
Explain Gomberg reaction with mechanism.
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: Gomberg reaction is known by the name of Gomberg-Bachmann reaction as this reaction is discovered by two scientists known as Gomberg and Bachmann. It is an aryl-aryl coupling reaction with the help of diazonium salt.
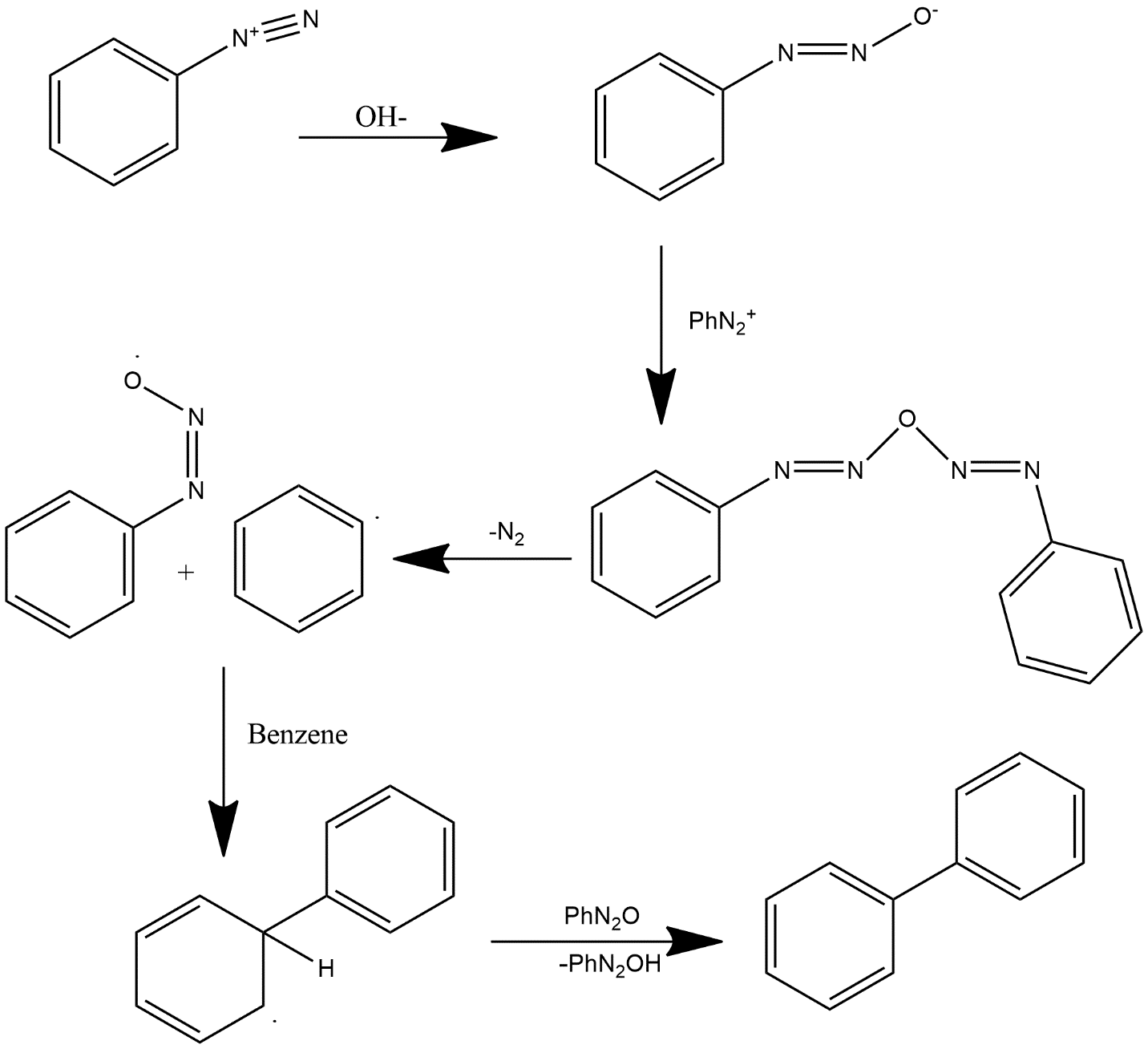
Complete answer: Gomberg reaction is basically start with the starting reactant diazonium salt and diazonium salt can be explained as a group of organic compounds which shares a common functional group represented by $R-{{N}_{2}}^{+}{{X}^{-}}$ where R can be any organic group may be alkyl or aryl and X is halogen.
The mechanism of Gomberg-Bachmann reaction can be explained as follows:
1. In the first step diazonium salt derivative is reacted with hydroxide ion and forms diazonium oxide which further reacts with $Ph{{N}_{2}}^{+}$ and forms a double ring compound.
2. After this loss of nitrogen gas is there which dissociates the molecule into two fragments out of which one is in the form of diazonium oxide and other one is a radical form of benzene.
3. After that diazonium gets reacted with benzene group and forms a biaryl group with the presence of aryl intermediate in this product i.e. H ion is present in this compound.
4. This H atom firstly gets reacted with $Ph{{N}_{2}}O$ which immediately form $Ph{{N}_{2}}OH$ which readily get lost from the compound and it forms biaryl product.
Mechanism can be shown as follows:
Note: Gomberg reaction is generally classified as coupling reaction; these are those reactions in which two fragments are joined together with the help of a metal catalyst. The most common coupling reaction is the cross coupling reaction.
Complete answer: Gomberg reaction is basically start with the starting reactant diazonium salt and diazonium salt can be explained as a group of organic compounds which shares a common functional group represented by $R-{{N}_{2}}^{+}{{X}^{-}}$ where R can be any organic group may be alkyl or aryl and X is halogen.
The mechanism of Gomberg-Bachmann reaction can be explained as follows:
1. In the first step diazonium salt derivative is reacted with hydroxide ion and forms diazonium oxide which further reacts with $Ph{{N}_{2}}^{+}$ and forms a double ring compound.
2. After this loss of nitrogen gas is there which dissociates the molecule into two fragments out of which one is in the form of diazonium oxide and other one is a radical form of benzene.
3. After that diazonium gets reacted with benzene group and forms a biaryl group with the presence of aryl intermediate in this product i.e. H ion is present in this compound.
4. This H atom firstly gets reacted with $Ph{{N}_{2}}O$ which immediately form $Ph{{N}_{2}}OH$ which readily get lost from the compound and it forms biaryl product.
Mechanism can be shown as follows:

Note: Gomberg reaction is generally classified as coupling reaction; these are those reactions in which two fragments are joined together with the help of a metal catalyst. The most common coupling reaction is the cross coupling reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




