
Explain damped oscillations. Give an example.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In simple words, damped oscillations is the type of oscillations that diminishes in amplitude with time. Here, in this question, we will first understand the concept involved in oscillations and then, explain damped oscillations with an appropriate example.
Complete step by step solution:
The regular change in location and/or magnitude around a central point or a mean position is known as oscillation. In general, oscillations are expressed in Hertz. Example: Simple pendulum, tuning forks, guitar strings are some of the examples of undertaking oscillatory motion.
Types of oscillations:
1. Damped Oscillation
2. Forced Oscillation
3. Free Oscillation
Damped oscillation is an oscillation that diminishes with time. The amplitude of oscillations decreases with time due to damping. The oscillation is given resistance by the damping. The loss of energy from the system in resisting external forces such as friction, air resistance, and other resistive factors causes a reduction in amplitude. As a result, as the amplitude of the system decreases, so does its energy.
Example: The motion of the oscillating pendulum kept inside an oil-filled tank.
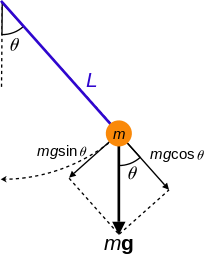
Image: Simple Pendulum
Here, a simple pendulum of mass “$m$” is in the damped oscillation motion such that the length of the string attached is “$L$”. The restoring force in the damped oscillations will always remain the same (constant) with respect to time and displacement. Here, the damping force always acts opposite to the motion of the bob (pendulum) which decreases the oscillation.
When the pendulum is moving from right-hand side to left-hand side then, the damping force will be the \[mg\cos\theta\] while the pendulum is moving from left-hand side to right-hand side then, the damping force will be the \[mg\sin\theta\].
Note: Candidates get confused with the term’s simple harmonic motion and oscillatory motion. These two terms are completely different in the sense that the restoring force in the simple harmonic motion is directly proportional to the displacement whereas in oscillatory motion (damped), the restoring force is constant.
Complete step by step solution:
The regular change in location and/or magnitude around a central point or a mean position is known as oscillation. In general, oscillations are expressed in Hertz. Example: Simple pendulum, tuning forks, guitar strings are some of the examples of undertaking oscillatory motion.
Types of oscillations:
1. Damped Oscillation
2. Forced Oscillation
3. Free Oscillation
Damped oscillation is an oscillation that diminishes with time. The amplitude of oscillations decreases with time due to damping. The oscillation is given resistance by the damping. The loss of energy from the system in resisting external forces such as friction, air resistance, and other resistive factors causes a reduction in amplitude. As a result, as the amplitude of the system decreases, so does its energy.
Example: The motion of the oscillating pendulum kept inside an oil-filled tank.

Image: Simple Pendulum
Here, a simple pendulum of mass “$m$” is in the damped oscillation motion such that the length of the string attached is “$L$”. The restoring force in the damped oscillations will always remain the same (constant) with respect to time and displacement. Here, the damping force always acts opposite to the motion of the bob (pendulum) which decreases the oscillation.
When the pendulum is moving from right-hand side to left-hand side then, the damping force will be the \[mg\cos\theta\] while the pendulum is moving from left-hand side to right-hand side then, the damping force will be the \[mg\sin\theta\].
Note: Candidates get confused with the term’s simple harmonic motion and oscillatory motion. These two terms are completely different in the sense that the restoring force in the simple harmonic motion is directly proportional to the displacement whereas in oscillatory motion (damped), the restoring force is constant.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Advanced 2026 Revision Notes for Vectors - Free PDF Download

JEE Advanced 2026 Revision Notes for Trigonometry - Free PDF Download

JEE Advanced 2026 Surface Chemistry Revision Notes - Free PDF Download

JEE Advanced Study Plan 2026: Expert Tips and Preparation Guide

JEE Advanced 2026 Revision Notes for Chemistry Solutions - Free PDF Download

Solutions Class 12 Notes JEE Advanced Chemistry [PDF]

Trending doubts
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Difference Between Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions Explained

IIT CSE Cutoff: Category‐Wise Opening and Closing Ranks

IIT Fees Structure 2025

Top IIT Colleges in India 2025

Other Pages
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




