
Explain briefly the coil and magnet experiment to demonstrate electromagnetic induction.
Answer
564.3k+ views
Hint: This experiment is based on the principle of magnetic induction. The electric generators work on this principle to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, the principle states that when a conducting coil is rotated in an alternating magnetic field a current is induced in the coil.
Complete solution:
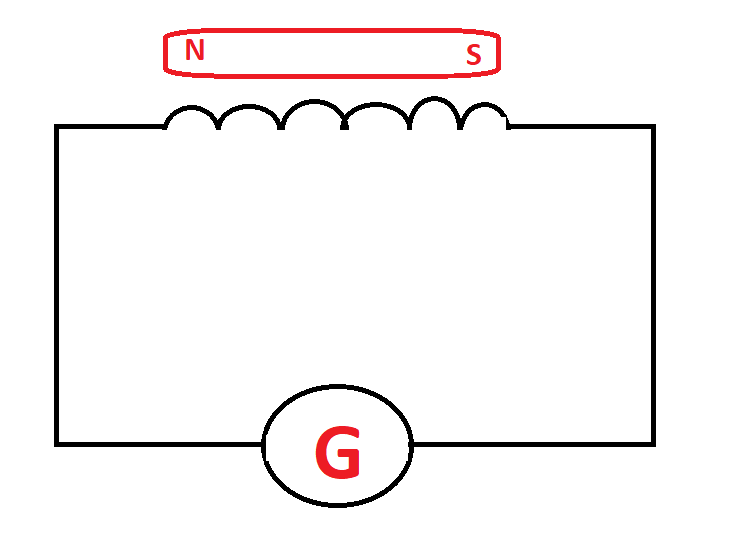 The experiment consists of a coil containing ‘n’ no of turns. To make a coil the coil of wire is winded on a paper cylinder and the setup is connected to a sensitive galvanometer.
The experiment consists of a coil containing ‘n’ no of turns. To make a coil the coil of wire is winded on a paper cylinder and the setup is connected to a sensitive galvanometer.
A sensitive galvanometer is a special type of galvanometer that detects the smallest induces a current.
Bow we take a bar magnet when the bar magnet is held at rest position at some distance away from the coil the galvanometer doesn’t show any deflection. Now the bar magnet is slightly moved towards the coil the Galvanometer starts showing deflection. Now we insert the magnet in the coil and move it back and forth inside the coil. When the North pole of a magnet is pushed towards the coil, the galvanometer shows a deflection.
Now as we can see that when we move the bar magnet back in the coil the galvanometer shows deflection on the opposite side. Or we can say that when the North pole of a magnet is pulled out, the deflection is in the opposite direction.
Now we flip the magnets and reverse the poles now the south pole of the magnet faces the coil. Now when the South pole of the bar magnet is pushed towards or pulled away from the coil the deflections in the galvanometer are opposite to that observed with the North pole for similar movement.
So from here, we can conclude that the induced current depends upon the polarity of the magnet.
Now we stop the movement of the magnet we see the galvanometer has also come at rest. So we understand that if the magnet is stopped or held stationary, there is no deflection in the galvanometer.
So it is important to have some relative velocity between magnet and coil for the generation of induced current. The relative motion between the Coil and the magnet causes a change in the magnetic flux through the coil and thus a current is induced in the coil. The magnitude of the current depends on the magnitude of their relative velocity and the strength of the magnet.
Note: 1. To have an induced emf there should always need to be some relative motion between the coil and magnet.
2. The current induced largely depends upon the magnitude of relative velocity between the coil and the magnet.
3. The relative motion between the Coil and the magnet causes a change in the magnetic flux through the coil and thus a current is induced in the coil.
Complete solution:

A sensitive galvanometer is a special type of galvanometer that detects the smallest induces a current.
Bow we take a bar magnet when the bar magnet is held at rest position at some distance away from the coil the galvanometer doesn’t show any deflection. Now the bar magnet is slightly moved towards the coil the Galvanometer starts showing deflection. Now we insert the magnet in the coil and move it back and forth inside the coil. When the North pole of a magnet is pushed towards the coil, the galvanometer shows a deflection.
Now as we can see that when we move the bar magnet back in the coil the galvanometer shows deflection on the opposite side. Or we can say that when the North pole of a magnet is pulled out, the deflection is in the opposite direction.
Now we flip the magnets and reverse the poles now the south pole of the magnet faces the coil. Now when the South pole of the bar magnet is pushed towards or pulled away from the coil the deflections in the galvanometer are opposite to that observed with the North pole for similar movement.
So from here, we can conclude that the induced current depends upon the polarity of the magnet.
Now we stop the movement of the magnet we see the galvanometer has also come at rest. So we understand that if the magnet is stopped or held stationary, there is no deflection in the galvanometer.
So it is important to have some relative velocity between magnet and coil for the generation of induced current. The relative motion between the Coil and the magnet causes a change in the magnetic flux through the coil and thus a current is induced in the coil. The magnitude of the current depends on the magnitude of their relative velocity and the strength of the magnet.
Note: 1. To have an induced emf there should always need to be some relative motion between the coil and magnet.
2. The current induced largely depends upon the magnitude of relative velocity between the coil and the magnet.
3. The relative motion between the Coil and the magnet causes a change in the magnetic flux through the coil and thus a current is induced in the coil.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




