
Explain and derive equivalent Resistance formula for 3 Resistors connected in Pure series. Generalize the formula?
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: When three resistors are concealed in derives then the same current passes through each resistor but the voltage drop is different for each resistor.
Complete step by step solution:
According to Ohm’s formula V = IR.
When three resistors are connected in series then the same current passes through each resistor but the voltage drop is different for each resistor. If V is the applied voltage and \[{V_1},\,\,\,{V_2}\] and \[{V_3}\] is voltage across resistance \[{R_1},\,\,{R_2}\,\,and\,\,{R_3}\] respectively then.
\[V = \,\,{V_1}\,\, + \,\,{V_2}\,\, + \,\,{V_3}\] …(1)
According to ohm’s law
V = IR
\[\therefore \] \[I{R_{eq}}\,\, = \,\,I{R_1} + I{R_2} + I{R_3}\]
\[I{R_{eq}}\,\, = \,\,I\left( {{R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}} \right)\]
\[{R_{eq}}\,\, = \,\,{R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}\]
So, the equivalent resistance or the total resistance of the circuit can be defined as a single value of resistance that can replace any number of resistors connected in series without altering the value of the current or the voltage of the circuit.
If we have n resistance connected in series, then generalized formula for equivalent resistance is
\[{R_{eq}}\,\, = \,\,{R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}....... + {R_n}\]
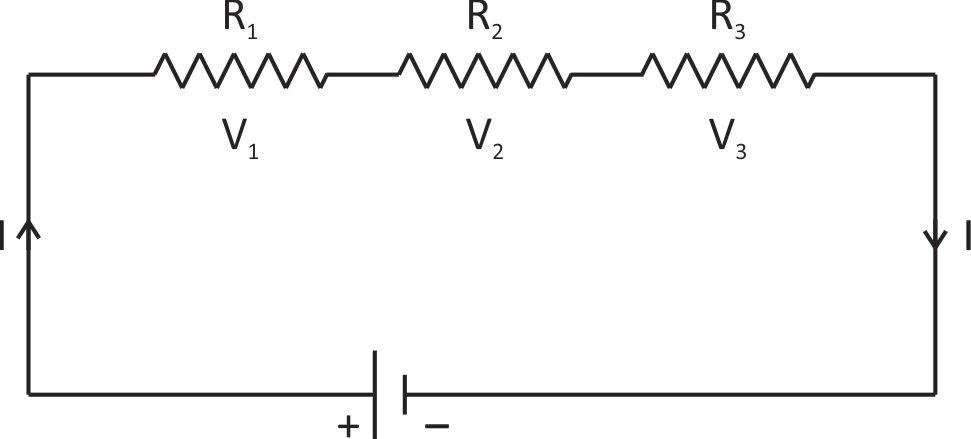
We know that applied voltage is (v)
\[\therefore \,\,V = {V_1} + {V_2} + {V_3}\]
We also know that
V = IR (from ohm’s law)
\[\therefore \,I\,{R_{eq}} = I{R_1} + I{R_2} + I{R_1}\]
\[ \Rightarrow I\,{R_{eq}} = I\left( {{R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}\]
So, the equivalent resistance or the total resistance of the circuit can be defined as a single value of resistor connected in series with altering the values of the current or voltage in the circuit.
Note: If three or more resistors with the same value are connected in parallel, then the equivalent resistance is equal to \[\dfrac{R}{n}\].
Complete step by step solution:
According to Ohm’s formula V = IR.
When three resistors are connected in series then the same current passes through each resistor but the voltage drop is different for each resistor. If V is the applied voltage and \[{V_1},\,\,\,{V_2}\] and \[{V_3}\] is voltage across resistance \[{R_1},\,\,{R_2}\,\,and\,\,{R_3}\] respectively then.
\[V = \,\,{V_1}\,\, + \,\,{V_2}\,\, + \,\,{V_3}\] …(1)
According to ohm’s law
V = IR
\[\therefore \] \[I{R_{eq}}\,\, = \,\,I{R_1} + I{R_2} + I{R_3}\]
\[I{R_{eq}}\,\, = \,\,I\left( {{R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}} \right)\]
\[{R_{eq}}\,\, = \,\,{R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}\]
So, the equivalent resistance or the total resistance of the circuit can be defined as a single value of resistance that can replace any number of resistors connected in series without altering the value of the current or the voltage of the circuit.
If we have n resistance connected in series, then generalized formula for equivalent resistance is
\[{R_{eq}}\,\, = \,\,{R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}....... + {R_n}\]

We know that applied voltage is (v)
\[\therefore \,\,V = {V_1} + {V_2} + {V_3}\]
We also know that
V = IR (from ohm’s law)
\[\therefore \,I\,{R_{eq}} = I{R_1} + I{R_2} + I{R_1}\]
\[ \Rightarrow I\,{R_{eq}} = I\left( {{R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}\]
So, the equivalent resistance or the total resistance of the circuit can be defined as a single value of resistor connected in series with altering the values of the current or voltage in the circuit.
Note: If three or more resistors with the same value are connected in parallel, then the equivalent resistance is equal to \[\dfrac{R}{n}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




