
Explain how does the OH group attached to a carbon of benzene ring activate it towards electrophilic substitution?
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Electrophilic substitution reaction involves the displacement of the functional group by an electrophile (generally a hydrogen atom). Electrophiles are those that are attracted to electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
- Let’s discuss about how the OH group attached to a carbon of benzene ring activate it towards electrophilic substitution:
- It is found that if any electrophile has to react with a benzene ring, then the benzene ring should have more electron density inside the ring. So that the electrophile can attack on it.
- In all these cases, the negative charge of Ortho and para position is slightly more conserved. So, any electrophile that will react on it will give Ortho and para products.
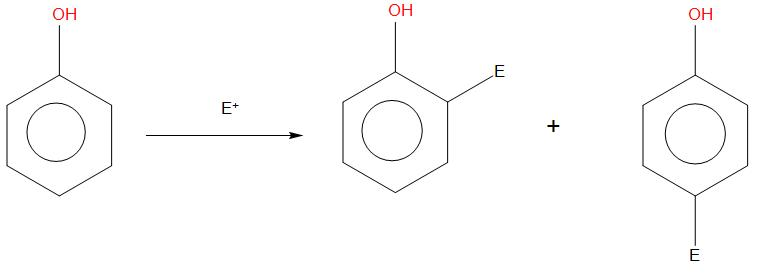
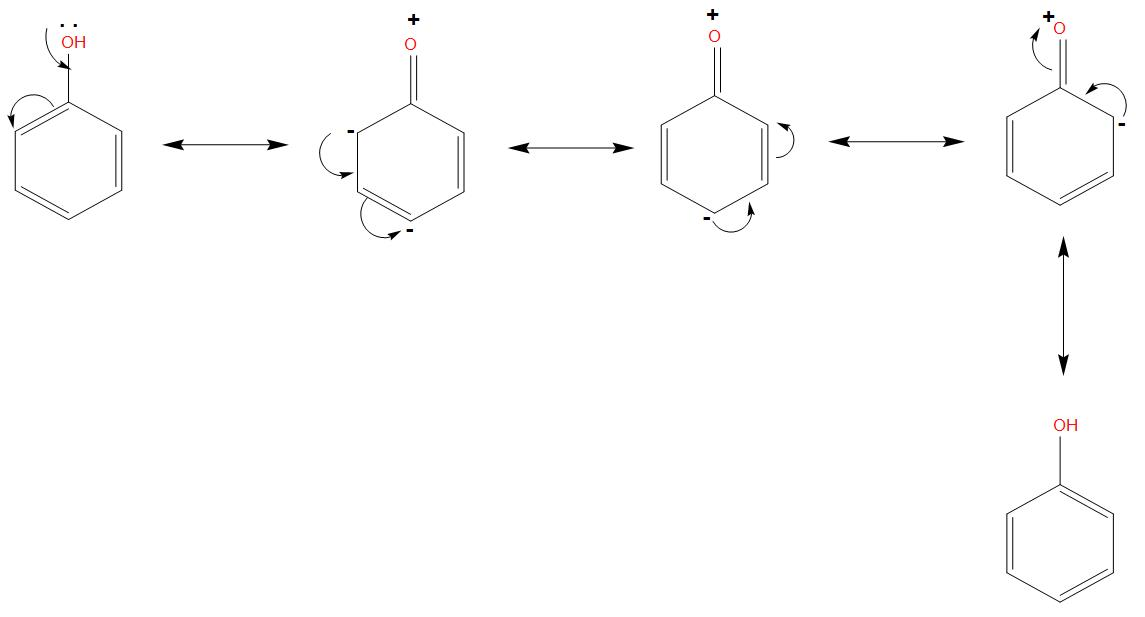
- If we will see the resonating structure of phenol, in that due to the lone pair of oxygen, its resonating structures will be formed like:
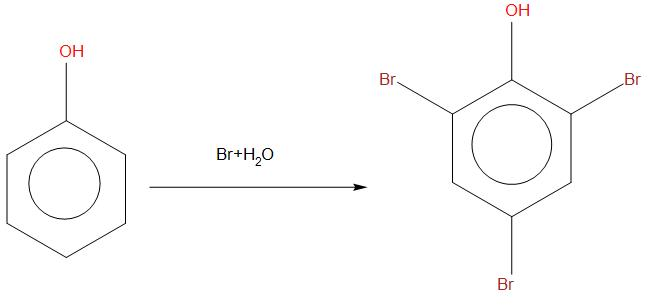
- In case of phenol rapid reaction takes place and gives ortho and para products. When phenol is reacted in presence of bromine, then bromine will attack on all the three positions, this happens because their rings become more activated. We can see the reaction as:
Note: - We should not get confused in between electrophilic substitution reaction and electrophilic addition reaction. Electrophilic substitution reaction involves the displacement of a functional group by an electrophile. Whereas, in electrophilic addition reaction species add into a molecule, but don't replace a leaving group.
Complete step by step answer:
- Let’s discuss about how the OH group attached to a carbon of benzene ring activate it towards electrophilic substitution:
- It is found that if any electrophile has to react with a benzene ring, then the benzene ring should have more electron density inside the ring. So that the electrophile can attack on it.
- In all these cases, the negative charge of Ortho and para position is slightly more conserved. So, any electrophile that will react on it will give Ortho and para products.

- If we will see the resonating structure of phenol, in that due to the lone pair of oxygen, its resonating structures will be formed like:

- In case of phenol rapid reaction takes place and gives ortho and para products. When phenol is reacted in presence of bromine, then bromine will attack on all the three positions, this happens because their rings become more activated. We can see the reaction as:

Note: - We should not get confused in between electrophilic substitution reaction and electrophilic addition reaction. Electrophilic substitution reaction involves the displacement of a functional group by an electrophile. Whereas, in electrophilic addition reaction species add into a molecule, but don't replace a leaving group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




