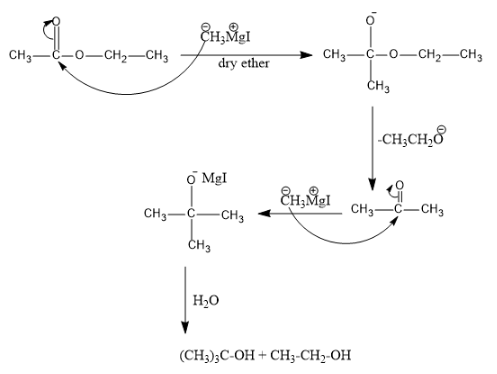
Hence by comparing the answer with the given options, option (d) is the correct answer for the question.
Note:We should take care of the arrows we use to denote the direction of flow of the electrons. And while shifting the bonds give proper charge for the atoms and always double check whether the valency of all the atoms are satisfied or not.
Complete step-by-step answer: So in the question reaction with various steps are given after completion of each step we will obtain a product which on treatment with another reagent will give entirely different product.
The first reactant here is ethyl acetate with methyl magnesium iodide. We know that ethyl acetate is an acetate molecule which has which has ethyl group as the alkyl chain and the molecular formulae is$C{{H}_{3}}C{{O}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}$.
And we know that the other reactant is Grignard reagent, all the alkyl magnesium halides are Grignard reagent, which is a good nucleophile for the electrophilic species like carbonyl groups. So the reaction involved here is nucleophilic addition reaction.
The double bond present in O atom of acetate molecule shift towards the O atoms giving it a negative charge and the C atom will be positively charged.
The methyl group in Grignard reagent will have partial negative charge and the Mg will have positive charge. The negatively charged C in Grignard reagent attacks the C and an adduct is formed, it is hydrolyzed and gets a ketone.
Since in the question it is given that excess of Grignard reagent is used, hence this ketone will again react with the Grignard reagent following the same mechanism as above and is treated with water, the final product obtained is an alcohol.
The reaction mechanism is as follows:

Hence by comparing the answer with the given options, option (d) is the correct answer for the question.
Note:We should take care of the arrows we use to denote the direction of flow of the electrons. And while shifting the bonds give proper charge for the atoms and always double check whether the valency of all the atoms are satisfied or not.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




