
Explain Geranyl pyrophosphate.
Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint: Proteins that function as biological catalysts are known as enzymes (biocatalysts). Catalysts help to speed up chemical reactions. Substrates are the molecules on which enzymes can operate, and the enzyme transforms the substrates into various molecules called drugs.
Complete answer:
Geraniol is a monoterpenoid that also happens to be an alcohol. It's the main ingredient of rose, palmarosa, and citronella oils. While commercial samples can appear yellow, it is a colourless oil. It has a low water solubility but is soluble in other organic solvents. Geranyl is the functional group originating from geraniol (in principle, geraniol without the terminal OH).
Pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions with two phosphorus atoms linked together in a P-O-P linkage in chemistry. A variety of pyrophosphate salts are available. Pyrophosphates are sometimes referred to as diphosphates. The parent pyrophosphates are made by neutralising pyrophosphoric acid partially or completely. Disodium pyrophosphate and tetrasodium pyrophosphate are two important salts. The pyrophosphate bond is also known as a phosphoanhydride bond, a term that highlights the loss of water that happens when two phosphates form a new P-O-P bond and corresponds to the nomenclature for carboxylic acid anhydrides.
Geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP), also known as geranyl diphosphate (GDP), is a step in the biosynthesis of farnesyl pyrophosphate and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate by organisms using the HMG-CoA reductase pathway. These organisms are precursors to sesquiterpenes and diterpenes, respectively.
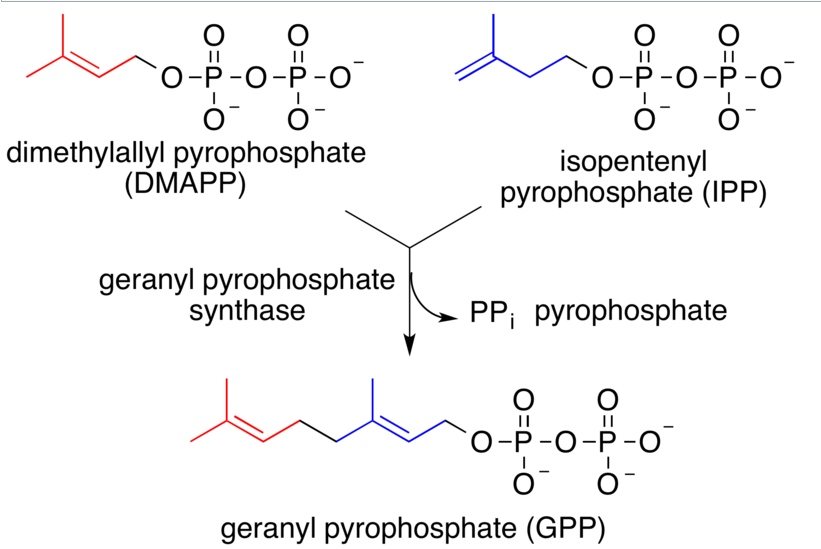
It’s chemical formula is $C_{10}H_{20}O_7P_2$.
Note:
Terpenes are isoprene-based linear or cyclic compounds that can be saturated or unsaturated, and modified in a variety of ways. Terpenoids are terpene compounds with extra functional groups and oxidised methyl groups transferred or withdrawn at different sites. According to their carbon units, terpenoids are classified as monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, diterpenes, sesterpenes, and triterpenes.
Complete answer:
Geraniol is a monoterpenoid that also happens to be an alcohol. It's the main ingredient of rose, palmarosa, and citronella oils. While commercial samples can appear yellow, it is a colourless oil. It has a low water solubility but is soluble in other organic solvents. Geranyl is the functional group originating from geraniol (in principle, geraniol without the terminal OH).
Pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions with two phosphorus atoms linked together in a P-O-P linkage in chemistry. A variety of pyrophosphate salts are available. Pyrophosphates are sometimes referred to as diphosphates. The parent pyrophosphates are made by neutralising pyrophosphoric acid partially or completely. Disodium pyrophosphate and tetrasodium pyrophosphate are two important salts. The pyrophosphate bond is also known as a phosphoanhydride bond, a term that highlights the loss of water that happens when two phosphates form a new P-O-P bond and corresponds to the nomenclature for carboxylic acid anhydrides.
Geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP), also known as geranyl diphosphate (GDP), is a step in the biosynthesis of farnesyl pyrophosphate and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate by organisms using the HMG-CoA reductase pathway. These organisms are precursors to sesquiterpenes and diterpenes, respectively.

It’s chemical formula is $C_{10}H_{20}O_7P_2$.
Note:
Terpenes are isoprene-based linear or cyclic compounds that can be saturated or unsaturated, and modified in a variety of ways. Terpenoids are terpene compounds with extra functional groups and oxidised methyl groups transferred or withdrawn at different sites. According to their carbon units, terpenoids are classified as monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, diterpenes, sesterpenes, and triterpenes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




