
Explain any five movable joints with examples.
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint:Joints are that part of our body where two or more bones are attached to allow free movement. Most joints in the adult body are diarthroses or freely movable joints due to the presence of some lubricating fluid.
Complete answer:
In movable joints, ends of the opposing bones are covered with cartilage, the articular cartilage, and that they are separated by an area called the joint cavity. The components of these joints are enclosed in a dense fibrous joint capsule.
In the outer layer of the capsule, the ligaments are present that hold the bones together.
In the inner layer, synovial fluid is secreted by the synovial membrane into the joint cavity for lubrication.
There are six sorts of freely movable joints - ball and socket, saddle, hinge, condyloid, pivot, and gliding.
Five of them are explained below:-
(1)Ball and socket joint: In this joint, the ball-shaped head of a bone is fitted in the socket made by another bone in such a manner that it allows free movement in all the directions. Example, the joint between the head of the humerus and the glenoid cavity of the pectoral girdle.
(2)Saddle joint: This joint is similar to the ball and socket joint but it is underdeveloped which means there is no free movement of the ball inside the socket. Only a limited movement is allowed. Example, the metacarpal of the thumb and trapezium of the wrist.
(3)Hinge joint: At this joint, one bone can move in one direction upto a certain limit, like the hinge of doors and windows. Example: joint of the knee, elbow, etc.
(4)Pivot joint: In this joint, a pointed end of a bone is fitted in a pit of another bone in such a manner that the later can show rotational movement around the former. For example, the joint between the axis vertebra and atlas vertebra holding the skull.
(5)Gliding joint: In this joint, surfaces of bones near the joint are flat so that the bones can glide over each other. For Example, tibia, and fibula, between the articular processes of vertebrae, between the clavicle and sternum.
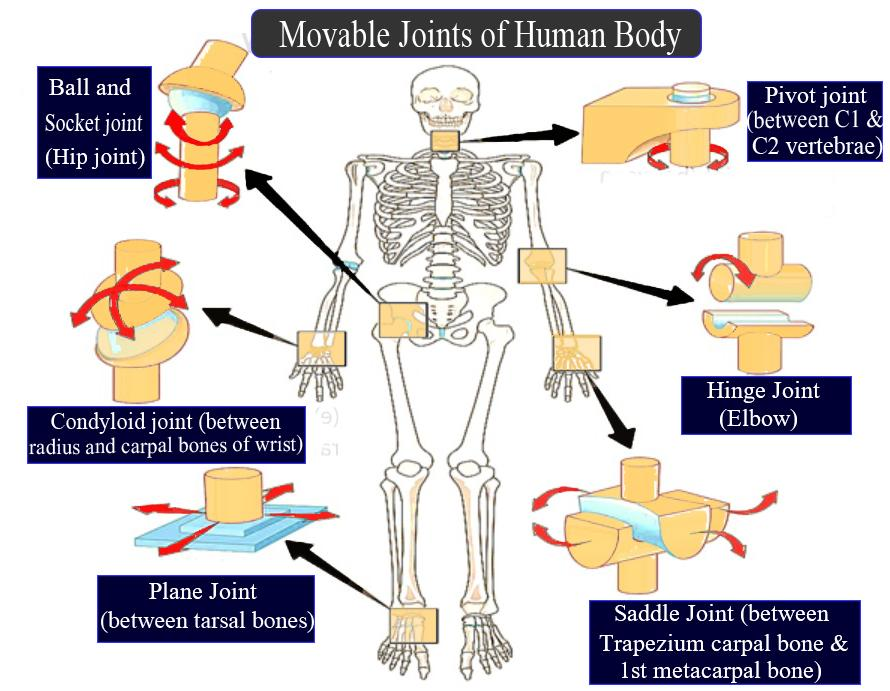
Diagram showing six movable joints of the Human body:(a) Pivot joint,
(b) Hinge joint, (c) Saddle joint, (d) Plane joints, (e) Condyloid joint, and
(f) Ball and Socket joint.
Note:
- The Glenoid cavity is found in the shoulder. Atlas is the first and axis is the second cervical vertebrae. The projections of the vertebra that serve the aim of fitting with an adjacent vertebrae are the articular processes of vertebrae.
- The greater the range of movement at joints, the higher the risk of injury because the strength of the joint is reduced.
- Babies are born with a cartilage plate that by times turns to the bone and into a kneecap between the age of 3 and 5 years
- Rheumatoid and osteoarthritis are two medical conditions triggered by the immune system that results in the body effectively attacking its tissues. This may lead to an inflammatory response and result in actual damage to the joint.
Complete answer:
In movable joints, ends of the opposing bones are covered with cartilage, the articular cartilage, and that they are separated by an area called the joint cavity. The components of these joints are enclosed in a dense fibrous joint capsule.
In the outer layer of the capsule, the ligaments are present that hold the bones together.
In the inner layer, synovial fluid is secreted by the synovial membrane into the joint cavity for lubrication.
There are six sorts of freely movable joints - ball and socket, saddle, hinge, condyloid, pivot, and gliding.
Five of them are explained below:-
(1)Ball and socket joint: In this joint, the ball-shaped head of a bone is fitted in the socket made by another bone in such a manner that it allows free movement in all the directions. Example, the joint between the head of the humerus and the glenoid cavity of the pectoral girdle.
(2)Saddle joint: This joint is similar to the ball and socket joint but it is underdeveloped which means there is no free movement of the ball inside the socket. Only a limited movement is allowed. Example, the metacarpal of the thumb and trapezium of the wrist.
(3)Hinge joint: At this joint, one bone can move in one direction upto a certain limit, like the hinge of doors and windows. Example: joint of the knee, elbow, etc.
(4)Pivot joint: In this joint, a pointed end of a bone is fitted in a pit of another bone in such a manner that the later can show rotational movement around the former. For example, the joint between the axis vertebra and atlas vertebra holding the skull.
(5)Gliding joint: In this joint, surfaces of bones near the joint are flat so that the bones can glide over each other. For Example, tibia, and fibula, between the articular processes of vertebrae, between the clavicle and sternum.

Diagram showing six movable joints of the Human body:(a) Pivot joint,
(b) Hinge joint, (c) Saddle joint, (d) Plane joints, (e) Condyloid joint, and
(f) Ball and Socket joint.
Note:
- The Glenoid cavity is found in the shoulder. Atlas is the first and axis is the second cervical vertebrae. The projections of the vertebra that serve the aim of fitting with an adjacent vertebrae are the articular processes of vertebrae.
- The greater the range of movement at joints, the higher the risk of injury because the strength of the joint is reduced.
- Babies are born with a cartilage plate that by times turns to the bone and into a kneecap between the age of 3 and 5 years
- Rheumatoid and osteoarthritis are two medical conditions triggered by the immune system that results in the body effectively attacking its tissues. This may lead to an inflammatory response and result in actual damage to the joint.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




