
Explain double circulation with a schematic diagram?
Answer
607.2k+ views
Hint: The system of transport of blood from the heart to the body and then again returning to the heart.
Complete answer:
The circulatory system is responsible for the transportation of nutrients and gases to the body and waste products away from the body.
Types of the circulatory system
1. Open circulatory system – it is simpler and contains open-ended vessels that help transport blood.
2. Closed circulatory system – it is complex and involves different types of vessels that are all connected through which blood flows.
Types of blood circulation
- Single Circulation – the blood will pass through different parts of the body. Only one cardiac cycle is completed. It is present in birds, fish, reptiles, etc.
- Double Circulation – the blood flows through two routes – one for oxygenated blood and the other for deoxygenated blood. It is found in mammals.
In double the two pathways are present:
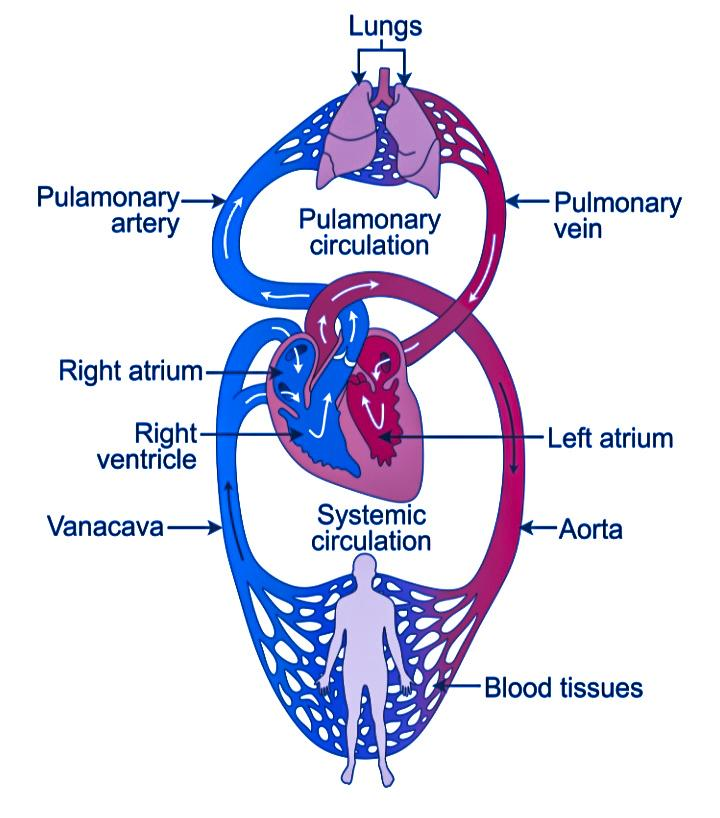
Systemic circulation:
- It carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricles to the tissue capillaries.
- Oxygenated blood is carried through the aorta to the body.
- Deoxygenated blood is carried from body to heart through veins.
- The right atrium then carries deoxygenated blood to the right ventricle.
Pulmonary circulation
- The blood circulation starts from the right atrium to the left atrium.
- The pulmonary artery collects blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
- Blood becomes oxygenated and pure and is pumped back to the left atrium through the pulmonary vein to the left ventricle.
- The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the aorta.
- This cycle continues and together constitutes double circulation.
Note: It helps in the maintenance of homeothermy or regulates the body temperature in mammals by supplying sufficient oxygen in the body.
Complete answer:
The circulatory system is responsible for the transportation of nutrients and gases to the body and waste products away from the body.
Types of the circulatory system
1. Open circulatory system – it is simpler and contains open-ended vessels that help transport blood.
2. Closed circulatory system – it is complex and involves different types of vessels that are all connected through which blood flows.
Types of blood circulation
- Single Circulation – the blood will pass through different parts of the body. Only one cardiac cycle is completed. It is present in birds, fish, reptiles, etc.
- Double Circulation – the blood flows through two routes – one for oxygenated blood and the other for deoxygenated blood. It is found in mammals.
In double the two pathways are present:
Systemic circulation:
- It carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricles to the tissue capillaries.
- Oxygenated blood is carried through the aorta to the body.
- Deoxygenated blood is carried from body to heart through veins.
- The right atrium then carries deoxygenated blood to the right ventricle.
Pulmonary circulation
- The blood circulation starts from the right atrium to the left atrium.
- The pulmonary artery collects blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
- Blood becomes oxygenated and pure and is pumped back to the left atrium through the pulmonary vein to the left ventricle.
- The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the aorta.
- This cycle continues and together constitutes double circulation.

Note: It helps in the maintenance of homeothermy or regulates the body temperature in mammals by supplying sufficient oxygen in the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




