
Explain how corpuscular theory predicts the speed of light in a medium, say, water, to be greater than the speed of light in the vacuum. Is the prediction confirmed by experimental determination of the speed of light in water? If not, which alternative picture of light is consistent with the experiment?
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: The given question is on a drawback of Newton’s corpuscular theory it says that the velocity of light in the denser medium is greater than the rarer medium because there will be an attraction between corpuscles and medium particles as they having attraction.
Complete step by step solution:
Step 1:
No Newton’s corpuscular theory fails to explain the simultaneous phenomenon of partial reflection and refraction on media such as glass or water also the surface of transparency
According to the theory velocity of light Denser medium is larger than the rarer medium, Which was experimentally wrong.
Step 2:
The theory says if the velocity of light in air is $c$ incident at a surface.
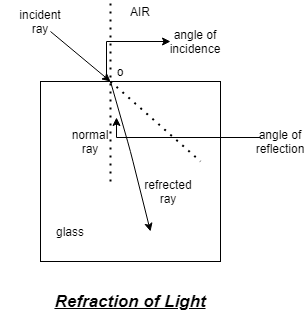
Separating air with water/glass surface as shown
At an angle of incidence, $I$ as shown and angle of refraction is $r$
Due to change in medium velocity found is now = $v$
Then by Snell’s law
$c\sin i = v\sin r$……. (1)
And relation between refractive index and given velocities will be as-
$\dfrac{v}{c} = \mu $…………. (2)
By equating (1) and (2) we have
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{v}{c} = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}} = \mu $…… (3)
But $\mu > 1$ so $v > c$ is not possible.
So Huygens now only the picture which can explain the velocity of light when the medium is changed is Huygens wave theory.
Note:
The above relation we are getting by the application of Snell’s law where the momentum of light energy along the striking surface remains unchanged and in the case of corpuscles theory there can be an increment in the momentum of corpuscles’ as they are attracted by denser medium resulting speed of light increases is the main drawback of Newton corpuscles theory.
Complete step by step solution:
Step 1:
No Newton’s corpuscular theory fails to explain the simultaneous phenomenon of partial reflection and refraction on media such as glass or water also the surface of transparency
According to the theory velocity of light Denser medium is larger than the rarer medium, Which was experimentally wrong.
Step 2:
The theory says if the velocity of light in air is $c$ incident at a surface.

Separating air with water/glass surface as shown
At an angle of incidence, $I$ as shown and angle of refraction is $r$
Due to change in medium velocity found is now = $v$
Then by Snell’s law
$c\sin i = v\sin r$……. (1)
And relation between refractive index and given velocities will be as-
$\dfrac{v}{c} = \mu $…………. (2)
By equating (1) and (2) we have
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{v}{c} = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}} = \mu $…… (3)
But $\mu > 1$ so $v > c$ is not possible.
So Huygens now only the picture which can explain the velocity of light when the medium is changed is Huygens wave theory.
Note:
The above relation we are getting by the application of Snell’s law where the momentum of light energy along the striking surface remains unchanged and in the case of corpuscles theory there can be an increment in the momentum of corpuscles’ as they are attracted by denser medium resulting speed of light increases is the main drawback of Newton corpuscles theory.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




