
How is ethyl methanoate converted into propan-2-ol?
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: To convert ethyl methanoate to propan-2-ol we need to attach more carbon atoms to it. So, we need to use a reagent which is capable of adding extra carbon atoms. This compound is basically an organometallic compound and functions as a nucleophile.
Complete step by step answer:
-First of all we will see the structures of ethyl methanoate and propan-2-ol.
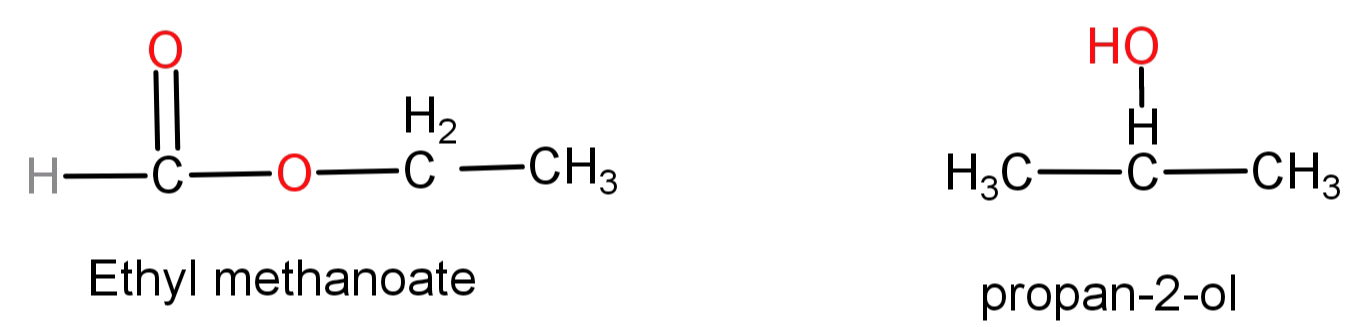
Since we can see that in ethyl methanoate there are only 2 carbons connected to each other while in propan-2-ol there are 3 carbons. So, we need to use a reagent which has the ability to create new C-C bonds.
So, we can convert ethyl methanoate to propan-2-ol by reacting it with Grignard reagent. Grignard reagent has a generic formula of R-Mg-X and is an organometallic compound where X is any halogen and R is an alkyl group. It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis for formation of new C-C bonds. While reacting the R-Mg-X molecule usually functions as a nucleophile (${R^ - }Mg{X^ + }$). The general form of this reaction is:
$2C{H_3}MgX + HCOOC{H_2}C{H_3}\xrightarrow{{{H_3}{O^ + }}}C{H_3}CH(OH)C{H_3}$
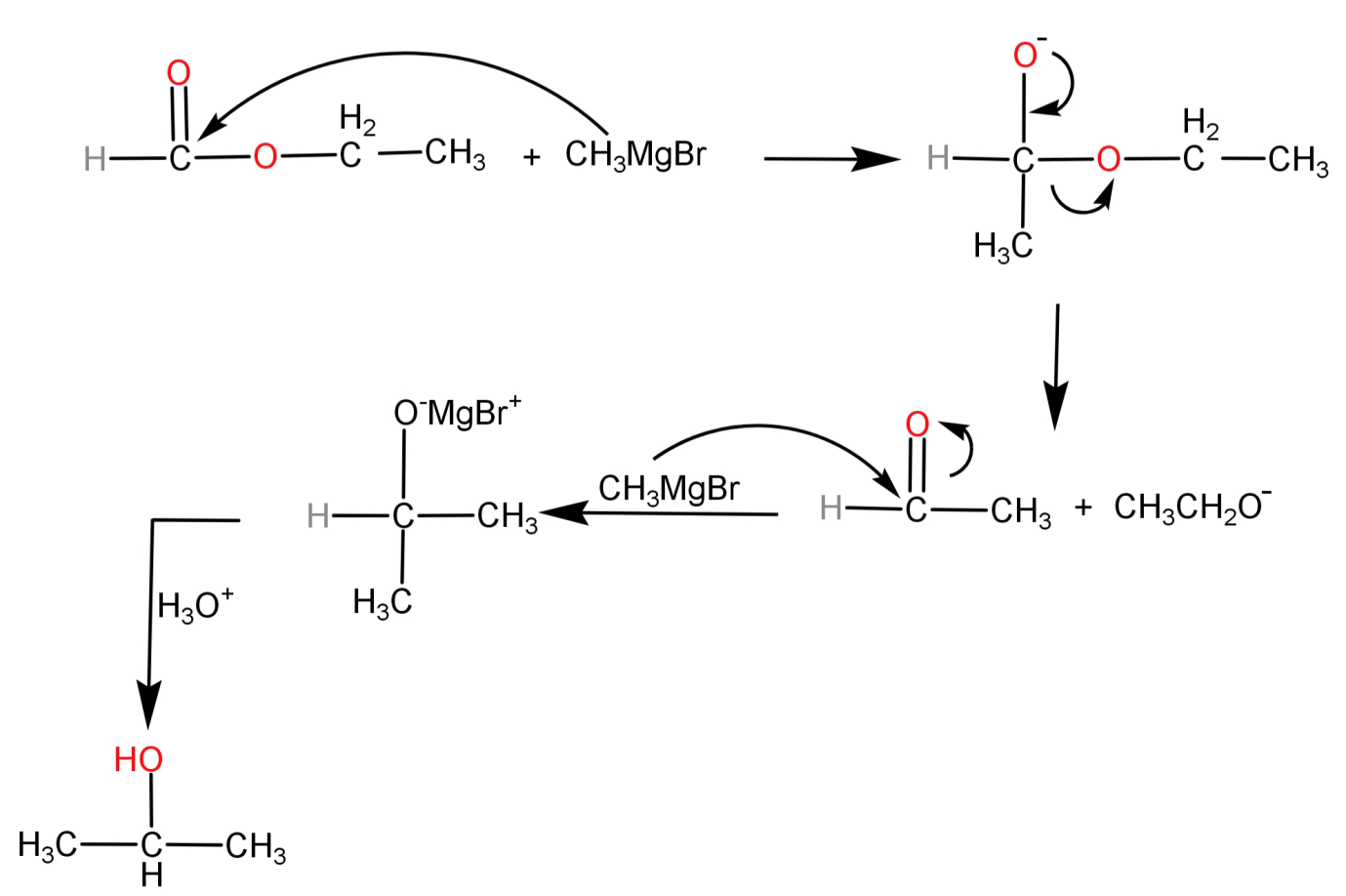
-Now let us see how the Grignard reagent reacts with ethyl methanoate.
Here we can see that first the nucleophile ($CH_3^ - $ from the Grignard reagent) attacks on the carbonyl carbon and its addition takes place to that carbon. Then there is elimination of the $C{H_3}C{H_2}{O^ - }$ group occurs leaving behind an aldehyde $C{H_3}CHO$. To this we need to attach one more methyl group so it is reacted with another R-Mg-X molecule. Finally after addition of another methyl group, hydrolysis occurs and propan-2-ol is formed.
This can be shown in a much better way in the form of the following reaction mechanism:
Finally we can say that ethyl methanoate is converted into propan-2-ol using Grignard reagent ($C{H_3}MgX$).
Note: The Grignard reagents are highly reactive compounds. They are extremely sensitive to water and oxygen and thus are usually stored as solutions in diethyl ether or THF (Tetrahydrofuran) solvents. Also Grignard reagent is industrially used as an important reagent in manufacture of Tamoxifen which is used in the treatment of breast cancer.
Complete step by step answer:
-First of all we will see the structures of ethyl methanoate and propan-2-ol.

Since we can see that in ethyl methanoate there are only 2 carbons connected to each other while in propan-2-ol there are 3 carbons. So, we need to use a reagent which has the ability to create new C-C bonds.
So, we can convert ethyl methanoate to propan-2-ol by reacting it with Grignard reagent. Grignard reagent has a generic formula of R-Mg-X and is an organometallic compound where X is any halogen and R is an alkyl group. It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis for formation of new C-C bonds. While reacting the R-Mg-X molecule usually functions as a nucleophile (${R^ - }Mg{X^ + }$). The general form of this reaction is:
$2C{H_3}MgX + HCOOC{H_2}C{H_3}\xrightarrow{{{H_3}{O^ + }}}C{H_3}CH(OH)C{H_3}$
-Now let us see how the Grignard reagent reacts with ethyl methanoate.
Here we can see that first the nucleophile ($CH_3^ - $ from the Grignard reagent) attacks on the carbonyl carbon and its addition takes place to that carbon. Then there is elimination of the $C{H_3}C{H_2}{O^ - }$ group occurs leaving behind an aldehyde $C{H_3}CHO$. To this we need to attach one more methyl group so it is reacted with another R-Mg-X molecule. Finally after addition of another methyl group, hydrolysis occurs and propan-2-ol is formed.
This can be shown in a much better way in the form of the following reaction mechanism:

Finally we can say that ethyl methanoate is converted into propan-2-ol using Grignard reagent ($C{H_3}MgX$).
Note: The Grignard reagents are highly reactive compounds. They are extremely sensitive to water and oxygen and thus are usually stored as solutions in diethyl ether or THF (Tetrahydrofuran) solvents. Also Grignard reagent is industrially used as an important reagent in manufacture of Tamoxifen which is used in the treatment of breast cancer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




