
Explain briefly about plastids.
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: The cell is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known organisms. A cell is the smallest unit inside the living organisms. Cells can be plant cells or animal cells.
Complete answer:
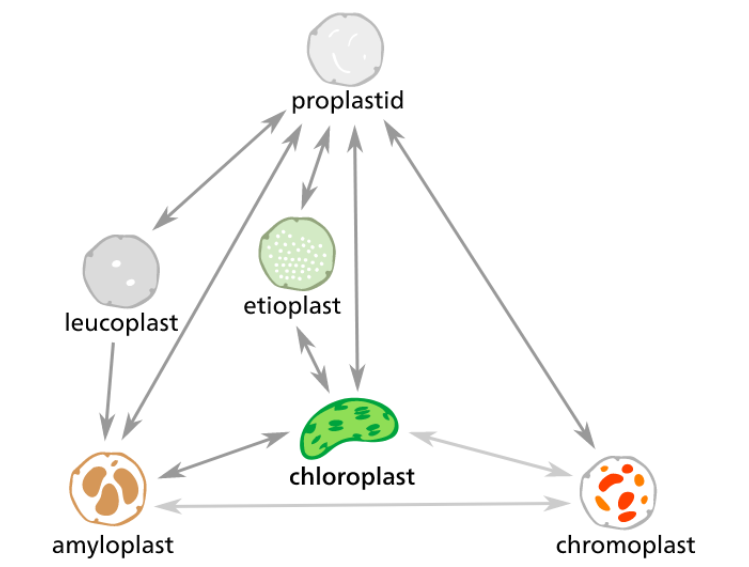
Plastids are double-membrane organelle which is present in the plant cell.
Plastids are mainly responsible for production and storing of food. They often contain pigments that are used in photosynthesis. These types of pigments in a plastid determine the cell's color.
The four main types of plastids are:
> Chloroplast: These green plastids are used for photosynthesis.
> Chromoplast: These colored plastids are used for pigment synthesis and storage.
> Gerontoplasts: It controls the dismantling of the photosynthetic apparatus during plant senescence.
> Leucoplasts: It is colorless plastids used for the synthesis of monoterpene.
Additional information:
We all know that a cell is the smallest unit or the basic unit of living organisms.
Two types of cells are:
1. Plant cell
2. Animal cell
1. Plant cell is the type of cell present in plants. Plants cells consist of following contents:
> Outer coverings
- Cell wall
- Cell membrane
> Nucleus
> Cytoplasm
> Protoplasmic Components
- Golgi bodies
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
- A single large vacuole
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Peroxisome
- Ribosome
- Plastids
2. Animal cells are the type of cells found in animals. Animal cells consist of following components:
> Outer covering
- Cell membrane
> Nucleus
> Cytoplasm
> Protoplasm components
- Mitochondria
- Many small vacuoles
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi bodies
- Centromere
- Lysosome
Note: Plasmolysis is the process in which cells lose water in a hypertonic solution. So the turgor pressure decreases to that level where the protoplasm of the cell peel off from the cell wall and leaves the gaps between the cell wall and the membrane. This gap makes the plant cell shrink. A continued decrease in pressure leads to complete collapse of the cell wall.
Complete answer:
Plastids are double-membrane organelle which is present in the plant cell.
Plastids are mainly responsible for production and storing of food. They often contain pigments that are used in photosynthesis. These types of pigments in a plastid determine the cell's color.
The four main types of plastids are:
> Chloroplast: These green plastids are used for photosynthesis.
> Chromoplast: These colored plastids are used for pigment synthesis and storage.
> Gerontoplasts: It controls the dismantling of the photosynthetic apparatus during plant senescence.
> Leucoplasts: It is colorless plastids used for the synthesis of monoterpene.

Additional information:
We all know that a cell is the smallest unit or the basic unit of living organisms.
Two types of cells are:
1. Plant cell
2. Animal cell
1. Plant cell is the type of cell present in plants. Plants cells consist of following contents:
> Outer coverings
- Cell wall
- Cell membrane
> Nucleus
> Cytoplasm
> Protoplasmic Components
- Golgi bodies
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
- A single large vacuole
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Peroxisome
- Ribosome
- Plastids
2. Animal cells are the type of cells found in animals. Animal cells consist of following components:
> Outer covering
- Cell membrane
> Nucleus
> Cytoplasm
> Protoplasm components
- Mitochondria
- Many small vacuoles
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi bodies
- Centromere
- Lysosome
Note: Plasmolysis is the process in which cells lose water in a hypertonic solution. So the turgor pressure decreases to that level where the protoplasm of the cell peel off from the cell wall and leaves the gaps between the cell wall and the membrane. This gap makes the plant cell shrink. A continued decrease in pressure leads to complete collapse of the cell wall.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




