
Explain crystallisation with the help of labelled diagrams.
Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: A separation procedure is a system for separating two or more separate product mixtures from a combination or solution of chemical substances. At least one of the isolation effects is enriched in one or more of the constituents of the source mixture. In certain cases, separating the mixture into pure constituents is possible. Separations take advantage of variations in a mixture's constituents' chemical or physical properties (such as scale, form, mass, density, or chemical affinity).
Complete answer:Crystallization is the mechanism by which a substance's atoms/molecules organise themselves in a well-defined three-dimensional lattice, reducing the system's total capacity. As a matter crystallises, the atoms or molecules form well-defined angles that tie them together.
When a solid material is mixed with a liquid and stirred, the solid dissolves in the liquid. However, if more material is applied to the liquid, a stage is reached where no more solid can melt. This is referred to as a saturation point, and the solvent is referred to as a saturation solution.
Process of Crystallization
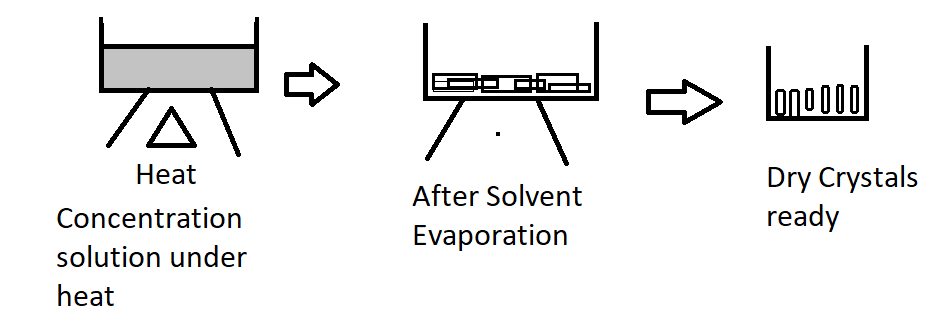
When you heat a solution in an enclosed bottle, the solvent ions evaporate, leaving the solutes behind.
As the solution cools, solute crystals begin to accumulate on the solution's surface.
Crystals are extracted and dried according to product specifications.
The method of filtration separates the liquid's undissolved solids.
The size of the crystals produced during this process is determined by the rate of cooling.
As a solution is rapidly cooled, a large number of tiny crystals form.
Slow cooling rates result in the formation of large crystals.
Crystallization in Practice:
Seawater purification
Alum crystal separation from impure samples
For the synthesis and isolation of co-crystals, pure active pharmaceutical ingredients (API), controlled release pulmonary drug delivery, and separation of chiral isomers, crystallisation is used as a separation and purification method in the pharmaceutical industry.
Note:
The solidification of a liquid material into a strongly ordered solid whose atoms or molecules are arranged in a well-defined three-dimensional crystal lattice is known as crystallisation. A unit cell is the smallest individual element of a crystal. Millions of these unit cells make up the crystal.
Complete answer:Crystallization is the mechanism by which a substance's atoms/molecules organise themselves in a well-defined three-dimensional lattice, reducing the system's total capacity. As a matter crystallises, the atoms or molecules form well-defined angles that tie them together.
When a solid material is mixed with a liquid and stirred, the solid dissolves in the liquid. However, if more material is applied to the liquid, a stage is reached where no more solid can melt. This is referred to as a saturation point, and the solvent is referred to as a saturation solution.
Process of Crystallization
When you heat a solution in an enclosed bottle, the solvent ions evaporate, leaving the solutes behind.
As the solution cools, solute crystals begin to accumulate on the solution's surface.
Crystals are extracted and dried according to product specifications.
The method of filtration separates the liquid's undissolved solids.
The size of the crystals produced during this process is determined by the rate of cooling.
As a solution is rapidly cooled, a large number of tiny crystals form.
Slow cooling rates result in the formation of large crystals.
Crystallization in Practice:
Seawater purification
Alum crystal separation from impure samples
For the synthesis and isolation of co-crystals, pure active pharmaceutical ingredients (API), controlled release pulmonary drug delivery, and separation of chiral isomers, crystallisation is used as a separation and purification method in the pharmaceutical industry.

Note:
The solidification of a liquid material into a strongly ordered solid whose atoms or molecules are arranged in a well-defined three-dimensional crystal lattice is known as crystallisation. A unit cell is the smallest individual element of a crystal. Millions of these unit cells make up the crystal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




